Roles of NF-κB in Cancer and Inflammatory Diseases and Their Therapeutic Approaches
- PMID: 27043634
- PMCID: PMC4931664
- DOI: 10.3390/cells5020015
Roles of NF-κB in Cancer and Inflammatory Diseases and Their Therapeutic Approaches
Abstract
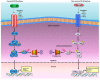
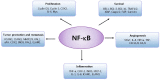
Nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) is a transcription factor that plays a crucial role in various biological processes, including immune response, inflammation, cell growth and survival, and development. NF-κB is critical for human health, and aberrant NF-κB activation contributes to development of various autoimmune, inflammatory and malignant disorders including rheumatoid arthritis, atherosclerosis, inflammatory bowel diseases, multiple sclerosis and malignant tumors. Thus, inhibiting NF-κB signaling has potential therapeutic applications in cancer and inflammatory diseases.
Keywords: NF-κB; cancer; canonical pathway; inflammatory disease; non-canonical pathway; therapeutic approaches.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Non-canonical NF-κB signaling in rheumatoid arthritis: Dr Jekyll and Mr Hyde?Arthritis Res Ther. 2015 Jan 28;17(1):15. doi: 10.1186/s13075-015-0527-3. Arthritis Res Ther. 2015. PMID: 25774937 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The non-canonical NF-κB pathway in immunity and inflammation.Nat Rev Immunol. 2017 Sep;17(9):545-558. doi: 10.1038/nri.2017.52. Epub 2017 Jun 5. Nat Rev Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28580957 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aqueous synthesized quantum dots interfere with the NF-κB pathway and confer anti-tumor, anti-viral and anti-inflammatory effects.Biomaterials. 2016 Nov;108:187-96. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2016.08.047. Epub 2016 Aug 31. Biomaterials. 2016. PMID: 27639114
-
The role of nuclear factor-kappaB in the development of autoimmune diseases: a link between genes and environment.Acta Biochim Pol. 2008;55(4):629-47. Epub 2008 Dec 16. Acta Biochim Pol. 2008. PMID: 19081854 Review.
-
IkappaB kinases: key regulators of the NF-kappaB pathway.Trends Biochem Sci. 2004 Feb;29(2):72-9. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2003.12.003. Trends Biochem Sci. 2004. PMID: 15102433 Review.
Cited by
-
Galactooligosaccharides and Limosilactobacillus reuteri synergistically alleviate gut inflammation and barrier dysfunction by enriching Bacteroides acidifaciens for pentadecanoic acid biosynthesis.Nat Commun. 2024 Oct 28;15(1):9291. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-53144-1. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39468026 Free PMC article.
-
Physiological and cellular mechanisms of ischemic preconditioning microRNAs-mediated in underlying of ischemia/reperfusion injury in different organs.Mol Cell Biochem. 2024 Jul 13. doi: 10.1007/s11010-024-05052-7. Online ahead of print. Mol Cell Biochem. 2024. PMID: 39001984 Review.
-
Pien Tze Huang Alleviates Relapsing-Remitting Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis Mice by Regulating Th1 and Th17 Cells.Front Pharmacol. 2018 Oct 31;9:1237. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.01237. eCollection 2018. Front Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 30429789 Free PMC article.
-
The Integrative Studies on the Functional A-to-I RNA Editing Events in Human Cancers.Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2023 Jun;21(3):619-631. doi: 10.1016/j.gpb.2022.12.010. Epub 2023 Jan 25. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2023. PMID: 36708807 Free PMC article.
-
Structure-based identification of a new IAP-targeting compound that induces cancer cell death inducing NF-κB pathway.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2021 Nov 26;19:6366-6374. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2021.11.034. eCollection 2021. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2021. PMID: 34938412 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

