Control of Mosquito-Borne Infectious Diseases: Sex and Gene Drive
- PMID: 26897660
- PMCID: PMC4767671
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pt.2015.12.003
Control of Mosquito-Borne Infectious Diseases: Sex and Gene Drive
Abstract
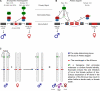
Sterile male releases have successfully reduced local populations of the dengue vector, Aedes aegypti, but challenges remain in scale and in separating sexes before release. The recent discovery of the first mosquito male determining factor (M factor) will facilitate our understanding of the genetic programs that initiate sexual development in mosquitoes. Manipulation of the M factor and possible intermediary factors may result in female-to-male conversion or female killing, enabling efficient sex separation and effective reduction of target mosquito populations. Given recent breakthroughs in the development of CRISPR-Cas9 reagents as a source of gene drive, more advanced technologies at driving maleness, the ultimate disease refractory phenotype, become possible and may represent efficient and self-limiting methods to control mosquito populations.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
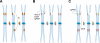
Similar articles
-
The future of mosquito-borne diseases in the world.J Am Mosq Control Assoc. 1985 Dec;1(4):419-22. J Am Mosq Control Assoc. 1985. PMID: 2906682
-
Cage trials using an endogenous meiotic drive gene in the mosquito Aedes aegypti to promote population replacement.Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2006 Jan;74(1):62-8. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2006. PMID: 16407347
-
Sexual chemoecology of mosquitoes (Diptera, Culicidae): Current knowledge and implications for vector control programs.Parasitol Int. 2017 Apr;66(2):190-195. doi: 10.1016/j.parint.2016.09.010. Epub 2016 Sep 28. Parasitol Int. 2017. PMID: 27692501 Review.
-
[Research progress on malaria vector control].Zhongguo Xue Xi Chong Bing Fang Zhi Za Zhi. 2013 Jun;25(3):312-5, 319. Zhongguo Xue Xi Chong Bing Fang Zhi Za Zhi. 2013. PMID: 24024458 Review. Chinese.
-
[Progress in application of genetic control of mosquitoes].Zhongguo Xue Xi Chong Bing Fang Zhi Za Zhi. 2013 Jun;25(3):316-9. Zhongguo Xue Xi Chong Bing Fang Zhi Za Zhi. 2013. PMID: 24024459 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Integral gene drives for population replacement.Biol Open. 2019 Jan 3;8(1):bio037762. doi: 10.1242/bio.037762. Biol Open. 2019. PMID: 30498016 Free PMC article.
-
Modulating signaling networks by CRISPR/Cas9-mediated transposable element insertion.Curr Genet. 2018 Apr;64(2):405-412. doi: 10.1007/s00294-017-0765-9. Epub 2017 Oct 14. Curr Genet. 2018. PMID: 29032444 Review.
-
Knowledge on exotic mosquitoes in Germany, and public acceptance and effectiveness of Bti and two self-prepared insecticides against Aedes japonicus japonicus.Sci Rep. 2020 Nov 3;10(1):18901. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-75780-5. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 33144626 Free PMC article.
-
GUY1 confers complete female lethality and is a strong candidate for a male-determining factor in Anopheles stephensi.Elife. 2016 Sep 20;5:e19281. doi: 10.7554/eLife.19281. Elife. 2016. PMID: 27644420 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of the Genetic Variation of the Fruitless Gene within the Anopheles gambiae (Diptera: Culicidae) Complex Populations in Africa.Insects. 2022 Nov 13;13(11):1048. doi: 10.3390/insects13111048. Insects. 2022. PMID: 36421951 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

