Genome-Wide Identification, Characterization and Phylogenetic Analysis of ATP-Binding Cassette (ABC) Transporter Genes in Common Carp (Cyprinus carpio)
- PMID: 27058731
- PMCID: PMC4825979
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0153246
Genome-Wide Identification, Characterization and Phylogenetic Analysis of ATP-Binding Cassette (ABC) Transporter Genes in Common Carp (Cyprinus carpio)
Abstract
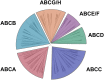
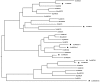
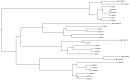
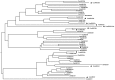
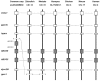
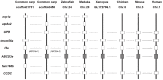
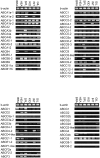
The ATP-binding cassette (ABC) gene family is considered to be one of the largest gene families in all forms of prokaryotic and eukaryotic life. Although the ABC transporter genes have been annotated in some species, detailed information about the ABC superfamily and the evolutionary characterization of ABC genes in common carp (Cyprinus carpio) are still unclear. In this research, we identified 61 ABC transporter genes in the common carp genome. Phylogenetic analysis revealed that they could be classified into seven subfamilies, namely 11 ABCAs, six ABCBs, 19 ABCCs, eight ABCDs, two ABCEs, four ABCFs, and 11 ABCGs. Comparative analysis of the ABC genes in seven vertebrate species including common carp, showed that at least 10 common carp genes were retained from the third round of whole genome duplication, while 12 duplicated ABC genes may have come from the fourth round of whole genome duplication. Gene losses were also observed for 14 ABC genes. Expression profiles of the 61 ABC genes in six common carp tissues (brain, heart, spleen, kidney, intestine, and gill) revealed extensive functional divergence among the ABC genes. Different copies of some genes had tissue-specific expression patterns, which may indicate some gene function specialization. This study provides essential genomic resources for future studies in common carp.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Genome wide identification, phylogeny, and expression of bone morphogenetic protein genes in tetraploidized common carp (Cyprinus carpio).Gene. 2017 Sep 5;627:157-163. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2017.06.020. Epub 2017 Jun 13. Gene. 2017. PMID: 28627438
-
Identification and expression analysis of ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporters revealed its role in regulating stress response in pear (Pyrus bretchneideri).BMC Genomics. 2024 Feb 12;25(1):169. doi: 10.1186/s12864-024-10063-1. BMC Genomics. 2024. PMID: 38347517 Free PMC article.
-
Genome Wide Identification, Phylogeny, and Expression of Aquaporin Genes in Common Carp (Cyprinus carpio).PLoS One. 2016 Dec 9;11(12):e0166160. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0166160. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27935978 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide identification of ATP binding cassette (ABC) transporter and heavy metal associated (HMA) gene families in flax (Linum usitatissimum L.).BMC Genomics. 2020 Oct 19;21(1):722. doi: 10.1186/s12864-020-07121-9. BMC Genomics. 2020. PMID: 33076828 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evolution of the ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter superfamily in vertebrates.Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet. 2005;6:123-42. doi: 10.1146/annurev.genom.6.080604.162122. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet. 2005. PMID: 16124856 Review.
Cited by
-
Genome-Wide Identification, Characterisation and Phylogenetic Analysis of 52 Striped Catfish (Pangasianodon hypophthalmus) ATP-Binding Cassette (ABC) Transporter Genes.Trop Life Sci Res. 2022 Jul;33(2):257-293. doi: 10.21315/tlsr2022.33.2.12. Epub 2022 Jul 15. Trop Life Sci Res. 2022. PMID: 35966264 Free PMC article.
-
The human ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter superfamily.Hum Mutat. 2022 Sep;43(9):1162-1182. doi: 10.1002/humu.24418. Epub 2022 Jun 22. Hum Mutat. 2022. PMID: 35642569 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ABCF2, an Nrf2 target gene, contributes to cisplatin resistance in ovarian cancer cells.Mol Carcinog. 2017 Jun;56(6):1543-1553. doi: 10.1002/mc.22615. Epub 2017 May 2. Mol Carcinog. 2017. PMID: 28112439 Free PMC article.
-
Expression and Function of ABC Proteins in Fish Intestine.Front Physiol. 2021 Dec 9;12:791834. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2021.791834. eCollection 2021. Front Physiol. 2021. PMID: 34955897 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genome-Wide Identification and Analysis of the ABCF Gene Family in Triticum aestivum.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Nov 18;24(22):16478. doi: 10.3390/ijms242216478. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38003668 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

