Risks of developing breast and colorectal cancer in association with incomes and geographic locations in Texas: a retrospective cohort study
- PMID: 27118258
- PMCID: PMC4847204
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-016-2324-z
Risks of developing breast and colorectal cancer in association with incomes and geographic locations in Texas: a retrospective cohort study
Abstract
Background: No study has been conducted to investigate the spatial pattern and association of socioeconomic status (such as income) with breast and colorectal cancer incidence in Texas, United States. This study aimed to determine whether median household income was associated with the risk of developing breast and colorectal cancer in Texas and to identify higher cancer risks by race/ethnicity and geographic areas.
Methods: This was a retrospective cohort study with an ecological component in using aggregated measures at the county level. We identified 243,677 women with breast cancer and 155,534 men and women with colorectal cancer residing in 254 counties in Texas in 1995-2011 from the public-use dataset of Texas Cancer Registry. The denominator population and median household income at the county level was obtained from the U.S. Bureau of the Census. Cancer incidence rates were calculated as number of cases per 100,000 persons and age-adjusted using the 2000 US population data. We used the ArcGIS v10.1 (geographic information system software) to identify multiple clustered counties with high and low cancer incidences in Texas.
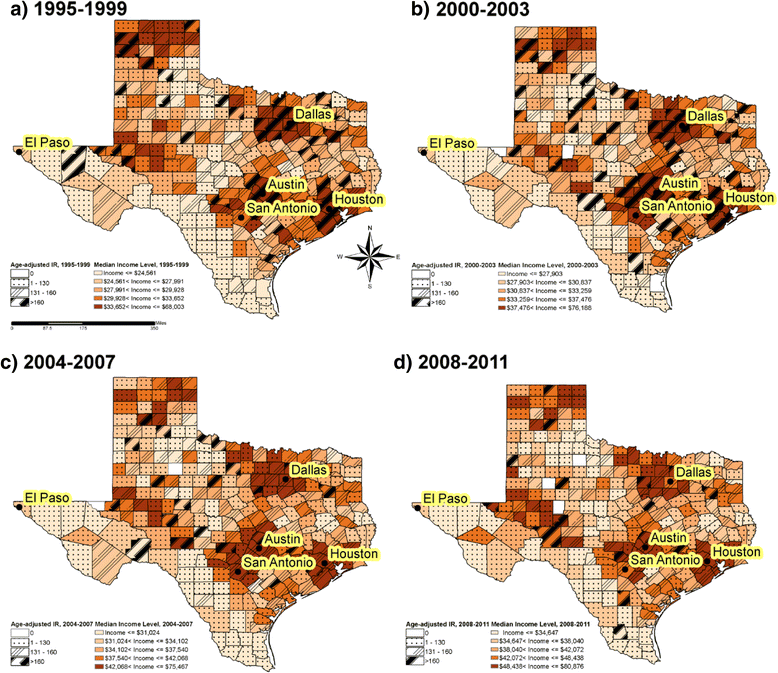
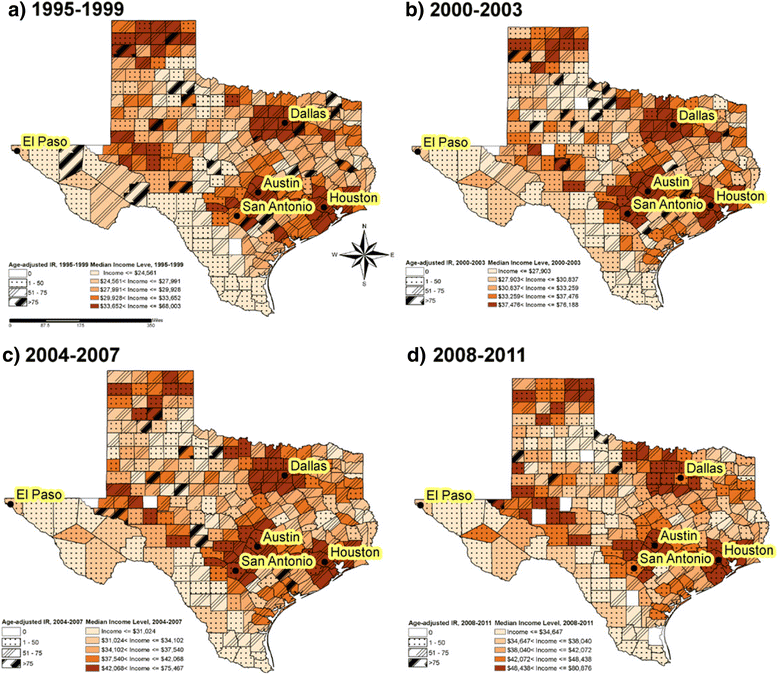
Results: Age-adjusted breast cancer incidence rate in the highest median income quintile group was 151.51 cases per 100,000 in 2008-2011 as compared to 98.95 cases per 100,000 in the lowest median income quintile group. The risk of colorectal cancer appeared to decrease with increasing median income in racial/ethnic population. Spatial analysis revealed the significant low breast cancer incidence cluster regions located in southwest US-Mexico border counties in Texas.
Conclusions: This study demonstrated that higher income was associated with an increased risk of breast cancer and a decreased risk of colorectal cancer in Texas. There were geographic variations with cancer incidence clustered in high risk areas in Texas. Future studies may need to explore more factors that might explain income and cancer risk associations and their geographic variations.
Keywords: Breast cancer; Cancer incidence; Colorectal cancer; Geographic variation; Income; Spatial analysis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Affluence and Breast Cancer.Breast J. 2016 Sep;22(5):564-7. doi: 10.1111/tbj.12630. Epub 2016 Jun 14. Breast J. 2016. PMID: 27296617 Free PMC article.
-
Racial/Ethnic, socioeconomic, and geographic disparities of cervical cancer advanced-stage diagnosis in Texas.Womens Health Issues. 2014 Sep-Oct;24(5):519-27. doi: 10.1016/j.whi.2014.06.009. Epub 2014 Aug 12. Womens Health Issues. 2014. PMID: 25128038
-
Trends and variations in breast and colorectal cancer incidence from 1995 to 2011: a comparative study between Texas Cancer Registry and National Cancer Institute's Surveillance, Epidemiology and End Results data.Int J Oncol. 2015 Apr;46(4):1819-26. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2015.2881. Epub 2015 Feb 6. Int J Oncol. 2015. PMID: 25672365 Free PMC article.
-
Patterns of Colorectal Cancer in Texas Counties From 2000 to 2017.JCO Oncol Pract. 2022 May;18(5):e770-e779. doi: 10.1200/OP.22.00093. JCO Oncol Pract. 2022. PMID: 35544648
-
An Ecological Evaluation of Vinyl Chloride Exposure and Liver Cancer Incidence and Mortality in Texas.J Clin Transl Hepatol. 2021 Feb 28;9(1):99-105. doi: 10.14218/JCTH.2020.00073. Epub 2020 Dec 30. J Clin Transl Hepatol. 2021. PMID: 33604260 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
MicroRNAs and Apoptosis in Colorectal Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jul 28;21(15):5353. doi: 10.3390/ijms21155353. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32731413 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of Socioeconomic Status on Cancer Incidence Risk, Cancer Staging, and Survival of Patients with Colorectal Cancer under Universal Health Insurance Coverage in Taiwan.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 Nov 19;18(22):12164. doi: 10.3390/ijerph182212164. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34831918 Free PMC article.
-
Management of metastatic melanoma in Texas: disparities in the utilization of immunotherapy following the regulatory approval of immune checkpoint inhibitors.BMC Cancer. 2023 Jul 13;23(1):655. doi: 10.1186/s12885-023-11142-4. BMC Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37442992 Free PMC article.
-
Area-Level Determinants in Colorectal Cancer Spatial Clustering Studies: A Systematic Review.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 Oct 6;18(19):10486. doi: 10.3390/ijerph181910486. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34639786 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Time Trends in Colorectal Cancer Incidence Rates by Income and Age at Diagnosis in Canada From 1992 to 2016.JAMA Netw Open. 2021 Jul 1;4(7):e2117556. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.17556. JAMA Netw Open. 2021. PMID: 34279645 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kohler BA, Sherman RL, Howlader N, Jemal A, Ryerson AB, Henry KA, et al. Annual report to the nation on the status of cancer, 1975–2011, featuring incidence of breast cancer subtypes by race/ethnicity, poverty, and state. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2015;107(6):djv048. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djv048. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Edwards BK, Ward E, Kohler BA, Eheman C, Zauber AG, Anderson RN, et al. Annual report to the nation on the status of cancer, 1975–2006, featuring colorectal cancer trends and impact of interventions (risk factors, screening, and treatment) to reduce future rates. Cancer. 2010;116(3):544–73. doi: 10.1002/cncr.24760. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical