Activation of the PI3K/mTOR Pathway following PARP Inhibition in Small Cell Lung Cancer
- PMID: 27055253
- PMCID: PMC4824499
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0152584
Activation of the PI3K/mTOR Pathway following PARP Inhibition in Small Cell Lung Cancer
Abstract
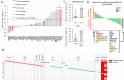
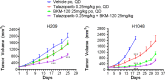
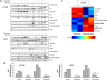
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is an aggressive malignancy with limited treatment options. We previously found that PARP is overexpressed in SCLC and that targeting PARP reduces cell line and tumor growth in preclinical models. However, SCLC cell lines with PI3K/mTOR pathway activation were relatively less sensitive to PARP inhibition. In this study, we investigated the proteomic changes in PI3K/mTOR and other pathways that occur following PAPR inhibition and/or knockdown in vitro and in vivo. Using reverse-phase protein array, we found the proteins most significantly upregulated following treatment with the PARP inhibitors olaparib and rucaparib were in the PI3K/mTOR pathway (p-mTOR, p-AKT, and pS6) (p≤0.02). Furthermore, amongst the most significantly down-regulated proteins were LKB1 and its targets AMPK and TSC, which negatively regulate the PI3K pathway (p≤0.042). Following PARP knockdown in cell lines, phosphorylated mTOR, AKT and S6 were elevated and LKB1 signaling was diminished. Global ATP concentrations increased following PARP inhibition (p≤0.02) leading us to hypothesize that the observed increased PI3K/mTOR pathway activation following PARP inhibition results from decreased ATP usage and a subsequent decrease in stress response signaling via LKB1. Based on these results, we then investigated whether co-targeting with a PARP and PI3K inhibitor (BKM-120) would work better than either single agent alone. A majority of SCLC cell lines were sensitive to BKM-120 at clinically achievable doses, and cMYC expression was the strongest biomarker of response. At clinically achievable doses of talazoparib (the most potent PARP inhibitor in SCLC clinical testing) and BKM-120, an additive effect was observed in vitro. When tested in two SCLC animal models, a greater than additive interaction was seen (p≤0.008). The data presented here suggest that combining PARP and PI3K inhibitors enhances the effect of either agent alone in preclinical models of SCLC, warranting further investigation of such combinations in SCLC patients.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
Proteomic markers of DNA repair and PI3K pathway activation predict response to the PARP inhibitor BMN 673 in small cell lung cancer.Clin Cancer Res. 2013 Nov 15;19(22):6322-8. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-13-1975. Epub 2013 Sep 27. Clin Cancer Res. 2013. PMID: 24077350 Free PMC article.
-
The dual HDAC-PI3K inhibitor CUDC-907 displays single-agent activity and synergizes with PARP inhibitor olaparib in small cell lung cancer.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2020 Oct 17;39(1):219. doi: 10.1186/s13046-020-01728-2. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 33069237 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomic profiling identifies dysregulated pathways in small cell lung cancer and novel therapeutic targets including PARP1.Cancer Discov. 2012 Sep;2(9):798-811. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-12-0112. Epub 2012 Sep 6. Cancer Discov. 2012. PMID: 22961666 Free PMC article.
-
Progression and metastasis of small cell lung carcinoma: the role of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway and metabolic alterations.Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2021 Dec;40(4):1141-1157. doi: 10.1007/s10555-021-10012-4. Epub 2021 Dec 27. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2021. PMID: 34958428 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/AKT/mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) pathway: an emerging treatment strategy for squamous cell lung carcinoma.Cancer Treat Rev. 2014 Sep;40(8):980-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2014.06.006. Epub 2014 Jul 3. Cancer Treat Rev. 2014. PMID: 25037117 Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting DNA Damage Response Promotes Antitumor Immunity through STING-Mediated T-cell Activation in Small Cell Lung Cancer.Cancer Discov. 2019 May;9(5):646-661. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-18-1020. Epub 2019 Feb 18. Cancer Discov. 2019. PMID: 30777870 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of BAD-Ser99 phosphorylation synergizes with PARP inhibition to ablate PTEN-deficient endometrial carcinoma.Cell Death Dis. 2022 Jun 20;13(6):558. doi: 10.1038/s41419-022-04982-8. Cell Death Dis. 2022. PMID: 35725817 Free PMC article.
-
PTEN deficiency sensitizes endometrioid endometrial cancer to compound PARP-PI3K inhibition but not PARP inhibition as monotherapy.Oncogene. 2018 Jan 18;37(3):341-351. doi: 10.1038/onc.2017.326. Epub 2017 Sep 25. Oncogene. 2018. PMID: 28945226 Free PMC article.
-
The PI3K Pathway in Human Disease.Cell. 2017 Aug 10;170(4):605-635. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.07.029. Cell. 2017. PMID: 28802037 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PARP Inhibitors in Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Rational Combinations to Improve Responses.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Feb 10;13(4):727. doi: 10.3390/cancers13040727. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33578789 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Govindan R, Page N, Morgensztern D, Read W, Tierney R, Vlahiotis A, et al. Changing epidemiology of small-cell lung cancer in the United States over the last 30 years: analysis of the surveillance, epidemiologic, and end results database. Journal of clinical oncology: official journal of the American Society of Clinical Oncology. 2006;24(28):4539–44. Epub 2006/09/30. doi: 24/28/4539 [pii] 10.1200/JCO.2005.04.4859 . - DOI - PubMed
-
- U.S. Cancer Statistics Working Group. United States Cancer Statistics: 1999–2011 Incidence and Mortality Web-based Report. Atlanta: U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and National Cancer Institute; 2014. Available at: www.cdc.gov/uscs.
-
- Byers LA, Wang J, Nilsson MB, Fujimoto J, Saintigny P, Yordy J, et al. Proteomic Profiling Identifies Dysregulated Pathways in Small Cell Lung Cancer and Novel Therapeutic Targets Including PARP1. Cancer discovery. 2012;2(9):798–811. Epub 2012/09/11. doi: 2159-8290.CD-12-0112 [pii] 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-12-0112 . - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cardnell RJ, Feng Y, Diao L, Fan YH, Masrorpour F, Wang J, et al. Proteomic markers of DNA repair and PI3K pathway activation predict response to the PARP inhibitor BMN 673 in small cell lung cancer. Clinical cancer research: an official journal of the American Association for Cancer Research. 2013;19(22):6322–8. Epub 2013/10/01. 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-13-1975 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

