Anticonvulsant and Toxicological Evaluation of Parafluorinated/Chlorinated Derivatives of 3-Hydroxy-3-ethyl-3-phenylpropionamide
- PMID: 27006945
- PMCID: PMC4783531
- DOI: 10.1155/2016/3978010
Anticonvulsant and Toxicological Evaluation of Parafluorinated/Chlorinated Derivatives of 3-Hydroxy-3-ethyl-3-phenylpropionamide
Abstract
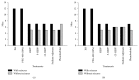
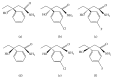
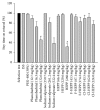
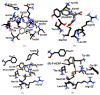
Although the anticonvulsant activity of 3-hydroxy-3-ethyl-3-phenylproionamide (HEPP) is well-known, its use is limited by the pharmacotoxicological profile. We herein tested its fluorinated and chlorinated derivatives (F-HEPP and Cl-HEPP) with two seizure models, maximal electroshock seizures (MES), and intraperitoneal pentylenetetrazole (PTZ) administration. Neurotoxicity was examined via the rotarod test. With in silico methods, binding was probed on possible protein targets-GABAA receptors and the sodium channel Nav1.2. The median effective doses (ED50) of HEPP, F-HEPP, and Cl-HEPP in the MES seizure model were 129.6, 87.1, and 62.0 mg/kg, respectively, and 66.4, 43.5, and in the PTZ seizure model 43.5 mg/kg. The HEPP-induced neurotoxic effect, which occurred at twice the ED50 against MES (p < 0.05), did not occur with F-HEPP or Cl-HEPP. Docking studies revealed that all tested ligands bound to GABAA receptors on a site near to the benzodiazepine binding site. However, on the sodium channel open pore Nav1.2, R-HEPP had interactions similar to those reported for phenytoin, while its enantiomer and the ligands F-HEPP and Cl-HEPP reached a site that could disrupt the passage of sodium. Our results show that, as anticonvulsant agents, parahalogen substituted compounds have an advantageous pharmacotoxicological profile compared to their precursor.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Anticonvulsive profile of two GABAB receptor antagonists on acute seizure mice models.Epilepsy Res. 2021 Aug;174:106644. doi: 10.1016/j.eplepsyres.2021.106644. Epub 2021 Apr 20. Epilepsy Res. 2021. PMID: 33932748
-
Design, synthesis, pharmacological evaluation, and docking study of new acridone-based 1,2,4-oxadiazoles as potential anticonvulsant agents.Eur J Med Chem. 2016 Apr 13;112:91-98. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2016.01.054. Epub 2016 Feb 1. Eur J Med Chem. 2016. PMID: 26890115
-
Design, Synthesis, and Biological Evaluation of 6-(2-Amino-substituted phenyl)-4-(substituted phenyl)-1,2,4-triazine-3,5(2H,4H)-dione Derivatives as Anticonvulsant Agents.Arch Pharm (Weinheim). 2016 Apr;349(4):277-92. doi: 10.1002/ardp.201500448. Epub 2016 Mar 21. Arch Pharm (Weinheim). 2016. PMID: 26996080
-
Novel fused 1,2,3-triazolo-benzodiazepine derivatives as potent anticonvulsant agents: design, synthesis, in vivo, and in silico evaluations.Mol Divers. 2020 Feb;24(1):179-189. doi: 10.1007/s11030-019-09940-9. Epub 2019 Mar 20. Mol Divers. 2020. PMID: 30895449
-
Synthesis, in vivo and in silico evaluation of novel 2,3-dihydroquinazolin-4(1H)-one derivatives as potential anticonvulsant agents.Drug Dev Res. 2019 May;80(3):343-352. doi: 10.1002/ddr.21506. Epub 2018 Dec 19. Drug Dev Res. 2019. PMID: 30565722
Cited by
-
Developmental Toxicity Study of DL-4-Hydroxy-4-Phenylhexanamide (DL-HEPB) in Rats.Life (Basel). 2023 Aug 10;13(8):1714. doi: 10.3390/life13081714. Life (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37629571 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fisher R. S., Boas W. V., Blume W., et al. Epileptic seizures and epilepsy: definitions proposed by the International League against Epilepsy (ILAE) and the International Bureau for Epilepsy (IBE) Epilepsia. 2005;46(4):470–472. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

