Using ultra-sensitive next generation sequencing to dissect DNA damage-induced mutagenesis
- PMID: 27122023
- PMCID: PMC4848531
- DOI: 10.1038/srep25310
Using ultra-sensitive next generation sequencing to dissect DNA damage-induced mutagenesis
Abstract
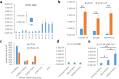
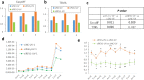
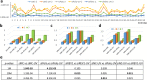
Next generation sequencing (NGS) technologies have dramatically improved studies in biology and biomedical science. However, no optimal NGS approach is available to conveniently analyze low frequency mutations caused by DNA damage treatments. Here, by developing an exquisite ultra-sensitive NGS (USNGS) platform "EasyMF" and incorporating it with a widely used supF shuttle vector-based mutagenesis system, we can conveniently dissect roles of lesion bypass polymerases in damage-induced mutagenesis. In this improved mutagenesis analysis pipeline, the initial steps are the same as in the supF mutation assay, involving damaging the pSP189 plasmid followed by its transfection into human 293T cells to allow replication to occur. Then "EasyMF" is employed to replace downstream MBM7070 bacterial transformation and other steps for analyzing damage-induced mutation frequencies and spectra. This pipeline was validated by using UV damaged plasmid after its replication in lesion bypass polymerase-deficient 293T cells. The increased throughput and reduced cost of this system will allow us to conveniently screen regulators of translesion DNA synthesis pathway and monitor environmental genotoxic substances, which can ultimately provide insight into the mechanisms of genome stability and mutagenesis.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Development of a versatile high-throughput mutagenesis assay with multiplexed short-read NGS using DNA-barcoded supF shuttle vector library amplified in E. coli.Elife. 2022 Oct 10;11:e83780. doi: 10.7554/eLife.83780. Elife. 2022. PMID: 36214452 Free PMC article.
-
The role of DNA polymerase eta in UV mutational spectra.DNA Repair (Amst). 2005 Feb 3;4(2):211-20. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2004.09.006. DNA Repair (Amst). 2005. PMID: 15590329
-
Effects of peroxynitrite dose and dose rate on DNA damage and mutation in the supF shuttle vector.Chem Res Toxicol. 2005 Jan;18(1):76-86. doi: 10.1021/tx049777m. Chem Res Toxicol. 2005. PMID: 15651852
-
High-throughput sequencing in mutation detection: A new generation of genotoxicity tests?Mutat Res. 2015 Jun;776:136-43. doi: 10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2015.03.014. Epub 2015 Apr 20. Mutat Res. 2015. PMID: 25934519 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Next-Generation Genotoxicology: Using Modern Sequencing Technologies to Assess Somatic Mutagenesis and Cancer Risk.Environ Mol Mutagen. 2020 Jan;61(1):135-151. doi: 10.1002/em.22342. Epub 2019 Nov 11. Environ Mol Mutagen. 2020. PMID: 31595553 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Enhancing the accuracy of next-generation sequencing for detecting rare and subclonal mutations.Nat Rev Genet. 2018 May;19(5):269-285. doi: 10.1038/nrg.2017.117. Epub 2018 Mar 26. Nat Rev Genet. 2018. PMID: 29576615 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NGS-based analysis of base-substitution signatures created by yeast DNA polymerase eta and zeta on undamaged and abasic DNA templates in vitro.DNA Repair (Amst). 2017 Nov;59:34-43. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2017.08.011. Epub 2017 Sep 12. DNA Repair (Amst). 2017. PMID: 28946034 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrasensitive and high-efficiency screen of de novo low-frequency mutations by o2n-seq.Nat Commun. 2017 May 22;8:15335. doi: 10.1038/ncomms15335. Nat Commun. 2017. PMID: 28530222 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a versatile high-throughput mutagenesis assay with multiplexed short-read NGS using DNA-barcoded supF shuttle vector library amplified in E. coli.Elife. 2022 Oct 10;11:e83780. doi: 10.7554/eLife.83780. Elife. 2022. PMID: 36214452 Free PMC article.
-
DNA Damage and Repair in Eye Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 15;24(4):3916. doi: 10.3390/ijms24043916. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36835325 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

