Identification and characterization of novel and conserved microRNAs in several tissues of the Chinese rare minnow (Gobiocypris rarus) based on illumina deep sequencing technology
- PMID: 27066897
- PMCID: PMC4828758
- DOI: 10.1186/s12864-016-2606-5
Identification and characterization of novel and conserved microRNAs in several tissues of the Chinese rare minnow (Gobiocypris rarus) based on illumina deep sequencing technology
Abstract
Background: MicroRNAs (miRNAs), which comprise a large family of endogenous small non-coding RNA molecules, play important roles in the regulation of gene expression in various biological processes. The Chinese rare minnow (Gobiocypris rarus) is a Chinese native fish species and is used extensively as an experimental fish in China; however, relevant biological data, especially miRNA transcriptome data, have not been well documented. To discover conserved and potential novel miRNAs in Chinese rare minnows, a pool of equal amounts of RNA obtained from 6 different adult rare minnow tissues (brain, eye, gill, liver, muscle and heart) was sequenced using illumina deep sequencing technology.
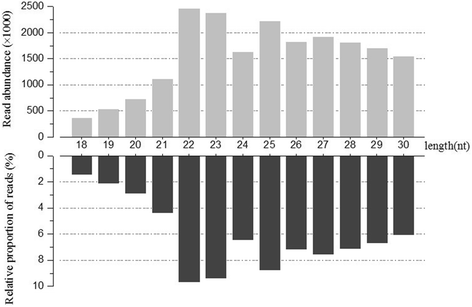
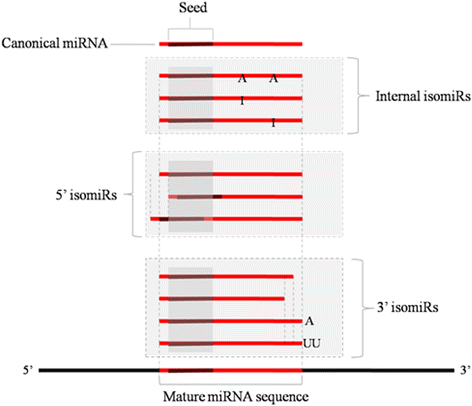
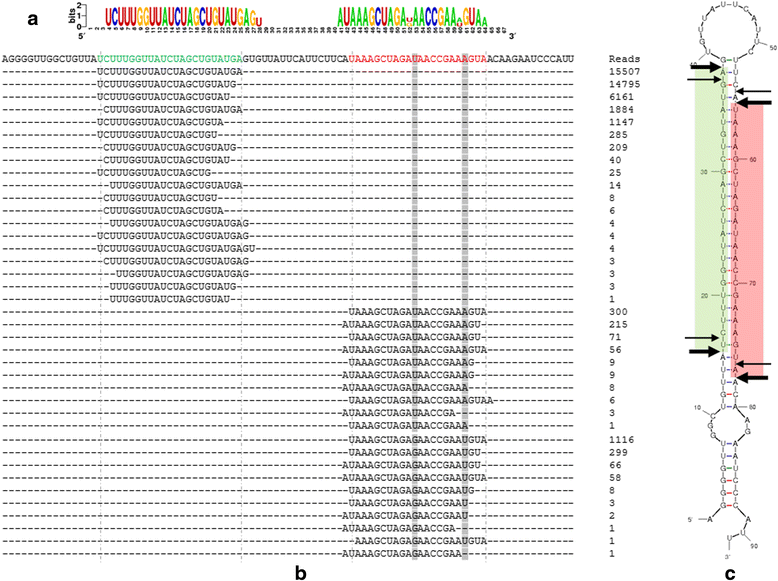
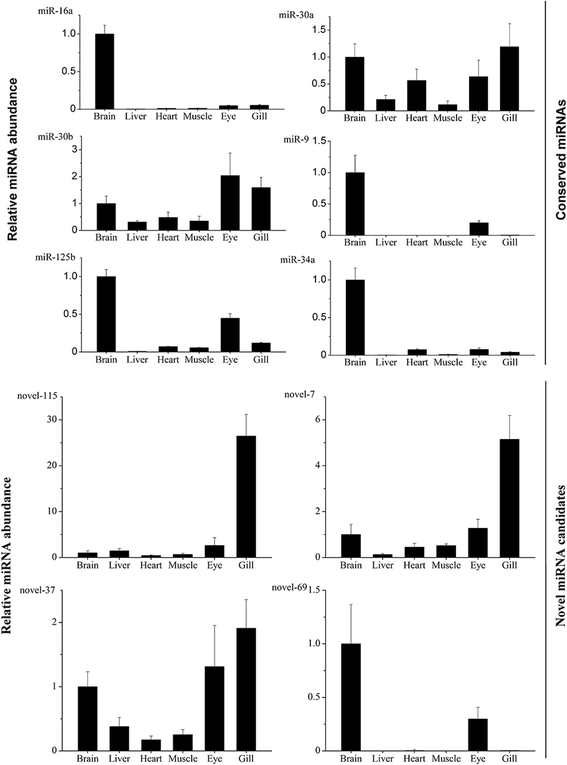
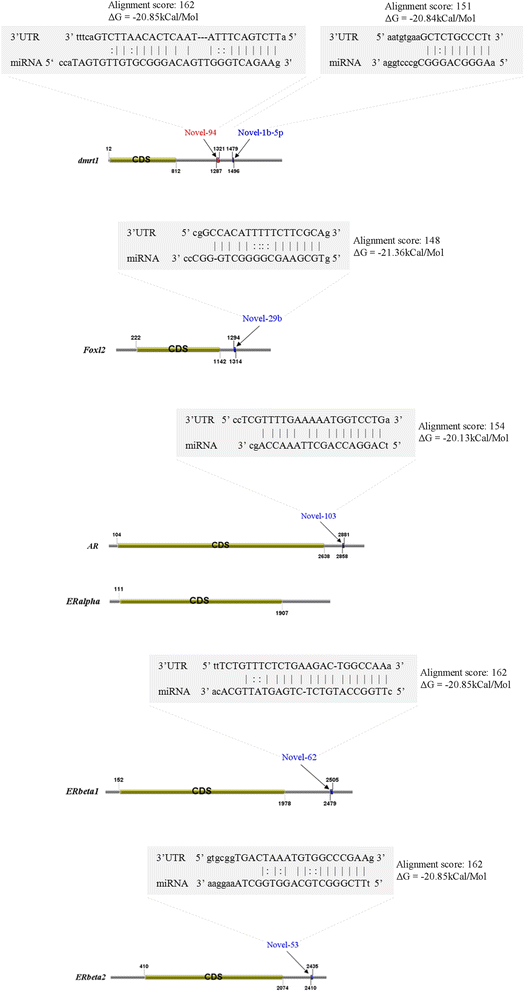
Results: In the present study, 26,930,553 raw reads, representing 2,118,439 unique high-quality reads, were obtained from the pooled small RNA library. Using bioinformatics analysis, 352 conserved and 112 novel Chinese rare minnow miRNAs were first discovered and characterized in this study. Moreover, we found extensive sequence variations (isomiRs) in rare minnow miRNAs, including internal miRNA isomiRs and terminal isomiRs at both the 5' and 3' ends and nucleotide variants. Six conserved and 4 novel miRNAs were selected and validated in 6 different adult rare minnow tissues using quantitative real-time PCR (qPCR). The results showed that miR-30a, miR-30b, and Novel-37 are ubiquitously expressed in a variety of tissues. miR-16a, miR-9, miR-125b, miR-34a, and Novel-69 were predominantly expressed in the brain. Novel-115 and Novel-7 were highly expressed in gills, but were relatively weakly expressed in other tissues. These results provided the expression patterns of miRNA genes in Chinese rare minnow. Finally, based on bioinformatics predictions, we mainly found that Novel-94 and Novel-1b-5p were simultaneously targeted to the 3'UTR of Dmrt1, which controls sex determination and/or sexual differentiation in a variety of metazoans at different sites. Novel-29b targeted the 3'UTR of Foxl2, which is involved in the maintenance of ovarian function and the transcriptional regulation of gonadal differentiation-related genes. Novel-62 and Novel-53 targeted the 3'UTR of ERbeta1 and ERbeta2 (which regulate the transcription of target genes), respectively.
Conclusions: Rare minnow is a widely used model for assessing the risk of environmental pollution in China. Identifying and characterizing rare minnow miRNA genes is necessary to discover the biological function of miRNAs and to screen for new molecule biomarkers to assess the risk of environmental pollution in the future.
Keywords: Deep sequencing; Gobiocypris rarus; IsomiRs; Target prediction; microRNA.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Identification and characterization of known and novel microRNAs in three tissues of Chinese giant salamander base on deep sequencing approach.Genomics. 2017 Jul;109(3-4):258-264. doi: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2017.04.007. Epub 2017 May 2. Genomics. 2017. PMID: 28476431
-
Global microRNA and isomiR expression associated with liver metabolism is induced by organophosphorus flame retardant exposure in male Chinese rare minnow (Gobiocypris rarus).Sci Total Environ. 2019 Feb 1;649:829-838. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.08.305. Epub 2018 Aug 24. Sci Total Environ. 2019. PMID: 30176492
-
Deep sequencing, profiling and detailed annotation of microRNAs in Takifugu rubripes.BMC Genomics. 2015 Jun 16;16(1):457. doi: 10.1186/s12864-015-1622-1. BMC Genomics. 2015. PMID: 26078057 Free PMC article.
-
Toxicogenomic applications of Chinese rare minnow (Gobiocypris rarus) in aquatic toxicology.Comp Biochem Physiol Part D Genomics Proteomics. 2016 Sep;19:174-180. doi: 10.1016/j.cbd.2016.06.007. Epub 2016 Jun 21. Comp Biochem Physiol Part D Genomics Proteomics. 2016. PMID: 27373348 Review.
-
Species and Life-Stage Sensitivity of Chinese Rare Minnow (Gobiocypris rarus) to Chemical Exposure: A Critical Review.Environ Toxicol Chem. 2021 Oct;40(10):2680-2692. doi: 10.1002/etc.5165. Epub 2021 Sep 9. Environ Toxicol Chem. 2021. PMID: 34265131 Review.
Cited by
-
A New Type of Allodiploid Hybrids Derived From Female Megalobrama amblycephala × Male Gobiocypris rarus.Front Genet. 2021 Jul 19;12:685914. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.685914. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 34349781 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and profiling of growth-related microRNAs in Chinese perch (Siniperca chuatsi).BMC Genomics. 2017 Jun 28;18(1):489. doi: 10.1186/s12864-017-3851-y. BMC Genomics. 2017. PMID: 28659132 Free PMC article.
-
High-throughput sequencing analysis of differentially expressed miRNAs and target genes in ischemia/reperfusion injury and apelin-13 neuroprotection.Neural Regen Res. 2018 Feb;13(2):265-271. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.226397. Neural Regen Res. 2018. PMID: 29557376 Free PMC article.
-
Small RNA sequencing reveals a role for sugarcane miRNAs and their targets in response to Sporisorium scitamineum infection.BMC Genomics. 2017 Apr 24;18(1):325. doi: 10.1186/s12864-017-3716-4. BMC Genomics. 2017. PMID: 28438123 Free PMC article.
-
Deep Illumina sequencing reveals conserved and novel microRNAs in grass carp in response to grass carp reovirus infection.BMC Genomics. 2017 Feb 20;18(1):195. doi: 10.1186/s12864-017-3562-4. BMC Genomics. 2017. PMID: 28219339 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Starner T, Mann S, Rhodes B, Levine J, Healey J, Kirsch D, Picard RW, Pentland A. Augmented reality through wearable computing. Presence Teleoperators Virtual Environ. 1997;6:386–98.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

