Extensive surface protein profiles of extracellular vesicles from cancer cells may provide diagnostic signatures from blood samples
- PMID: 27086589
- PMCID: PMC4834364
- DOI: 10.3402/jev.v5.25355
Extensive surface protein profiles of extracellular vesicles from cancer cells may provide diagnostic signatures from blood samples
Abstract
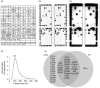
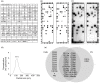
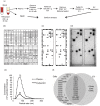
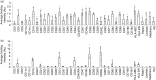
Extracellular vesicles (EV) are membranous particles (30-1,000 nm in diameter) secreted by cells. Important biological functions have been attributed to 2 subsets of EV, the exosomes (bud from endosomal membranes) and the microvesicles (MV; bud from plasma membranes). Since both types of particles contain surface proteins derived from their cell of origin, their detection in blood may enable diagnosis and prognosis of disease. We have used an antibody microarray (DotScan) to compare the surface protein profiles of live cancer cells with those of their EV, based on their binding patterns to immobilized antibodies. Initially, EV derived from the cancer cell lines, LIM1215 (colorectal cancer) and MEC1 (B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukaemia; CLL), were used for assay optimization. Biotinylated antibodies specific for EpCAM (CD326) and CD19, respectively, were used to detect captured particles by enhanced chemiluminescence. Subsequently, this approach was used to profile CD19(+) EV from the plasma of CLL patients. These EV expressed a subset (~40%) of the proteins detected on CLL cells from the same patients: moderate or high levels of CD5, CD19, CD31, CD44, CD55, CD62L, CD82, HLA-A,B,C, HLA-DR; low levels of CD21, CD49c, CD63. None of these proteins was detected on EV from the plasma of age- and gender-matched healthy individuals.
Keywords: CD antigen; chronic lymphocytic leukaemia; exosomes; luminescence; microvesicles.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Surface Profiling of Extracellular Vesicles from Plasma or Ascites Fluid Using DotScan Antibody Microarrays.Methods Mol Biol. 2017;1619:263-301. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-7057-5_20. Methods Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 28674892
-
Extracellular Vesicle (EV) Array: microarray capturing of exosomes and other extracellular vesicles for multiplexed phenotyping.J Extracell Vesicles. 2013 Jun 18;2. doi: 10.3402/jev.v2i0.20920. eCollection 2013. J Extracell Vesicles. 2013. PMID: 24009888 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of B-cell surface antigens in subpopulations of exosomes released from B-cell lymphoma cells.Clin Ther. 2014 Jun 1;36(6):847-862.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2014.05.010. Clin Ther. 2014. PMID: 24952935
-
Extracellular Vesicles: Recent Developments in Technology and Perspectives for Cancer Liquid Biopsy.Recent Results Cancer Res. 2020;215:319-344. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-26439-0_17. Recent Results Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 31605237 Review.
-
Diagnostic and Therapeutic Potential of Extracellular Vesicles in B-Cell Malignancies.Front Oncol. 2020 Sep 29;10:580874. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.580874. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 33117718 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles: role in oncogenic processes, bioengineering potential, and technical challenges.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019 Nov 26;10(1):347. doi: 10.1186/s13287-019-1468-6. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019. PMID: 31771657 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A novel strategy to identify candidate diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers for gastric cancer.Cancer Cell Int. 2021 Jul 2;21(1):335. doi: 10.1186/s12935-021-02007-6. Cancer Cell Int. 2021. PMID: 34215253 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular interactions at the surface of extracellular vesicles.Semin Immunopathol. 2018 Sep;40(5):453-464. doi: 10.1007/s00281-018-0682-0. Epub 2018 Apr 16. Semin Immunopathol. 2018. PMID: 29663027 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Roadmap of Colorectal Cancer Screening.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Mar 4;13(5):1101. doi: 10.3390/cancers13051101. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33806465 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of the hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells-derived extracellular vesicles in hematopoiesis.Heliyon. 2024 Jul 24;10(15):e35051. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e35051. eCollection 2024 Aug 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39157371 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

