Identification of miRNAs and their targets through high-throughput sequencing and degradome analysis in male and female Asparagus officinalis
- PMID: 27068118
- PMCID: PMC4828810
- DOI: 10.1186/s12870-016-0770-z
Identification of miRNAs and their targets through high-throughput sequencing and degradome analysis in male and female Asparagus officinalis
Abstract
Background: MicroRNAs (miRNAs), a class of non-coding small RNAs (sRNAs), regulate various biological processes. Although miRNAs have been identified and characterized in several plant species, miRNAs in Asparagus officinalis have not been reported. As a dioecious plant with homomorphic sex chromosomes, asparagus is regarded as an important model system for studying mechanisms of plant sex determination.
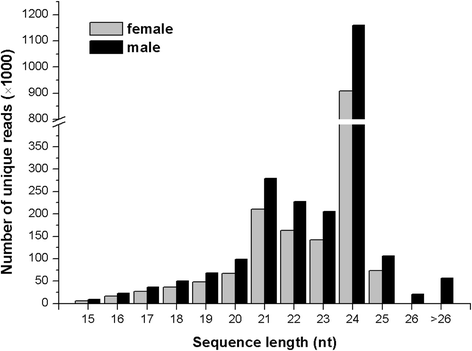
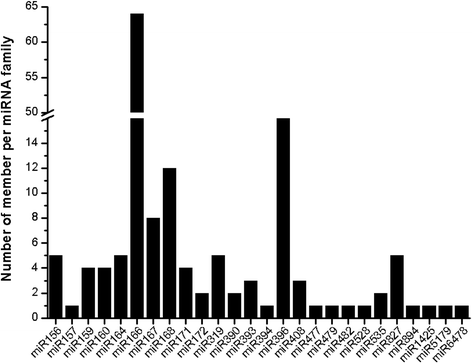
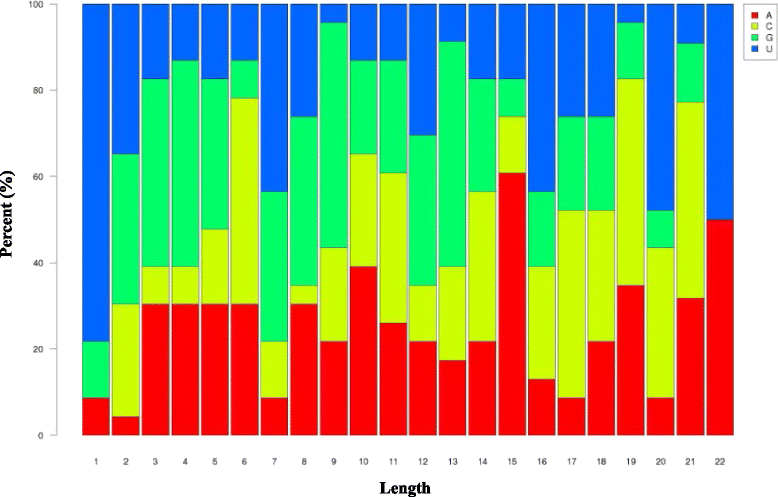
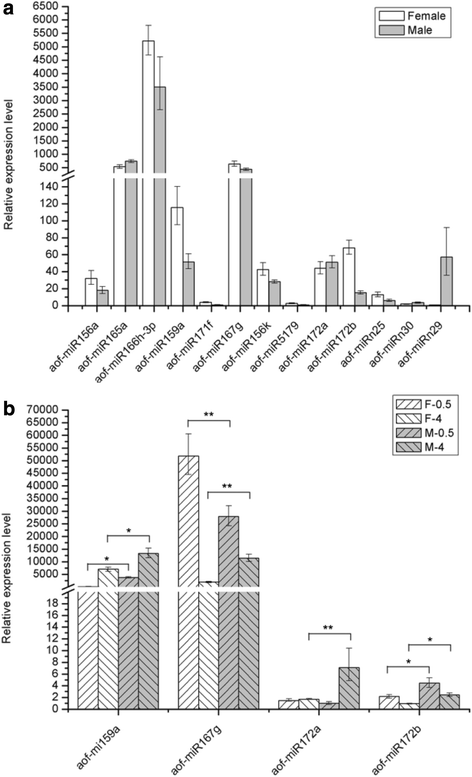
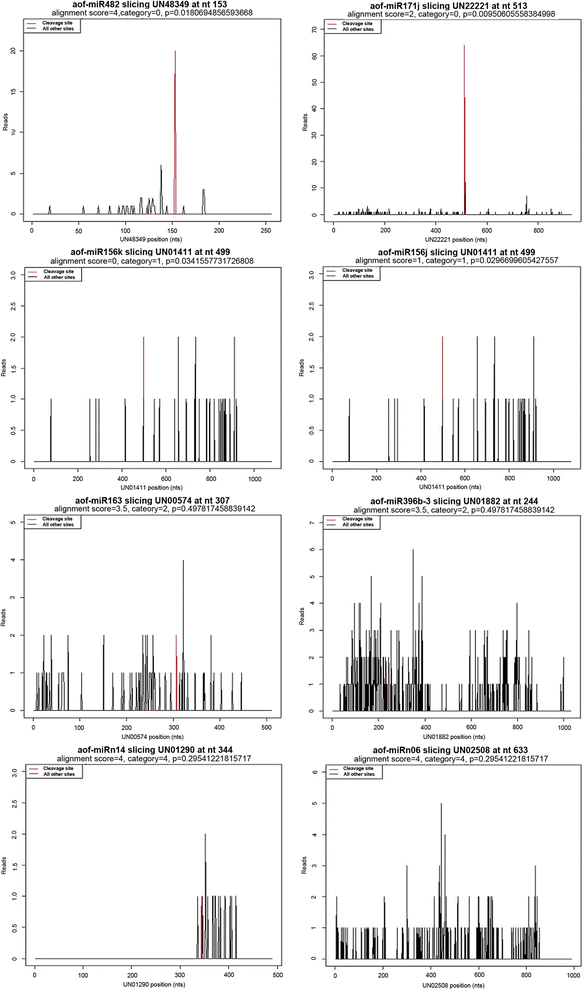
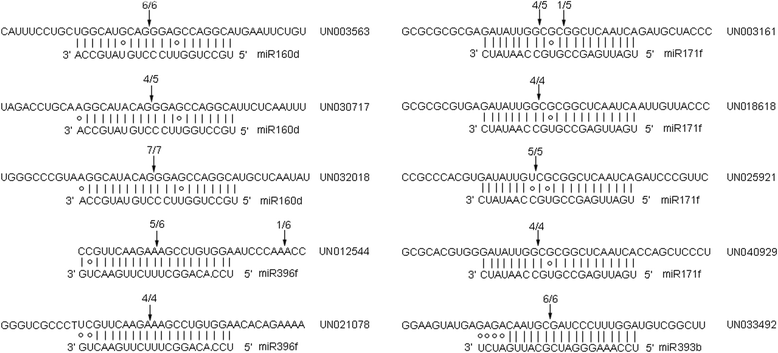
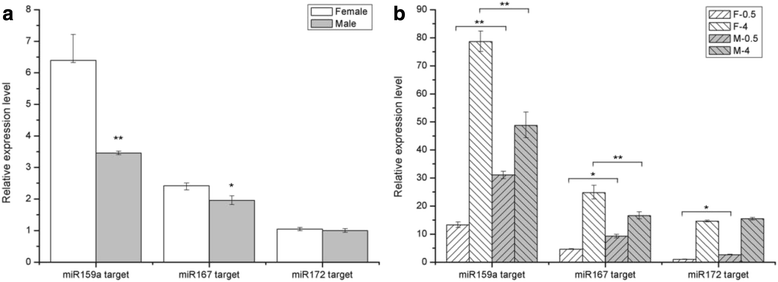
Results: Two independent sRNA libraries from male and female asparagus plants were sequenced with Illumina sequencing, thereby generating 4.13 and 5.88 million final clean reads, respectively. Both libraries predominantly contained 24-nt sRNAs, followed by 21-nt sRNAs. Further analysis identified 154 conserved miRNAs, which belong to 26 families, and 39 novel miRNA candidates seemed to be specific to asparagus. Comparative profiling revealed that 63 miRNAs exhibited significant differential expression between male and female plants, which was confirmed by real-time quantitative PCR analysis. Among them, 37 miRNAs were significantly up-regulated in the female library, whereas the others were preferentially expressed in the male library. Furthermore, 40 target mRNAs representing 44 conserved and seven novel miRNAs were identified in asparagus through high-throughput degradome sequencing. Functional annotation showed that these target mRNAs were involved in a wide range of developmental and metabolic processes.
Conclusions: We identified a large set of conserved and specific miRNAs and compared their expression levels between male and female asparagus plants. Several asparagus miRNAs, which belong to the miR159, miR167, and miR172 families involved in reproductive organ development, were differentially expressed between male and female plants, as well as during flower development. Consistently, several predicted targets of asparagus miRNAs were associated with floral organ development. These findings suggest the potential roles of miRNAs in sex determination and reproductive developmental processes in asparagus.
Keywords: Asparagus officinalis; Degradome analysis; High-throughput sequencing; Sex determination; miRNAs.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Identification of Taxus microRNAs and their targets with high-throughput sequencing and degradome analysis.Physiol Plant. 2012 Dec;146(4):388-403. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3054.2012.01668.x. Epub 2012 Jul 25. Physiol Plant. 2012. PMID: 22708792
-
Genome-wide characterization of rice black streaked dwarf virus-responsive microRNAs in rice leaves and roots by small RNA and degradome sequencing.Plant Cell Physiol. 2015 Apr;56(4):688-99. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcu213. Epub 2014 Dec 21. Plant Cell Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25535197
-
Identification and expression profiling of Vigna mungo microRNAs from leaf small RNA transcriptome by deep sequencing.J Integr Plant Biol. 2014 Jan;56(1):15-23. doi: 10.1111/jipb.12115. Epub 2013 Dec 19. J Integr Plant Biol. 2014. PMID: 24138283
-
The use of high-throughput sequencing methods for plant microRNA research.RNA Biol. 2015;12(7):709-19. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2015.1053686. RNA Biol. 2015. PMID: 26016494 Free PMC article. Review.
-
miRNAs and lncRNAs in reproductive development.Plant Sci. 2015 Sep;238:46-52. doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2015.05.017. Epub 2015 Jun 1. Plant Sci. 2015. PMID: 26259173 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of microRNAs and their gene targets in cytoplasmic male sterile and fertile maintainer lines of pigeonpea.Planta. 2021 Feb 4;253(2):59. doi: 10.1007/s00425-021-03568-6. Planta. 2021. PMID: 33538916
-
The emerging role of small RNAs in ovule development, a kind of magic.Plant Reprod. 2021 Dec;34(4):335-351. doi: 10.1007/s00497-021-00421-4. Epub 2021 Jun 17. Plant Reprod. 2021. PMID: 34142243 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcriptome analysis of miRNAs expression reveals novel insights into adventitious root formation in lotus (Nelumbo nucifera Gaertn.).Mol Biol Rep. 2019 Jun;46(3):2893-2905. doi: 10.1007/s11033-019-04749-z. Epub 2019 Mar 12. Mol Biol Rep. 2019. PMID: 30864113
-
Genome-Wide Identification of MicroRNAs and Their Targets in the Leaves and Fruits of Eucommia ulmoides Using High-Throughput Sequencing.Front Plant Sci. 2016 Nov 8;7:1632. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2016.01632. eCollection 2016. Front Plant Sci. 2016. PMID: 27877179 Free PMC article.
-
Non-coding RNAs and plant male sterility: current knowledge and future prospects.Plant Cell Rep. 2018 Feb;37(2):177-191. doi: 10.1007/s00299-018-2248-y. Epub 2018 Jan 13. Plant Cell Rep. 2018. PMID: 29332167 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

