Lysophosphatidic Acid Signaling through the Lysophosphatidic Acid-1 Receptor Is Required for Alveolarization
- PMID: 27082727
- PMCID: PMC4942205
- DOI: 10.1165/rcmb.2015-0152OC
Lysophosphatidic Acid Signaling through the Lysophosphatidic Acid-1 Receptor Is Required for Alveolarization
Abstract
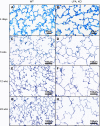
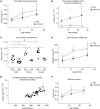
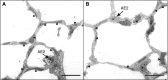
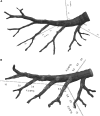
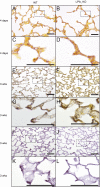
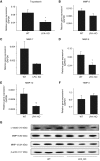
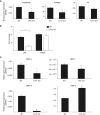
Lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) signaling through one of its receptors, LPA1, contributes to both the development and the pathological remodeling after injury of many organs. Because we found previously that LPA-LPA1 signaling contributes to pulmonary fibrosis, here we investigated whether this pathway is also involved in lung development. Quantitative assessment of lung architecture of LPA1-deficient knock-out (KO) and wild-type (WT) mice at 3, 12, and 24 weeks of age using design-based stereology suggested the presence of an alveolarization defect in LPA1 KO mice at 3 weeks, which persisted as alveolar numbers increased in WT mice into adulthood. Across the ages examined, the lungs of LPA1 KO mice exhibited decreased alveolar numbers, septal tissue volumes, and surface areas, and increased volumes of the distal airspaces. Elastic fibers, critical to the development of alveolar septa, appeared less organized and condensed and more discontinuous in KO alveoli starting at P4. Tropoelastin messenger RNA expression was decreased in KO lungs, whereas expression of matrix metalloproteinases degrading elastic fibers was either decreased or unchanged. These results are consistent with the abnormal lung phenotype of LPA1 KO mice, being attributable to reduced alveolar septal formation during development, rather than to increased septal destruction as occurs in the emphysema of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Peripheral septal fibroblasts and myofibroblasts, which direct septation in late alveolarization, demonstrated reduced production of tropoelastin and matrix metalloproteinases, and diminished LPA-induced migration, when isolated from LPA1 KO mice. Taken together, our data suggest that LPA-LPA1 signaling is critically required for septation during alveolarization.
Keywords: LPA1; alveolarization; elastin; lung development; matrix metalloproteinase.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Lysophosphatidic acid signaling through its receptor initiates profibrotic epithelial cell fibroblast communication mediated by epithelial cell derived connective tissue growth factor.Kidney Int. 2017 Mar;91(3):628-641. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2016.09.030. Epub 2016 Dec 4. Kidney Int. 2017. PMID: 27927603 Free PMC article.
-
The lysophosphatidic acid receptor LPA1 promotes epithelial cell apoptosis after lung injury.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2012 Mar;46(3):355-64. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2010-0155OC. Epub 2011 Oct 20. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 22021336 Free PMC article.
-
LPA1 receptor-mediated thromboxane A2 release is responsible for lysophosphatidic acid-induced vascular smooth muscle contraction.FASEB J. 2017 Apr;31(4):1547-1555. doi: 10.1096/fj.201600735R. Epub 2017 Jan 9. FASEB J. 2017. PMID: 28069828 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Regulation of Lysophosphatidic Acid Receptor 1 Maturation and Desensitization.Cell Biochem Biophys. 2021 Sep;79(3):477-483. doi: 10.1007/s12013-021-00999-6. Epub 2021 May 25. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2021. PMID: 34032994 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diverse effects of LPA receptors on cell motile activities of cancer cells.J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 2014 Jun;34(3):149-53. doi: 10.3109/10799893.2013.876042. Epub 2014 Jan 24. J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 2014. PMID: 24460191 Review.
Cited by
-
Fra-2 negatively regulates postnatal alveolar septation by modulating myofibroblast function.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2017 Nov 1;313(5):L878-L888. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00062.2017. Epub 2017 Aug 17. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2017. PMID: 28818870 Free PMC article.
-
Advancements in understanding the role of lysophospholipids and their receptors in lung disorders including bronchopulmonary dysplasia.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. 2020 Jul;1865(7):158685. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2020.158685. Epub 2020 Mar 10. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. 2020. PMID: 32169655 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adult Lysophosphatidic Acid Receptor 1-Deficient Rats with Hyperoxia-Induced Neonatal Chronic Lung Disease Are Protected against Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Acute Lung Injury.Front Physiol. 2017 Mar 22;8:155. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2017.00155. eCollection 2017. Front Physiol. 2017. PMID: 28382003 Free PMC article.
-
Stereology as the 3D tool to quantitate lung architecture.Histochem Cell Biol. 2021 Feb;155(2):163-181. doi: 10.1007/s00418-020-01927-0. Epub 2020 Oct 13. Histochem Cell Biol. 2021. PMID: 33051774 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular Lipids in the Lung and Their Role in Pulmonary Fibrosis.Cells. 2022 Apr 3;11(7):1209. doi: 10.3390/cells11071209. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35406772 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

