Anticancer properties of nimbolide and pharmacokinetic considerations to accelerate its development
- PMID: 27027349
- PMCID: PMC5190135
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.8316
Anticancer properties of nimbolide and pharmacokinetic considerations to accelerate its development
Abstract
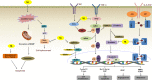
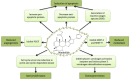
Nimbolide is one of the main components in the leaf extract of Azadirachta indica (A. indica). Accumulating evidence from various in vitro and in vivo studies indicates that nimbolide possesses potent anticancer activity against several types of cancer and also shows potential chemopreventive activity in animal models. The main mechanisms of action of nimbolide include anti-proliferation, induction of apoptosis, inhibition of metastasis and angiogenesis, and modulation of carcinogen-metabolizing enzymes. Although multiple pharmacodynamic (PD) studies have been carried out, nimbolide is still at the infant stage in the drug development pipeline due to the lack of systematic pharmacokinetic (PK) studies and long-term toxicological studies. Preclinical PK and toxicological studies are vital in determining the dosage range to support the safety of nimbolide for first-in-human clinical trials. In this review, we will provide a comprehensive summary for the current status of nimbolide as an anticancer and chemopreventive lead compound, and highlight the importance of systematic preclinical PK and toxicological studies in accelerating the process of application of nimbolide as a therapeutic agent against various malignancies.
Keywords: anticancer property; nimbolide; pharmacodynamics; pharmacokinetics; toxicology.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Insights into Nimbolide molecular crosstalk and its anticancer properties.Med Oncol. 2024 May 18;41(6):158. doi: 10.1007/s12032-024-02379-5. Med Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38761317 Review.
-
Nimbolide, a Neem Limonoid, Is a Promising Candidate for the Anticancer Drug Arsenal.J Med Chem. 2021 Apr 8;64(7):3560-3577. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.0c02239. Epub 2021 Mar 19. J Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 33739088 Review.
-
Nimbolide, a neem limonoid inhibits cytoprotective autophagy to activate apoptosis via modulation of the PI3K/Akt/GSK-3β signalling pathway in oral cancer.Cell Death Dis. 2018 Oct 23;9(11):1087. doi: 10.1038/s41419-018-1126-4. Cell Death Dis. 2018. PMID: 30352996 Free PMC article.
-
Antiproliferative effect on human cancer cell lines after treatment with nimbolide extracted from an edible part of the neem tree (Azadirachta indica).Phytother Res. 2007 Mar;21(3):245-50. doi: 10.1002/ptr.2058. Phytother Res. 2007. PMID: 17163581
-
A supercritical CO2 extract of neem leaf (A. indica) and its bioactive liminoid, nimbolide, suppresses colon cancer in preclinical models by modulating pro-inflammatory pathways.Mol Carcinog. 2018 Sep;57(9):1156-1165. doi: 10.1002/mc.22832. Epub 2018 May 8. Mol Carcinog. 2018. PMID: 29697164
Cited by
-
In vitro antimicrobial and cytotoxic activity of Neem and Kirata herbal formulation mediated Silver nanoparticles.Bioinformation. 2022 Nov 30;18(11):1069-1074. doi: 10.6026/973206300181069. eCollection 2022. Bioinformation. 2022. PMID: 37693082 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of actin cytoskeletal modifications in the inhibition of triple-negative breast cancer growth and metastasis by nimbolide.Mol Ther Oncolytics. 2021 Feb 24;20:596-606. doi: 10.1016/j.omto.2021.02.014. eCollection 2021 Mar 26. Mol Ther Oncolytics. 2021. PMID: 33768141 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro antibacterial activity of nimbolide against Helicobacter pylori.J Ethnopharmacol. 2022 Mar 1;285:114828. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2021.114828. Epub 2021 Nov 9. J Ethnopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 34763046 Free PMC article.
-
Nimbolide protects against endotoxin-induced acute respiratory distress syndrome by inhibiting TNF-α mediated NF-κB and HDAC-3 nuclear translocation.Cell Death Dis. 2019 Jan 28;10(2):81. doi: 10.1038/s41419-018-1247-9. Cell Death Dis. 2019. PMID: 30692512 Free PMC article.
-
Nimbolide ameliorates the streptozotocin-induced diabetic retinopathy in rats through the inhibition of TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway.Saudi J Biol Sci. 2021 Aug;28(8):4255-4262. doi: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2021.06.039. Epub 2021 Jun 19. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34354407 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Singh KK. I.K. International Pvt Ltd; 2008. Neem, a Treatise.
-
- Rochanakij S, Thebtaranonth Y, Yenjai C, Yuthavong Y. Nimbolide, a constituent of Azadirachta indica, inhibits Plasmodium falciparum in culture. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health. 1985;16(1):66–72. - PubMed
-
- Rojanapo W, Suwanno S, Somjaree R, Glinsukon T, Thebtaranont Y. Mutagenic and Antibacterial Activity Testing of Nimbolide and Nimbic Acid. Journal of the Science Society of Thailand. 1985;11(4):177–181.
-
- Suresh G, Gopalakrishnan G, Wesley SD, Pradeep Singh ND, Malathi R, Rajan SS. Insect antifeedant activity of tetranortriterpenoids from the Rutales. A perusal of structural relations. J Agric Food Chem. 2002;50(16):4484–4490. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

