Analytical Validation and Clinical Qualification of a New Immunohistochemical Assay for Androgen Receptor Splice Variant-7 Protein Expression in Metastatic Castration-resistant Prostate Cancer
- PMID: 27117751
- PMCID: PMC5015575
- DOI: 10.1016/j.eururo.2016.03.049
Analytical Validation and Clinical Qualification of a New Immunohistochemical Assay for Androgen Receptor Splice Variant-7 Protein Expression in Metastatic Castration-resistant Prostate Cancer
Abstract
Background: The androgen receptor splice variant-7 (AR-V7) has been implicated in the development of castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC) and resistance to abiraterone and enzalutamide.
Objective: To develop a validated assay for detection of AR-V7 protein in tumour tissue and determine its expression and clinical significance as patients progress from hormone-sensitive prostate cancer (HSPC) to CRPC.
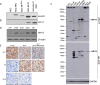
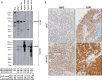
Design, setting, and participants: Following monoclonal antibody generation and validation, we retrospectively identified patients who had HSPC and CRPC tissue available for AR-V7 immunohistochemical (IHC) analysis.
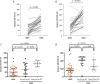
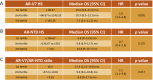
Outcome measurements and statistical analysis: Nuclear AR-V7 expression was determined using IHC H score (HS) data. The change in nuclear AR-V7 expression from HSPC to CRPC and the association between nuclear AR-V7 expression and overall survival (OS) was determined.
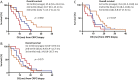
Results and limitations: Nuclear AR-V7 expression was significantly lower in HSPC (median HS 50, interquartile range [IQR] 17.5-90) compared to CRPC (HS 135, IQR 80-157.5; p<0.0001), and in biopsy tissue taken before (HS 80, IQR 30-136.3) compared to after (HS 140, IQR 105-167.5; p=0.007) abiraterone or enzalutamide treatment. Lower nuclear AR-V7 expression at CRPC biopsy was associated with longer OS (hazard ratio 1.012, 95% confidence interval 1.004-1.020; p=0.003). While this monoclonal antibody primarily binds to AR-V7 in PC biopsy tissue, it may also bind to other proteins.
Conclusions: We provide the first evidence that nuclear AR-V7 expression increases with emerging CRPC and is prognostic for OS, unlike antibody staining for the AR N-terminal domain. These data indicate that AR-V7 is important in CRPC disease biology; agents targeting AR splice variants are needed to test this hypothesis and further improve patient outcome from CRPC.
Patient summary: In this study we found that levels of the protein AR-V7 were higher in patients with advanced prostate cancer. A higher level of AR-V7 identifies a group of patients who respond less well to certain prostate cancer treatments and live for a shorter period of time.
Keywords: Androgen receptor; Androgen receptor variant-7; Castration-resistant prostate cancer; Metastatic biopsy; Predictor of outcome; Treatment resistance.
Copyright © 2016 European Association of Urology. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
Comment in
-
Making Predictive Biomarkers Readily Available.Eur Urol. 2016 Oct;70(4):609-610. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2016.05.003. Epub 2016 May 13. Eur Urol. 2016. PMID: 27184380 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
AR-V7 in Peripheral Whole Blood of Patients with Castration-resistant Prostate Cancer: Association with Treatment-specific Outcome Under Abiraterone and Enzalutamide.Eur Urol. 2017 Nov;72(5):828-834. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2017.07.024. Epub 2017 Aug 14. Eur Urol. 2017. PMID: 28818355
-
Androgen Receptor Splice Variant 7 and Efficacy of Taxane Chemotherapy in Patients With Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer.JAMA Oncol. 2015 Aug;1(5):582-91. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2015.1341. JAMA Oncol. 2015. PMID: 26181238 Free PMC article.
-
The Detection of Androgen Receptor Splice Variant 7 in Plasma-derived Exosomal RNA Strongly Predicts Resistance to Hormonal Therapy in Metastatic Prostate Cancer Patients.Eur Urol. 2017 Apr;71(4):680-687. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2016.08.012. Epub 2016 Oct 10. Eur Urol. 2017. PMID: 27733296
-
Androgen receptor splice variants in the era of enzalutamide and abiraterone.Horm Cancer. 2014 Oct;5(5):265-73. doi: 10.1007/s12672-014-0190-1. Epub 2014 Jul 22. Horm Cancer. 2014. PMID: 25048254 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[AR-V7 Androgen Receptor Variant as a Predictor of Response to Androgen-receptor Targeting Agents Used to Treat Castration-refractory Metastatic Prostate Cancer].Klin Onkol. 2017 Winter;31(1):9-14. doi: 10.14735/amko20189. Klin Onkol. 2017. PMID: 29488772 Review. Czech.
Cited by
-
Targeting Androgen Receptor Aberrations in Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer.Clin Cancer Res. 2016 Sep 1;22(17):4280-2. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-16-1137. Epub 2016 Jun 21. Clin Cancer Res. 2016. PMID: 27330057 Free PMC article.
-
Changes in prostate-specific antigen kinetics during androgen-deprivation therapy as a predictor of response to abiraterone in chemonaïve patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer.Investig Clin Urol. 2022 Sep;63(5):546-553. doi: 10.4111/icu.20210450. Investig Clin Urol. 2022. PMID: 36068000 Free PMC article.
-
The positive relationship between androgen receptor splice variant-7 expression and the risk of castration-resistant prostate cancer: A cumulative analysis.Front Oncol. 2023 Feb 14;13:1053111. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1053111. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36865799 Free PMC article.
-
ARv7 Represses Tumor-Suppressor Genes in Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer.Cancer Cell. 2019 Mar 18;35(3):401-413.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2019.01.008. Epub 2019 Feb 14. Cancer Cell. 2019. PMID: 30773341 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel, Circulating Tumor Cell Enrichment Method Reduces ARv7 False Positivity in Patients with Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer.Diagnostics (Basel). 2020 Mar 11;10(3):151. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics10030151. Diagnostics (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32168745 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

