Food-web complexity, meta-community complexity and community stability
- PMID: 27071716
- PMCID: PMC4829910
- DOI: 10.1038/srep24478
Food-web complexity, meta-community complexity and community stability
Abstract
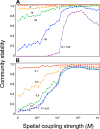
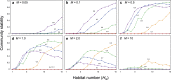
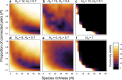
What allows interacting, diverse species to coexist in nature has been a central question in ecology, ever since the theoretical prediction that a complex community should be inherently unstable. Although the role of spatiality in species coexistence has been recognized, its application to more complex systems has been less explored. Here, using a meta-community model of food web, we show that meta-community complexity, measured by the number of local food webs and their connectedness, elicits a self-regulating, negative-feedback mechanism and thus stabilizes food-web dynamics. Moreover, the presence of meta-community complexity can give rise to a positive food-web complexity-stability effect. Spatiality may play a more important role in stabilizing dynamics of complex, real food webs than expected from ecological theory based on the models of simpler food webs.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Spatial complexity enhances predictability in food webs.Sci Rep. 2017 Feb 27;7:43440. doi: 10.1038/srep43440. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28240306 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-predator defence and the complexity-stability relationship of food webs.Proc Biol Sci. 2007 Jul 7;274(1618):1617-24. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2007.0335. Proc Biol Sci. 2007. PMID: 17456452 Free PMC article.
-
Reconciling complexity with stability in naturally assembling food webs.Nature. 2007 Oct 4;449(7162):599-602. doi: 10.1038/nature06154. Nature. 2007. PMID: 17914396
-
A landscape theory for food web architecture.Ecol Lett. 2008 Aug;11(8):867-81. doi: 10.1111/j.1461-0248.2008.01193.x. Ecol Lett. 2008. PMID: 18445027 Review.
-
Integrating food web diversity, structure and stability.Trends Ecol Evol. 2012 Jan;27(1):40-6. doi: 10.1016/j.tree.2011.09.001. Epub 2011 Sep 23. Trends Ecol Evol. 2012. PMID: 21944861 Review.
Cited by
-
Structural diversity across arbuscular mycorrhizal, ectomycorrhizal, and endophytic plant-fungus networks.BMC Plant Biol. 2018 Nov 21;18(1):292. doi: 10.1186/s12870-018-1500-5. BMC Plant Biol. 2018. PMID: 30463525 Free PMC article.
-
Far-ranging generalist top predators enhance the stability of meta-foodwebs.Sci Rep. 2019 Aug 22;9(1):12268. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-48731-y. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31439912 Free PMC article.
-
Recent advances in metacommunities and meta-ecosystem theories.F1000Res. 2017 May 2;6:610. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.10758.1. eCollection 2017. F1000Res. 2017. PMID: 28529720 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Persistence of a stage-structured food-web.Sci Rep. 2017 Sep 8;7(1):11055. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-11686-z. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28887530 Free PMC article.
-
Spatial compartmentation and food web stability.Sci Rep. 2018 Nov 2;8(1):16237. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-34716-w. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30390034 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Elton C. S. Ecology of invasions by animals and plants. (Chapman & Hall, 1958).
-
- Gardner M. R. & Ashby W. R. Connectance of large dynamic (cybernetic) systems: critical values of stability. Nature 228, 784 (1970). - PubMed
-
- May R. M. Stability in multispecies community models. Math Biosci. 12, 59–79 (1971).
-
- May R. M. Will a large complex system be stable? Nature 238, 413–414 (1972). - PubMed
-
- McCann K. S. The diversity-stability debate. Nature 405, 228–233 (2000). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

