IL‑6 and IL‑8 enhance factor H binding to the cell membranes
- PMID: 27035765
- PMCID: PMC4838138
- DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2016.5012
IL‑6 and IL‑8 enhance factor H binding to the cell membranes
Abstract
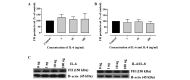
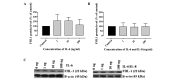
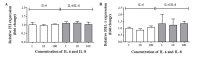
The aim of the present study was to assess the role of interleukin (IL)‑6 and IL‑8 on the expression of fluid‑phase complement inhibitor, factor H (FH), and FH‑like protein 1 (FHL‑1), in the A2780 ovarian carcinoma cell line. This cell line does not normally produce IL‑6, however, is IL‑6 responsive due to the presence of receptor for IL‑6. The presence of FH and FHL‑1 in the cell lysates was confirmed by western blotting. The levels of FH and FHL‑1 in the medium were determined by enzyme‑linked immunosorbent assay. To evaluate gene expression, reverse transcription‑quantitative polymerase chain reaction was performed. The cellular localization of FH and FHL‑1 in ovarian cancer cells was assessed by immunofluorescence. The present study revealed that FH, contrary to FHL‑1, was secreted by ovarian cancer cells, however, this process was independent of IL stimulation. No significant differences were observed in the concentration of FH in the control cells, when compared with the samples treated with IL‑6/IL‑8. The results of western blotting revealed that the protein expression levels of FH and FHL‑1 were not regulated by IL‑6 and IL‑8 in a dose‑dependent manner. Immunofluorescence analysis confirmed that the A2780 ovarian cancer cell line expressed both membrane bound and intracellular forms of FH and FHL‑1. The present data revealed that the A2780 cells expressed and secreted FH protein and are also able to bind FH and FHL‑1. This may influence the efficiency of complement mediated immunotherapy.
Figures
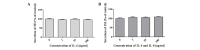
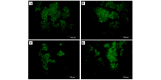
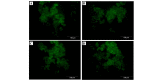
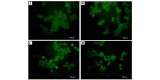
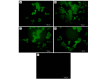
Similar articles
-
IL‑6 prevents CXCL8‑induced stimulation of EpCAM expression in ovarian cancer cells.Mol Med Rep. 2019 Mar;19(3):2317-2322. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2019.9890. Epub 2019 Jan 23. Mol Med Rep. 2019. PMID: 30747214
-
FHL1 inhibits the growth of tongue squamous cell carcinoma cells via G1/S cell cycle arrest.Mol Med Rep. 2015 Sep;12(3):3958-3964. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2015.3844. Epub 2015 May 25. Mol Med Rep. 2015. PMID: 26017856
-
Regulation of spontaneous and TNF/IFN-induced IL-6 expression in two human ovarian-carcinoma cell lines.Int J Cancer. 1999 Jul 19;82(2):244-9. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1097-0215(19990719)82:2<244::aid-ijc15>3.0.co;2-n. Int J Cancer. 1999. PMID: 10389759
-
Complement Factor H Family Proteins Modulate Monocyte and Neutrophil Granulocyte Functions.Front Immunol. 2021 Oct 4;12:660852. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.660852. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34671340 Free PMC article.
-
FHL family members suppress vascular endothelial growth factor expression through blockade of dimerization of HIF1α and HIF1β.IUBMB Life. 2012 Nov;64(11):921-30. doi: 10.1002/iub.1089. IUBMB Life. 2012. PMID: 23086815
Cited by
-
Low FHL1 expression indicates a good prognosis and drug sensitivity in ovarian cancer.Funct Integr Genomics. 2024 Feb 7;24(1):25. doi: 10.1007/s10142-024-01294-2. Funct Integr Genomics. 2024. PMID: 38324167
References
-
- Wcislo G, Szczylik C, editors. Ovarian cancer-pathobiology, diagnosis and overview of contemporary methods of treatment. Termedia; Poznan: 2010. Foreword; pp. 9–10.
-
- Urban A, Miszczyk L. Ovarian cancer-diagnostical and therapeutical dilema in oncological gynecology. Wspolczesna Onkol. 2003;7:294–300. In Polish.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

