Antiretroviral Drugs-Loaded Nanoparticles Fabricated by Dispersion Polymerization with Potential for HIV/AIDS Treatment
- PMID: 27013886
- PMCID: PMC4803317
- DOI: 10.4137/IDRT.S38108
Antiretroviral Drugs-Loaded Nanoparticles Fabricated by Dispersion Polymerization with Potential for HIV/AIDS Treatment
Abstract
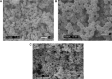
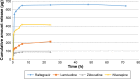
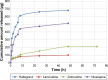
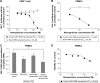
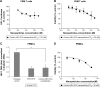
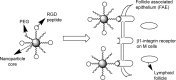
Highly active antiretroviral (ARV) therapy (HAART) for chronic suppression of HIV replication has revolutionized the treatment of HIV/AIDS. HAART is no panacea; treatments must be maintained for life. Although great progress has been made in ARV therapy, HIV continues to replicate in anatomical and intracellular sites where ARV drugs have restricted access. Nanotechnology has been considered a platform to circumvent some of the challenges in HIV/AIDS treatment. Dispersion polymerization was used to fabricate two types (PMM and ECA) of polymeric nanoparticles, and each was successfully loaded with four ARV drugs (zidovudine, lamivudine, nevirapine, and raltegravir), followed by physicochemical characterization: scanning electron microscope, particle size, zeta potential, drug loading, and in vitro availability. These nanoparticles efficiently inhibited HIV-1 infection in CEM T cells and peripheral blood mononuclear cells; they hold promise for the treatment of HIV/AIDS. The ARV-loaded nanoparticles with polyethylene glycol on the corona may facilitate tethering ligands for targeting specific receptors expressed on the cells of HIV reservoirs.
Keywords: ARV drugs; CEM T cells; GALT; PBMCs; dispersion polymerization; nanoparticles.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Nanoparticle-Based ARV Drug Combinations for Synergistic Inhibition of Cell-Free and Cell-Cell HIV Transmission.Mol Pharm. 2015 Dec 7;12(12):4363-74. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.5b00544. Epub 2015 Nov 18. Mol Pharm. 2015. PMID: 26529558
-
Stealth anti-CD4 conjugated immunoliposomes with dual antiretroviral drugs--modern Trojan horses to combat HIV.Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2015 Jan;89:300-11. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2014.11.021. Epub 2014 Dec 12. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2015. PMID: 25500283
-
Polymeric nanoparticles for enhancing antiretroviral drug therapy.Drug Deliv. 2008 Nov;15(8):493-501. doi: 10.1080/10717540802321776. Drug Deliv. 2008. PMID: 18720133 Review.
-
Antiretrovirals for reducing the risk of mother-to-child transmission of HIV infection.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007 Jan 24;(1):CD003510. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003510.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011 Jul 06;(7):CD003510. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003510.pub3. PMID: 17253490 Updated. Review.
-
Multi-state models for the analysis of time-to-treatment modification among HIV patients under highly active antiretroviral therapy in Southwest Ethiopia.BMC Infect Dis. 2017 Jun 27;17(1):453. doi: 10.1186/s12879-017-2533-3. BMC Infect Dis. 2017. PMID: 28655306 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Studies on polyethylene glycol-monoclonal antibody conjugates for fabrication of nanoparticles for biomedical applications.J Nanosci Nanomed. 2020 Jul;4(2):1-9. Epub 2020 Feb 3. J Nanosci Nanomed. 2020. PMID: 33564752 Free PMC article.
-
Drug Combinations in Breast Cancer Therapy.Pharm Nanotechnol. 2019;7(1):3-23. doi: 10.2174/2211738507666190122111224. Pharm Nanotechnol. 2019. PMID: 30666921 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanotechnology-based antiviral therapeutics.Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2021 Jun;11(3):748-787. doi: 10.1007/s13346-020-00818-0. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2021. PMID: 32748035 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Retrovirus Drugs-Loaded PEGylated PAMAM for Prolonging Drug Release and Enhancing Efficiency in HIV Treatment.Polymers (Basel). 2021 Dec 29;14(1):114. doi: 10.3390/polym14010114. Polymers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 35012136 Free PMC article.
-
Cellular uptake and cytotoxicity studies of pH-responsive polymeric nanoparticles fabricated by dispersion polymerization.J Nanosci Nanomed. 2018 Sep;2(1):3-18. Epub 2018 Apr 12. J Nanosci Nanomed. 2018. PMID: 34263267 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Richman DD, Margolis DM, Delaney M, Greene WC, Hazuda D, Pomerant RJ. The challenge of finding a cure for HIV infection. Science. 2009;323:1304–1307. - PubMed
-
- Dembri A, Montisd M-J, Gantier JC, Chacon H, Ponchell G. Targeting of 3′–Azido 3′-deoxythymidine (AZT)-loaded poly(isohexylcyanoacrylate) nano-spheres to the gastrointestinal mucosa and associated lymphoid tissues. Pharm Res. 2001;18(4):467–473. - PubMed
-
- Schrager LK, D’Souza MP. Cellular and anatomical reservoirs of HIV-1 in patients receiving potent antiretroviral combination therapy. JAMA. 1998;280(1):67–71. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

