Changes in gene expression of histone modification enzymes in rat granulosa cells undergoing luteinization during ovulation
- PMID: 26979106
- PMCID: PMC4793631
- DOI: 10.1186/s13048-016-0225-z
Changes in gene expression of histone modification enzymes in rat granulosa cells undergoing luteinization during ovulation
Abstract
Background: The ovulatory LH surge rapidly alters the expression of steroidogenesis-related genes such as steroidogenic acute regulatory protein (StAR) in granulosa cells (GCs) undergoing luteinization. We recently reported that histone modifications contribute to these changes. Histone modifications are regulated by a variety of histone modification enzymes. This study investigated the changes in gene expression of histone modification enzymes in rat GCs undergoing luteinization after the induction of ovulation. The extracellular regulated kinase (ERK)-1/2 is a mediator in the intracellular signaling pathway stimulated by the ovulatory LH surge and regulates the expression of a number of genes in GCs. We further investigated whether ERK-1/2 is involved in the regulation of the histone modification at the StAR promoter region in GCs undergoing luteinization.
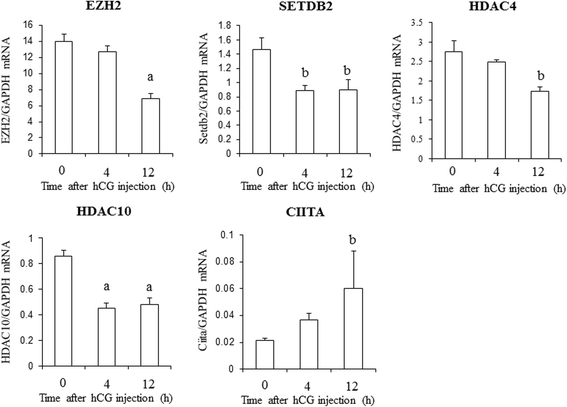
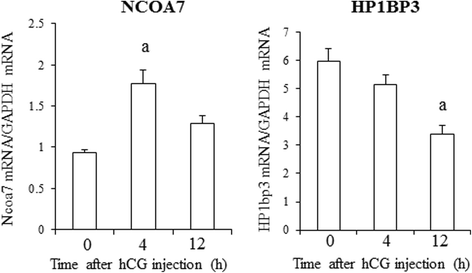
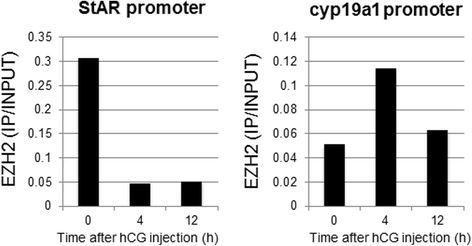
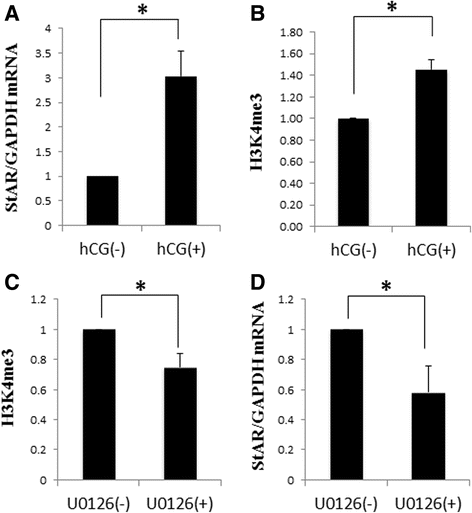
Results: GCs were obtained from rats treated with equine chorionic gonadotropin (CG) before (0 h) and after human (h) CG injection. The expressions of 84 genes regulating histone modifications or DNA methylation were measured using a PCR array. Five genes (HDAC4, HDAC10, EZH2, SETDB2, and CIITA) were identified as histone acetylation- or histone methylation-related genes, and were significantly altered after hCG injection. None of the genes were related to DNA methylation. mRNA levels of EZH2, SETDB2, HDAC4, and HDAC10 decreased and CIITA mRNA levels increased 4 or 12 h after hCG injection. GCs isolated after eCG injection were incubated with hCG for 4 h to induce luteinization. StAR mRNA levels were significantly increased by hCG accompanied by the increase in H3K4me3 of the StAR promoter region. StAR mRNA expression was inhibited by the ERK inhibitor with the significant decrease of H3K4me3. These results suggest that hCG increases StAR gene expression through the ERK-1/2-mediated signaling which is also associated with histone modification of the promoter region.
Conclusions: Gene expressions of histone modification enzymes change in GCs undergoing luteinization after ovulation induction. This change may play important roles in regulating the expression of various genes during the early stage of luteinization, which may be critical for the subsequent corpus luteum formation.
Keywords: Granulosa cells; Histone modification; Luteinization; Ovulation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
C/EBPβ regulates Vegf gene expression in granulosa cells undergoing luteinization during ovulation in female rats.Sci Rep. 2019 Jan 24;9(1):714. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-36566-y. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30679486 Free PMC article.
-
Changes in histone modification and DNA methylation of the StAR and Cyp19a1 promoter regions in granulosa cells undergoing luteinization during ovulation in rats.Endocrinology. 2013 Jan;154(1):458-70. doi: 10.1210/en.2012-1610. Epub 2012 Nov 26. Endocrinology. 2013. PMID: 23183184
-
Epigenetic Changes of the Cyp11a1 Promoter Region in Granulosa Cells Undergoing Luteinization During Ovulation in Female Rats.Endocrinology. 2016 Sep;157(9):3344-54. doi: 10.1210/en.2016-1264. Epub 2016 Jul 18. Endocrinology. 2016. PMID: 27428926
-
Integrated Analysis of Transcriptome and Histone Modifications in Granulosa Cells During Ovulation in Female Mice.Endocrinology. 2021 Sep 1;162(9):bqab128. doi: 10.1210/endocr/bqab128. Endocrinology. 2021. PMID: 34171084
-
Lactylation drives hCG-triggered luteinization in hypoxic granulosa cells.Int J Biol Macromol. 2024 Nov;280(Pt 4):135580. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.135580. Epub 2024 Sep 23. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024. PMID: 39322166
Cited by
-
C/EBPβ regulates Vegf gene expression in granulosa cells undergoing luteinization during ovulation in female rats.Sci Rep. 2019 Jan 24;9(1):714. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-36566-y. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30679486 Free PMC article.
-
The Expression of ERK1/2 in Female Yak (Bos grunniens) Reproductive Organs.Animals (Basel). 2020 Feb 20;10(2):334. doi: 10.3390/ani10020334. Animals (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32093255 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of the miRNA regulators of the human ovulatory cascade.Sci Rep. 2018 Oct 23;8(1):15605. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-33807-y. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30353018 Free PMC article.
-
Androgens Regulate Ovarian Gene Expression Through Modulation of Ezh2 Expression and Activity.Endocrinology. 2017 Sep 1;158(9):2944-2954. doi: 10.1210/en.2017-00145. Endocrinology. 2017. PMID: 28666321 Free PMC article.
-
The EZH2-H3K27me3 axis modulates aberrant transcription and apoptosis in cyclophosphamide-induced ovarian granulosa cell injury.Cell Death Discov. 2023 Nov 14;9(1):413. doi: 10.1038/s41420-023-01705-6. Cell Death Discov. 2023. PMID: 37963880 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wissing ML, Kristensen SG, Andersen CY, Mikkelsen AL, Host T, Borup R, Grondahl ML. Identification of new ovulation-related genes in humans by comaring the transcriptome of granulosa cells before and after ovulation triggering in the same controlled ovarian stimulation cycle. Hum Reprod. 2014;29:997–1010. - PubMed
-
- Ronen-Fuhrmann T, Timberg R, King SR, Hales KH, Hales DB, Stocco DM, Orly J. Spatio-temporal expression patterns of steroidogenic acute regulatory protein (StAR) during follicular development in the rat ovary. Endocrinology. 1998;139:303–15. - PubMed
-
- Hickey GJ, Chen SA, Besman MJ, Shively JE, Hall PF, Gaddy-Kurten D, Richards JS. Hormonal regulation, tissue distribution, and content of aromatase cytochrome P450 messenger ribonucleic acid and enzyme in rat ovarian follicles and corpora lutea: relationship to estradiol biosynthesis. Endocrinology. 1988;122:1426–36. - PubMed
-
- Tanaka N, Espey LL, Kawano T, Okamura H. Comparison of inhibitory actions of indomethacin and epostane on ovulation in rats. Am J Physiol. 1991;260:E170–174. - PubMed
-
- Lydon JP, DeMayo FJ, Funk CR, Mani SK, Hughes AR, Montgomery Jr CA, Shyamala G, Conneely OM, O'Malley BW. Mice lacking progesterone receptor exhibit pleiotropic reproductive abnormalities. Genes Dev. 1995;9:2266–78. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

