Glutamate dependent NMDA receptor 2D is a novel angiogenic tumour endothelial marker in colorectal cancer
- PMID: 26943033
- PMCID: PMC4991466
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.7812
Glutamate dependent NMDA receptor 2D is a novel angiogenic tumour endothelial marker in colorectal cancer
Abstract
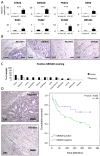
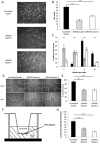
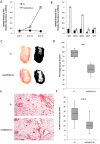
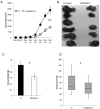
Current vascular-targeted therapies in colorectal cancer (CRC) have shown limited benefit. The lack of novel, specific treatment in CRC has been hampered by a dearth of specific endothelial markers. Microarray comparison of endothelial gene expression in patient-matched CRC and normal colon identified a panel of putative colorectal tumour endothelial markers. Of these the glutamate dependent NMDA receptor GRIN2D emerged as the most interesting target. GRIN2D expression was shown to be specific to colorectal cancer vessels by RTqPCR and IHC analysis. Its expression was additionally shown be predictive of improved survival in CRC. Targeted knockdown studies in vitro demonstrated a role for GRIN2D in endothelial function and angiogenesis. This effect was also shown in vivo as vaccination against the extracellular region of GRIN2D resulted in reduced vascularisation in the subcutaneous sponge angiogenesis assay. The utility of immunologically targeting GRIN2D in CRC was demonstrated by the vaccination approach inhibiting murine CRC tumour growth and vascularisation. GRIN2D represents a promising target for the future treatment of CRC.
Keywords: GRIN2D; active immunotherapy; colorectal cancer; tumour endothelial marker; vaccination.
Conflict of interest statement
The Authors certify that they have NO affiliations with or involvement in any organization or entity with any financial interest (such as honoraria; educational grants; participation in speakers' bureaus; membership, employment, consultancies, stock ownership, or other equity interest; and expert testimony or patent-licensing arrangements), or non-financial interest (such as personal or professional relationships, affiliations, knowledge or beliefs) in the subject matter or materials discussed in this manuscript.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Metastatic colorectal cancer cells maintain the TGFβ program and use TGFBI to fuel angiogenesis.Theranostics. 2021 Jan 1;11(4):1626-1640. doi: 10.7150/thno.51507. eCollection 2021. Theranostics. 2021. PMID: 33408771 Free PMC article.
-
Biomarkers Discovery for Colorectal Cancer: A Review on Tumor Endothelial Markers as Perspective Candidates.Dis Markers. 2016;2016:4912405. doi: 10.1155/2016/4912405. Epub 2016 Nov 14. Dis Markers. 2016. PMID: 27965519 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ursolic acid inhibits colorectal cancer angiogenesis through suppression of multiple signaling pathways.Int J Oncol. 2013 Nov;43(5):1666-74. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2013.2101. Epub 2013 Sep 16. Int J Oncol. 2013. PMID: 24042330
-
High levels of SIRT1 expression enhance tumorigenesis and associate with a poor prognosis of colorectal carcinoma patients.Sci Rep. 2014 Dec 15;4:7481. doi: 10.1038/srep07481. Sci Rep. 2014. PMID: 25500546 Free PMC article.
-
The role of tissue factor in colorectal cancer.Eur J Surg Oncol. 2003 Jun;29(5):417-22. doi: 10.1016/s0748-7983(03)00053-2. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2003. PMID: 12798743 Review.
Cited by
-
Emerging Roles of the Nervous System in Gastrointestinal Cancer Development.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Jul 30;14(15):3722. doi: 10.3390/cancers14153722. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35954387 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pan-cancer ion transport signature reveals functional regulators of glioblastoma aggression.EMBO J. 2024 Jan;43(2):196-224. doi: 10.1038/s44318-023-00016-x. Epub 2024 Jan 2. EMBO J. 2024. PMID: 38177502 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of GRIN2D as a novel therapeutic target in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.Biomark Res. 2023 Aug 8;11(1):74. doi: 10.1186/s40364-023-00514-4. Biomark Res. 2023. PMID: 37553583 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic value of long noncoding RNA LINC00924 in lung adenocarcinoma and its regulatory effect on tumor progression.Histol Histopathol. 2024 May;39(5):595-602. doi: 10.14670/HH-18-642. Epub 2023 Jun 26. Histol Histopathol. 2024. PMID: 37358073
-
Alterations in the Ca2+ toolkit in oesophageal adenocarcinoma.Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2021;2(6):543-575. doi: 10.37349/etat.2021.00063. Epub 2021 Dec 31. Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2021. PMID: 36046118 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Stewart BW, Wild CP. World Cancer Report. World Health Organisation. 2014
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Murray T, Xu J, Smigal C, Thun MJ. Cancer statistics, 2006. CA Cancer J Clin. 2006;56:106–30. - PubMed
-
- Quirke P, Durdey P, Dixon MF, Williams NS. Local recurrence of rectal adenocarcinoma due to inadequate surgical resection. Histopathological study of lateral tumour spread and surgical excision. Lancet. 1986;2:996–9. - PubMed
-
- Tebbutt NC, Cattell E, Midgley R, Cunningham D, Kerr D. Systemic treatment of colorectal cancer. Eur J Cancer. 2002;38:1000–15. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

