Directed evolution of G protein-coupled receptors in yeast for higher functional production in eukaryotic expression hosts
- PMID: 26911446
- PMCID: PMC4766470
- DOI: 10.1038/srep21508
Directed evolution of G protein-coupled receptors in yeast for higher functional production in eukaryotic expression hosts
Abstract
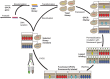
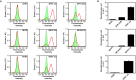
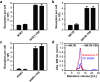
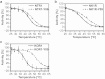
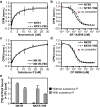
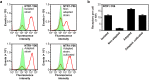
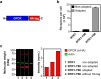
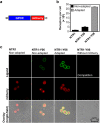
Despite recent successes, many G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) remained refractory to detailed molecular studies due to insufficient production yields, even in the most sophisticated eukaryotic expression systems. Here we introduce a robust method employing directed evolution of GPCRs in yeast that allows fast and efficient generation of receptor variants which show strongly increased functional production levels in eukaryotic expression hosts. Shown by evolving three different receptors in this study, the method is widely applicable, even for GPCRs which are very difficult to express. The evolved variants showed up to a 26-fold increase of functional production in insect cells compared to the wild-type receptors. Next to the increased production, the obtained variants exhibited improved biophysical properties, while functional properties remained largely unaffected. Thus, the presented method broadens the portfolio of GPCRs accessible for detailed investigations. Interestingly, the functional production of GPCRs in yeast can be further increased by induced host adaptation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare competing financial interests. A patent application that covers the SaBRE technology has been filed by the University of Zurich.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Co-expression of molecular chaperones does not improve the heterologous expression of mammalian G-protein coupled receptor expression in yeast.Biotechnol Bioeng. 2003 Nov 5;84(3):292-304. doi: 10.1002/bit.10771. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2003. PMID: 12968283
-
Human G protein-coupled receptor studies in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Biochem Pharmacol. 2016 Aug 15;114:103-15. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2016.02.010. Epub 2016 Feb 23. Biochem Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 26920251 Review.
-
Heterologous expression of G-protein-coupled receptors in yeast.Methods Enzymol. 2015;556:141-64. doi: 10.1016/bs.mie.2014.11.046. Epub 2015 Mar 20. Methods Enzymol. 2015. PMID: 25857781
-
Sf9 cells: a versatile model system to investigate the pharmacological properties of G protein-coupled receptors.Pharmacol Ther. 2010 Dec;128(3):387-418. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2010.07.005. Epub 2010 Aug 10. Pharmacol Ther. 2010. PMID: 20705094 Review.
-
A generic selection system for improved expression and thermostability of G protein-coupled receptors by directed evolution.Sci Rep. 2016 Feb 18;6:21294. doi: 10.1038/srep21294. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 26887595 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Directed evolution for high functional production and stability of a challenging G protein-coupled receptor.Sci Rep. 2021 Apr 21;11(1):8630. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-87793-9. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33883583 Free PMC article.
-
Elucidating the active δ-opioid receptor crystal structure with peptide and small-molecule agonists.Sci Adv. 2019 Nov 27;5(11):eaax9115. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aax9115. eCollection 2019 Nov. Sci Adv. 2019. PMID: 31807708 Free PMC article.
-
Towards high throughput GPCR crystallography: In Meso soaking of Adenosine A2A Receptor crystals.Sci Rep. 2018 Jan 8;8(1):41. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-18570-w. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29311713 Free PMC article.
-
Functional expression of opioid receptors and other human GPCRs in yeast engineered to produce human sterols.Nat Commun. 2022 May 24;13(1):2882. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-30570-7. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 35610225 Free PMC article.
-
Reprogramming G protein coupled receptor structure and function.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2018 Aug;51:187-194. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2018.07.008. Epub 2018 Jul 25. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2018. PMID: 30055347 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Fredriksson R., Lagerström M. C., Lundin L.-G. & Schiöth H. B. The G-protein-coupled receptors in the human genome form five main families. Phylogenetic analysis, paralogon groups, and fingerprints. Mol Pharmacol 63, 1256–1272 (2003). - PubMed
-
- Marinissen M. J. & Gutkind J. S. G-protein-coupled receptors and signaling networks: emerging paradigms. Trends Pharmacol Sci 22, 368–376 (2001). - PubMed
-
- Heng B. C., Aubel D. & Fussenegger M. An overview of the diverse roles of G-protein coupled receptors (GPCRs) in the pathophysiology of various human diseases. Biotechnol Adv 31, 1676–1694 (2013). - PubMed
-
- Overington J. P., Al-Lazikani B. & Hopkins A. L. How many drug targets are there? Nat Rev Drug Discov 5, 993–996 (2006). - PubMed
-
- Lagerström M. C. & Schiöth H. B. Structural diversity of G protein-coupled receptors and significance for drug discovery. Nat Rev Drug Discov 7, 339–357 (2008). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

