Contribution of the anaphylatoxin receptors, C3aR and C5aR, to the pathogenesis of pulmonary fibrosis
- PMID: 26956419
- PMCID: PMC4871799
- DOI: 10.1096/fj.201500044
Contribution of the anaphylatoxin receptors, C3aR and C5aR, to the pathogenesis of pulmonary fibrosis
Abstract
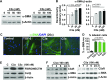
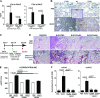
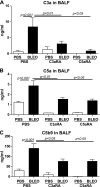
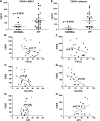
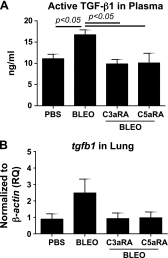
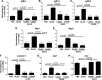
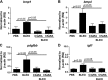
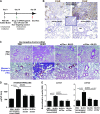
Complement activation, an integral arm of innate immunity, may be the critical link to the pathogenesis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF). Whereas we have previously reported elevated anaphylatoxins-complement component 3a (C3a) and complement component 5a (C5a)-in IPF, which interact with TGF-β and augment epithelial injury in vitro, their role in IPF pathogenesis remains unclear. The objective of the current study is to determine the mechanistic role of the binding of C3a/C5a to their respective receptors (C3aR and C5aR) in the progression of lung fibrosis. In normal primary human fetal lung fibroblasts, C3a and C5a induces mesenchymal activation, matrix synthesis, and the expression of their respective receptors. We investigated the role of C3aR and C5aR in lung fibrosis by using bleomycin-injured mice with fibrotic lungs, elevated local C3a and C5a, and overexpression of their receptors via pharmacologic and RNA interference interventions. Histopathologic examination revealed an arrest in disease progression and attenuated lung collagen deposition (Masson's trichrome, hydroxyproline, collagen type I α 1 chain, and collagen type I α 2 chain). Pharmacologic or RNA interference-specific interventions suppressed complement activation (C3a and C5a) and soluble terminal complement complex formation (C5b-9) locally and active TGF-β1 systemically. C3aR/C5aR antagonists suppressed local mRNA expressions of tgfb2, tgfbr1/2, ltbp1/2, serpine1, tsp1, bmp1/4, pdgfbb, igf1, but restored the proteoglycan, dcn Clinically, compared with pathologically normal human subjects, patients with IPF presented local induction of C5aR, local and systemic induction of soluble C5b-9, and amplified expression of C3aR/C5aR in lesions. The blockade of C3aR and C5aR arrested the progression of fibrosis by attenuating local complement activation and TGF-β/bone morphologic protein signaling as well as restoring decorin, which suggests a promising therapeutic strategy for patients with IPF.-Gu, H., Fisher, A. J., Mickler, E. A., Duerson, F., III, Cummings, O. W., Peters-Golden, M., Twigg, H. L., III, Woodruff, T. M., Wilkes, D. S., Vittal, R. Contribution of the anaphylatoxin receptors, C3aR and C5aR, to the pathogenesis of pulmonary fibrosis.
Keywords: BMP; C5b-9; IPF; TGF-β1; decorin.
© FASEB.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Crosstalk between TGF-β1 and complement activation augments epithelial injury in pulmonary fibrosis.FASEB J. 2014 Oct;28(10):4223-34. doi: 10.1096/fj.13-247650. Epub 2014 Jun 23. FASEB J. 2014. PMID: 24958208 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting C3a/C5a receptors inhibits human mesangial cell proliferation and alleviates immunoglobulin A nephropathy in mice.Clin Exp Immunol. 2017 Jul;189(1):60-70. doi: 10.1111/cei.12961. Epub 2017 Apr 10. Clin Exp Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28295247 Free PMC article.
-
IL-17A deficiency mitigates bleomycin-induced complement activation during lung fibrosis.FASEB J. 2017 Dec;31(12):5543-5556. doi: 10.1096/fj.201700289R. Epub 2017 Aug 17. FASEB J. 2017. PMID: 28821630 Free PMC article.
-
The Complement C3a and C5a Signaling in Renal Diseases: A Bridge between Acute and Chronic Inflammation.Nephron. 2024;148(10):712-723. doi: 10.1159/000538241. Epub 2024 Mar 8. Nephron. 2024. PMID: 38452744 Review.
-
Sphingolipids in pulmonary fibrosis.Adv Biol Regul. 2015 Jan;57:55-63. doi: 10.1016/j.jbior.2014.09.008. Epub 2014 Oct 13. Adv Biol Regul. 2015. PMID: 25446881 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Hypoxia-induced complement dysregulation is associated with microvascular impairments in mouse tracheal transplants.J Transl Med. 2020 Mar 31;18(1):147. doi: 10.1186/s12967-020-02305-z. J Transl Med. 2020. PMID: 32234039 Free PMC article.
-
Asthma and Post-Asthmatic Fibrosis: A Search for New Promising Molecular Markers of Transition from Acute Inflammation to Pulmonary Fibrosis.Biomedicines. 2022 Apr 28;10(5):1017. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10051017. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 35625754 Free PMC article.
-
C3a triggers formation of sub-retinal pigment epithelium deposits via the ubiquitin proteasome pathway.Sci Rep. 2018 Jun 26;8(1):9679. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-28143-0. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29946065 Free PMC article.
-
Wie sich COVID-19 in der 3D-Zellkultur simulieren lässt.Biospektrum (Heidelb). 2022;28(1):43-46. doi: 10.1007/s12268-022-1712-y. Epub 2022 Feb 13. Biospektrum (Heidelb). 2022. PMID: 35194332 Free PMC article. Review. German.
-
Toxicogenomic assessment of in vitro macrophages exposed to profibrotic challenge reveals a sustained transcriptomic immune signature.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2024 Oct 8;25:194-204. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2024.10.010. eCollection 2024 Dec. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2024. PMID: 39430886 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hutchinson J. P., McKeever T. M., Fogarty A. W., Navaratnam V., Hubbard R. B. (2014) Increasing global mortality from idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis in the twenty-first century. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 11, 1176–1185 - PubMed
-
- Ballanti E., Perricone C., Greco E., Ballanti M., Di Muzio G., Chimenti M. S., Perricone R. (2013) Complement and autoimmunity. Immunol. Res. 56, 477–491 - PubMed
-
- Syed S. N., Konrad S., Wiege K., Nieswandt B., Nimmerjahn F., Schmidt R. E., Gessner J. E. (2009) Both FcgammaRIV and FcgammaRIII are essential receptors mediating type II and type III autoimmune responses via FcRgamma-LAT-dependent generation of C5a. Eur. J. Immunol. 39, 3343–3356 - PubMed
-
- Atkinson C., Qiao F., Song H., Gilkeson G. S., Tomlinson S. (2008) Low-dose targeted complement inhibition protects against renal disease and other manifestations of autoimmune disease in MRL/lpr mice. J. Immunol. 180, 1231–1238 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

