Association of Peripheral Membrane Proteins with Membranes: Free Energy of Binding of GRP1 PH Domain with Phosphatidylinositol Phosphate-Containing Model Bilayers
- PMID: 26977543
- PMCID: PMC5593124
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpclett.6b00153
Association of Peripheral Membrane Proteins with Membranes: Free Energy of Binding of GRP1 PH Domain with Phosphatidylinositol Phosphate-Containing Model Bilayers
Abstract
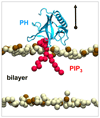
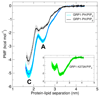
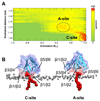
Understanding the energetics of peripheral protein-membrane interactions is important to many areas of biophysical chemistry and cell biology. Estimating free-energy landscapes by molecular dynamics (MD) simulation is challenging for such systems, especially when membrane recognition involves complex lipids, e.g., phosphatidylinositol phosphates (PIPs). We combined coarse-grained MD simulations with umbrella sampling to quantify the binding of the well-explored GRP1 pleckstrin homology (PH) domain to model membranes containing PIP molecules. The experimentally observed preference of GRP1-PH for PIP3 over PIP2 was reproduced. Mutation of a key residue (K273A) within the canonical PIP-binding site significantly reduced the free energy of PIP binding. The presence of a noncanonical PIP-interaction site, observed experimentally in other PH domains but not previously in GRP1-PH, was also revealed. These studies demonstrate how combining coarse-grained simulations and umbrella sampling can unmask the molecular basis of the energetics of interactions between peripheral membrane proteins and complex cellular membranes.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Molecular mechanism of membrane binding of the GRP1 PH domain.J Mol Biol. 2013 Sep 9;425(17):3073-90. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2013.05.026. Epub 2013 Jun 6. J Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 23747485 Free PMC article.
-
Interactions of Pleckstrin Homology Domains with Membranes: Adding Back the Bilayer via High-Throughput Molecular Dynamics.Structure. 2016 Aug 2;24(8):1421-1431. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2016.06.002. Epub 2016 Jul 14. Structure. 2016. PMID: 27427480 Free PMC article.
-
Modes of Interaction of Pleckstrin Homology Domains with Membranes: Toward a Computational Biochemistry of Membrane Recognition.J Mol Biol. 2018 Feb 2;430(3):372-388. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2017.12.011. Epub 2017 Dec 20. J Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 29273202
-
The energetics of protein-lipid interactions as viewed by molecular simulations.Biochem Soc Trans. 2020 Feb 28;48(1):25-37. doi: 10.1042/BST20190149. Biochem Soc Trans. 2020. PMID: 31872229 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Computational and theoretical approaches for studies of a lipid recognition protein on biological membranes.Biophys Physicobiol. 2017 Oct 26;14:153-160. doi: 10.2142/biophysico.14.0_153. eCollection 2017. Biophys Physicobiol. 2017. PMID: 29159013 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Dissecting peripheral protein-membrane interfaces.PLoS Comput Biol. 2022 Dec 14;18(12):e1010346. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1010346. eCollection 2022 Dec. PLoS Comput Biol. 2022. PMID: 36516231 Free PMC article.
-
Capturing Choline-Aromatics Cation-π Interactions in the MARTINI Force Field.J Chem Theory Comput. 2020 Apr 14;16(4):2550-2560. doi: 10.1021/acs.jctc.9b01194. Epub 2020 Mar 9. J Chem Theory Comput. 2020. PMID: 32096995 Free PMC article.
-
Flexible pivoting of dynamin pleckstrin homology domain catalyzes fission: insights into molecular degrees of freedom.Mol Biol Cell. 2021 Jul 1;32(14):1306-1319. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E20-12-0794. Epub 2021 May 12. Mol Biol Cell. 2021. PMID: 33979205 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanistic Understanding from Molecular Dynamics in Pharmaceutical Research 2: Lipid Membrane in Drug Design.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021 Oct 19;14(10):1062. doi: 10.3390/ph14101062. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34681286 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interactions of the EphA2 Kinase Domain with PIPs in Membranes: Implications for Receptor Function.Structure. 2018 Jul 3;26(7):1025-1034.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2018.05.003. Epub 2018 Jun 7. Structure. 2018. PMID: 29887500 Free PMC article.
References
-
- DiNitto JP, Lambright DG. Membrane and Juxtamembrane Targeting by PH and PTB Domains. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006;1761(8):850–867. - PubMed
-
- Di Paolo G, De Camilli P. Phosphoinositides in Cell Regulation and Membrane Dynamics. Nature. 2006;443(7112):651–657. - PubMed
-
- Clodi M, Vollenweider P, Klarlund J, Nakashima N, Martin S, Czech MP, Olefsky JM. Effects of General Receptor for Phosphoinositides 1 on Insulin and Insulin-like Growth Factor I-Induced Cytoskeletal Rearrangement, Glucose Transporter-4 Translocation, and Deoxyribonucleic Acid Synthesis. Endocrinology. 1998;139(12):4984–4990. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

