Microfluidic techniques for high throughput single cell analysis
- PMID: 27032065
- PMCID: PMC4975615
- DOI: 10.1016/j.copbio.2016.02.015
Microfluidic techniques for high throughput single cell analysis
Abstract
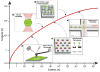
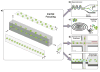
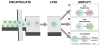
The microfabrication of microfluidic control systems and the development of increasingly sensitive molecular amplification tools have enabled the miniaturization of single cells analytical platforms. Only recently has the throughput of these platforms increased to a level at which populations can be screened at the single cell level. Techniques based upon both active and passive manipulation are now capable of discriminating between single cell phenotypes for sorting, diagnostic or prognostic applications in a variety of clinical scenarios. The introduction of multiphase microfluidics enables the segmentation of single cells into biochemically discrete picoliter environments. The combination of these techniques are enabling a class of single cell analytical platforms within great potential for data driven biomedicine, genomics and transcriptomics.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Development of Droplet Microfluidics Enabling High-Throughput Single-Cell Analysis.Molecules. 2016 Jul 5;21(7):881. doi: 10.3390/molecules21070881. Molecules. 2016. PMID: 27399651 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ultrahigh-Throughput Screening of Single-Cell Lysates for Directed Evolution and Functional Metagenomics.Methods Mol Biol. 2018;1685:297-309. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-7366-8_18. Methods Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 29086317
-
A design and optimization of a high throughput valve based microfluidic device for single cell compartmentalization and analysis.Sci Rep. 2021 Jun 21;11(1):12995. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-92472-w. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34155296 Free PMC article.
-
High-throughput, multiparameter analysis of single cells.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2014 May;406(14):3279-96. doi: 10.1007/s00216-013-7485-x. Epub 2013 Dec 1. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2014. PMID: 24292433 Review.
-
Micro-optics for microfluidic analytical applications.Chem Soc Rev. 2018 Feb 19;47(4):1391-1458. doi: 10.1039/c5cs00649j. Chem Soc Rev. 2018. PMID: 29308474 Review.
Cited by
-
Shape-based separation of micro-/nanoparticles in liquid phases.Biomicrofluidics. 2018 Oct 23;12(5):051503. doi: 10.1063/1.5052171. eCollection 2018 Sep. Biomicrofluidics. 2018. PMID: 30405868 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Population-based analysis of cell-penetrating peptide uptake using a microfluidic droplet trapping array.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2019 May;411(12):2729-2741. doi: 10.1007/s00216-019-01713-5. Epub 2019 Mar 11. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2019. PMID: 30854596 Free PMC article.
-
Bacteriuria and phenotypic antimicrobial susceptibility testing in 45 min by point-of-care Sysmex PA-100 System: first clinical evaluation.Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2024 Aug;43(8):1533-1543. doi: 10.1007/s10096-024-04862-3. Epub 2024 Jun 3. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 38825624 Free PMC article.
-
Cytocompatible cell encapsulation via hydrogel photopolymerization in microfluidic emulsion droplets.Biomicrofluidics. 2017 Jul 12;11(4):044102. doi: 10.1063/1.4993122. eCollection 2017 Jul. Biomicrofluidics. 2017. PMID: 28794813 Free PMC article.
-
Deterministic trapping, encapsulation and retrieval of single-cells.Lab Chip. 2017 Jun 27;17(13):2186-2192. doi: 10.1039/c7lc00283a. Lab Chip. 2017. PMID: 28585962 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Collins DJ, Neild A, deMello A, Liu A-Q, Ai Y. The Poisson distribution and beyond: methods for microfluidic droplet production and single cell encapsulation. Lab Chip. 2015;15:3439–3459. - PubMed
-
- Whitesides GM. The origins and the future of microfluidics. Nature. 2006;442:368–373. - PubMed
-
- Thorsen T, Maerkl SJ, Quake SR. Microfluidic large-scale integration. Science. 2002;298:580–584. - PubMed
-
- Oakey J, Allely J, Marr D. Laminar-flow-based separations at the microscale. Biotechnol Prog. 2002;18:1439–1442. - PubMed
-
- Huang S-B, Wu MH, Lin Y-H, Hsieh C-H, Yang C-L, Lin H-C, Tseng C-P, Lee G-B. High-purity and label-free isolation of circulating tumor cells (CTCs) in a microfluidic platform by using optically-induced-dielectrophoretic (ODEP) force. Lab Chip. 2013;13:1371–1383. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

