Insulin signaling misregulation underlies circadian and cognitive deficits in a Drosophila fragile X model
- PMID: 27090306
- PMCID: PMC5071102
- DOI: 10.1038/mp.2016.51
Insulin signaling misregulation underlies circadian and cognitive deficits in a Drosophila fragile X model
Abstract
Fragile X syndrome (FXS) is an undertreated neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by low intelligence quotent and a wide range of other symptoms including disordered sleep and autism. Although FXS is the most prevalent inherited cause of intellectual disability, its mechanistic underpinnings are not well understood. Using Drosophila as a model of FXS, we showed that select expression of dfmr1 in the insulin-producing cells (IPCs) of the brain was sufficient to restore normal circadian behavior and to rescue the memory deficits in the fragile X mutant fly. Examination of the insulin signaling (IS) pathway revealed elevated levels of Drosophila insulin-like peptide 2 (Dilp2) in the IPCs and elevated IS in the dfmr1 mutant brain. Consistent with a causal role for elevated IS in dfmr1 mutant phenotypes, the expression of dfmr1 specifically in the IPCs reduced IS, and genetic reduction of the insulin pathway also led to amelioration of circadian and memory defects. Furthermore, we showed that treatment with the FDA-approved drug metformin also rescued memory. Finally, we showed that reduction of IS is required at different time points to rescue circadian behavior and memory. Our results indicate that insulin misregulation underlies the circadian and cognitive phenotypes displayed by the Drosophila fragile X model, and thus reveal a metabolic pathway that can be targeted by new and already approved drugs to treat fragile X patients.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
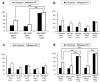
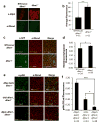
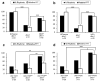
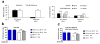
Similar articles
-
Drosophila melanogaster as a Model to Study Fragile X-Associated Disorders.Genes (Basel). 2022 Dec 28;14(1):87. doi: 10.3390/genes14010087. Genes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36672829 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Spontaneous motor-behavior abnormalities in two Drosophila models of neurodevelopmental disorders.J Neurogenet. 2021 Mar;35(1):1-22. doi: 10.1080/01677063.2020.1833005. Epub 2020 Nov 9. J Neurogenet. 2021. PMID: 33164597
-
Loss of Drosophila FMRP leads to alterations in energy metabolism and mitochondrial function.Hum Mol Genet. 2018 Jan 1;27(1):95-106. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddx387. Hum Mol Genet. 2018. PMID: 29106525 Free PMC article.
-
Circadian Rhythm and Sleep Analyses in a Fruit Fly Model of Fragile X Syndrome Using a Video-Based Automated Behavioral Research System.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 20;25(14):7949. doi: 10.3390/ijms25147949. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39063191 Free PMC article.
-
Learning and behavioral deficits associated with the absence of the fragile X mental retardation protein: what a fly and mouse model can teach us.Learn Mem. 2014 Sep 16;21(10):543-55. doi: 10.1101/lm.035956.114. Print 2014 Oct. Learn Mem. 2014. PMID: 25227249 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Metformin: The Winding Path from Understanding Its Molecular Mechanisms to Proving Therapeutic Benefits in Neurodegenerative Disorders.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Dec 11;16(12):1714. doi: 10.3390/ph16121714. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38139841 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Upregulation of neuronal PGC-1α ameliorates cognitive impairment induced by chronic cerebral hypoperfusion.Theranostics. 2020 Feb 3;10(6):2832-2848. doi: 10.7150/thno.37119. eCollection 2020. Theranostics. 2020. PMID: 32194838 Free PMC article.
-
Tet controls axon guidance in early brain development through glutamatergic signaling.iScience. 2024 Apr 1;27(5):109634. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.109634. eCollection 2024 May 17. iScience. 2024. PMID: 38655199 Free PMC article.
-
Neuronal fragile X mental retardation protein activates glial insulin receptor mediated PDF-Tri neuron developmental clearance.Nat Commun. 2021 Feb 19;12(1):1160. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-21429-4. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 33608547 Free PMC article.
-
Negative effect of treatment with mGluR5 negative allosteric modulator AFQ056 on blood biomarkers in young individuals with Fragile X syndrome.SAGE Open Med. 2024 Sep 29;12:20503121241282401. doi: 10.1177/20503121241282401. eCollection 2024. SAGE Open Med. 2024. PMID: 39483619 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Santoro MR, Bray SM, Warren ST. Molecular mechanisms of fragile X syndrome: a twenty-year perspective. Annual review of pathology. 2012;7:219–45. - PubMed
-
- Dolen G, Carpenter RL, Ocain TD, Bear MF. Mechanism-based approaches to treating fragile X. Pharmacology & therapeutics. 2010;127(1):78–93. - PubMed
-
- Jacquemont S, Hagerman RJ, Hagerman PJ, Leehey MA. Fragile-X syndrome and fragile X-associated tremor/ataxia syndrome: two faces of FMR1. Lancet neurology. 2007;6(1):45–55. - PubMed
-
- O'Donnell WT, Warren ST. A decade of molecular studies of fragile X syndrome. Annual review of neuroscience. 2002;25:315–38. - PubMed
-
- Turk J. Fragile X syndrome: lifespan developmental implications for those without as well as with intellectual disability. Current opinion in psychiatry. 2011;24(5):387–97. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

