Transcription factor‑microRNA synergistic regulatory network revealing the mechanism of polycystic ovary syndrome
- PMID: 27035648
- PMCID: PMC4838149
- DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2016.5019
Transcription factor‑microRNA synergistic regulatory network revealing the mechanism of polycystic ovary syndrome
Abstract
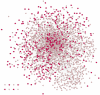
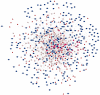
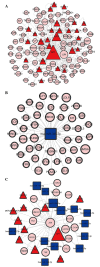
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is the most common type of endocrine disorder, affecting 5‑11% of women of reproductive age worldwide. Transcription factors (TFs) and microRNAs are considered to have crucial roles in the developmental process of several diseases and have synergistic regulatory actions. However, the effects of TFs and microRNAs, and the patterns of their cooperation in the synergistic regulatory network of PCOS, remain to be elucidated. The present study aimed to determine the possible mechanism of PCOS, based on a TF‑microRNA synergistic regulatory network. Initially, the differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in PCOS were identified using microarray data of the GSE34526 dataset. Subsequently, the TFs and microRNAs which regulated the DEGs of PCOS were identified, and a PCOS‑associated TF‑microRNA synergistic regulatory network was constructed. This network included 195 DEGs, 136 TFs and 283 microRNAs, and the DEGs were regulated by TFs and microRNAs. Based on topological and functional enrichment analyses, SP1, mir‑355‑5p and JUN were identified as potentially crucial regulators in the development of PCOS and in characterizing the regulatory mechanism. In conclusion, the TF‑microRNA synergistic regulatory network constructed in the present study provides novel insight on the molecular mechanism of PCOS in the form of synergistic regulated model.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Bioinformatics identification of microRNAs involved in polycystic ovary syndrome based on microarray data.Mol Med Rep. 2019 Jul;20(1):281-291. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2019.10253. Epub 2019 May 16. Mol Med Rep. 2019. PMID: 31115532 Free PMC article.
-
Several critical genes and microRNAs associated with the development of polycystic ovary syndrome.Ann Endocrinol (Paris). 2020 Feb;81(1):18-27. doi: 10.1016/j.ando.2019.10.002. Epub 2019 Nov 11. Ann Endocrinol (Paris). 2020. PMID: 32127169
-
Microarray analysis of obese women with polycystic ovary syndrome for key gene screening, key pathway identification and drug prediction.Gene. 2018 Jun 30;661:85-94. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2018.03.079. Epub 2018 Mar 28. Gene. 2018. PMID: 29601948
-
Epigenetic Marks in Polycystic Ovary Syndrome.Curr Med Chem. 2020;27(39):6727-6743. doi: 10.2174/0929867326666191003154548. Curr Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 31580245 Review.
-
Explore the potential molecular mechanism of polycystic ovarian syndrome by protein-protein interaction network analysis.Taiwan J Obstet Gynecol. 2021 Sep;60(5):807-815. doi: 10.1016/j.tjog.2021.07.005. Taiwan J Obstet Gynecol. 2021. PMID: 34507653 Review.
Cited by
-
Computational characterization and identification of human polycystic ovary syndrome genes.Sci Rep. 2018 Aug 28;8(1):12949. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-31110-4. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30154492 Free PMC article.
-
Systems biology and in silico-based analysis of PCOS revealed the risk of metabolic disorders.Heliyon. 2022 Dec 22;8(12):e12480. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e12480. eCollection 2022 Dec. Heliyon. 2022. PMID: 36619413 Free PMC article.
-
Pathway and network-based analysis of genome-wide association studies and RT-PCR validation in polycystic ovary syndrome.Int J Mol Med. 2017 Nov;40(5):1385-1396. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2017.3146. Epub 2017 Sep 20. Int J Mol Med. 2017. PMID: 28949383 Free PMC article.
-
Weighted Gene Co-Expression Network Analysis (WGCNA) Discovered Novel Long Non-Coding RNAs for Polycystic Ovary Syndrome.Biomedicines. 2023 Feb 10;11(2):518. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11020518. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 36831054 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Joham AE, Ranasinha S, Zoungas S, Moran L, Teede HJ. Gestational diabetes and type 2 diabetes in reproductive-aged women with polycystic ovary syndrome. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2014;99:447–452. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

