Acute inhibition of neurosteroid estrogen synthesis suppresses status epilepticus in an animal model
- PMID: 27083045
- PMCID: PMC4862752
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.12917
Acute inhibition of neurosteroid estrogen synthesis suppresses status epilepticus in an animal model
Erratum in
-
Correction: Acute inhibition of neurosteroid estrogen synthesis suppresses status epilepticus in an animal model.Elife. 2016 Jul 1;5:e19109. doi: 10.7554/eLife.19109. Elife. 2016. PMID: 27364569 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
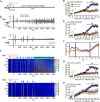
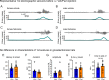
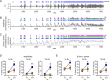
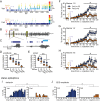
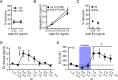
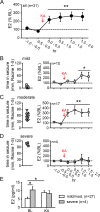
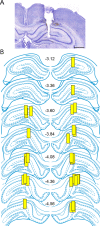
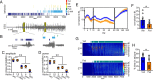
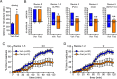
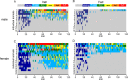
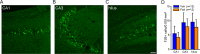
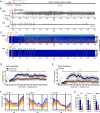
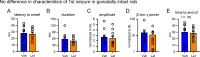
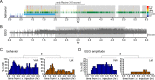
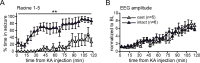
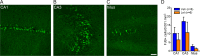
Status epilepticus (SE) is a common neurological emergency for which new treatments are needed. In vitro studies suggest a novel approach to controlling seizures in SE: acute inhibition of estrogen synthesis in the brain. Here, we show in rats that systemic administration of an aromatase (estrogen synthase) inhibitor after seizure onset strongly suppresses both electrographic and behavioral seizures induced by kainic acid (KA). We found that KA-induced SE stimulates synthesis of estradiol (E2) in the hippocampus, a brain region commonly involved in seizures and where E2 is known to acutely promote neural activity. Hippocampal E2 levels were higher in rats experiencing more severe seizures. Consistent with a seizure-promoting effect of hippocampal estrogen synthesis, intra-hippocampal aromatase inhibition also suppressed seizures. These results reveal neurosteroid estrogen synthesis as a previously unknown factor in the escalation of seizures and suggest that acute administration of aromatase inhibitors may be an effective treatment for SE.
Keywords: estradiol; hippocampus; kainic acid; microdialysis; neuroscience; rat; seizure.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that no competing interests exist.
Figures
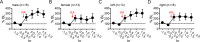
Similar articles
-
Aromatase inhibition by letrozole attenuates kainic acid-induced seizures but not neurotoxicity in mice.Epilepsy Res. 2018 Jul;143:60-69. doi: 10.1016/j.eplepsyres.2018.04.004. Epub 2018 Apr 9. Epilepsy Res. 2018. PMID: 29665500
-
Design and development of letrozole nanoemulsion: A comparative evaluation of brain targeted nanoemulsion with free letrozole against status epilepticus and neurodegeneration in mice.Int J Pharm. 2019 Jun 30;565:20-32. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2019.04.076. Epub 2019 Apr 30. Int J Pharm. 2019. PMID: 31051232
-
Hippocampal damage after intra-amygdala kainic acid-induced status epilepticus and seizure preconditioning-mediated neuroprotection in SJL mice.Epilepsy Res. 2010 Feb;88(2-3):151-61. doi: 10.1016/j.eplepsyres.2009.10.012. Epilepsy Res. 2010. PMID: 19931419
-
Acute and spontaneous seizure onset zones in the intraperitoneal kainic acid model.Epilepsy Behav. 2017 Mar;68:66-70. doi: 10.1016/j.yebeh.2016.12.017. Epub 2017 Jan 19. Epilepsy Behav. 2017. PMID: 28109992
-
Resistance of immature hippocampus to morphologic and physiologic alterations following status epilepticus or kindling.Hippocampus. 2001;11(6):615-25. doi: 10.1002/hipo.1076. Hippocampus. 2001. PMID: 11811655
Cited by
-
The Promise and Practicality of Addressing Sex as a Biological Variable and the Ovarian Cycle in Preclinical Epilepsy Research.Epilepsy Curr. 2024 Jul 25;24(4):274-279. doi: 10.1177/15357597241261463. eCollection 2024 Jul-Aug. Epilepsy Curr. 2024. PMID: 39309055 Free PMC article.
-
Clustering drug-drug interaction networks with energy model layouts: community analysis and drug repurposing.Sci Rep. 2016 Sep 7;6:32745. doi: 10.1038/srep32745. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27599720 Free PMC article.
-
Sex Differences in Estradiol Secretion by Trigeminal Brainstem Neurons.Front Integr Neurosci. 2019 Feb 12;13:3. doi: 10.3389/fnint.2019.00003. eCollection 2019. Front Integr Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 30809134 Free PMC article.
-
Neurosteroid regulation of GABAA receptors: A role in catamenial epilepsy.Brain Res. 2019 Jan 15;1703:31-40. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2018.02.031. Epub 2018 Feb 23. Brain Res. 2019. PMID: 29481795 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel Brain-Penetrating Oxime Acetylcholinesterase Reactivators Attenuate Organophosphate-Induced Neuropathology in the Rat Hippocampus.Toxicol Sci. 2019 Jun 1;169(2):465-474. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfz060. Toxicol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30835286 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Boulware MI, Weick JP, Becklund BR, Kuo SP, Groth RD, Mermelstein PG. Estradiol activates group I and II metabotropic glutamate receptor signaling, leading to opposing influences on cAMP response element-binding protein. Journal of Neuroscience. 2005;25:5066–5078. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1427-05.2005. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

