Development of a Multiplex PCR Method to Detect Fungal Pathogens for Quarantine on Exported Cacti
- PMID: 26889115
- PMCID: PMC4755675
- DOI: 10.5423/PPJ.NT.09.2015.0184
Development of a Multiplex PCR Method to Detect Fungal Pathogens for Quarantine on Exported Cacti
Abstract
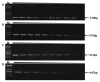
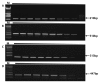
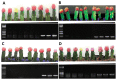
Major diseases in grafted cacti have been reported and Fusarium oxysporum, Bipolaris cactivora, Phytophthora spp. and Collectotrichum spp. are known as causal pathogens. These pathogens can lead to plant death after infection. Therefore, some European countries have quarantined imported cacti that are infected with specific fungal pathogens. Consequently, we developed PCR detection methods to identify four quarantined fungal pathogens and reduce export rejection rates of Korean grafted cacti. The pathogen specific primer sets F.oF-F.oR, B.CF-B.CR, P.nF-P.nR, and P.cF-P.CR were tested for F. oxysporum, B. cactivora, P. nicotinae, and P. cactorum, respectively. The F.oF-F.oR primer set was designed from the Fusarium ITS region; the B.CF-B.CR and P.nF-P.nR primers respectively from Bipolaris and Phytophthora ITS1; and the P.cF-P.CR primer set from the Ypt1protein gene region. The quarantine fungal pathogen primer pairs were amplified to the specific number of base pairs in each of the following fungal pathogens: 210-bp (F. oxysporum), 510-bp (B. cactivora), 313-bp (P. nicotinae), and 447-bp (P. cactorum). The detection limit for the mono- and multiplex PCR primer sets was 0.1 ng of template DNA under in vitro conditions. Therefore, each primer set successfully diagnosed contamination of quarantine pathogens in export grafted cacti. Consequently, our methodology is a viable tool to screen contamination of the fungal pathogen in exported grafted cacti.
Keywords: PCR detection; grafted cactus; quarantine pathogen.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Establishment and Application of a Multiplex PCR Assay for Detection of Sclerotium rolfsii, Lasiodiplodia theobromae, and Fusarium oxysporum in Peanut.Mol Biotechnol. 2023 Aug;65(8):1369-1377. doi: 10.1007/s12033-022-00647-1. Epub 2023 Jan 6. Mol Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 36607498
-
Specific PCR detection of Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. raphani: a causal agent of Fusarium wilt on radish plants.Lett Appl Microbiol. 2017 Aug;65(2):133-140. doi: 10.1111/lam.12761. Epub 2017 Jul 3. Lett Appl Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28585248
-
A newly developed real-time PCR assay for detection and quantification of Fusarium oxysporum and its use in compatible and incompatible interactions with grafted melon genotypes.Phytopathology. 2013 Aug;103(8):802-10. doi: 10.1094/PHYTO-11-12-0293-R. Phytopathology. 2013. PMID: 23464901
-
Development of the molecular methods for rapid detection and differentiation of Fusarium oxysporum and F. oxysporum f. sp. niveum in Taiwan.N Biotechnol. 2010 Sep 30;27(4):409-18. doi: 10.1016/j.nbt.2010.05.005. Epub 2010 May 13. N Biotechnol. 2010. PMID: 20471505
-
Molecular detection of Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. niveum and Mycosphaerella melonis in infected plant tissues and soil.FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2005 Aug 1;249(1):39-47. doi: 10.1016/j.femsle.2005.05.057. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2005. PMID: 16019161
Cited by
-
Establishment and Application of a Multiplex PCR Assay for Detection of Sclerotium rolfsii, Lasiodiplodia theobromae, and Fusarium oxysporum in Peanut.Mol Biotechnol. 2023 Aug;65(8):1369-1377. doi: 10.1007/s12033-022-00647-1. Epub 2023 Jan 6. Mol Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 36607498
-
Recent Advances in Molecular Diagnostics of Fungal Plant Pathogens: A Mini Review.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021 Jan 11;10:600234. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.600234. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33505921 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epidemiology and Control of Strawberry Bacterial Angular Leaf Spot Disease Caused by Xanthomonas fragariae.Plant Pathol J. 2016 Aug;32(4):290-9. doi: 10.5423/PPJ.OA.01.2016.0007. Epub 2016 Aug 1. Plant Pathol J. 2016. PMID: 27493604 Free PMC article.
-
The devastating oomycete phytopathogen Phytophthora cactorum: Insights into its biology and molecular features.Mol Plant Pathol. 2023 Sep;24(9):1017-1032. doi: 10.1111/mpp.13345. Epub 2023 May 5. Mol Plant Pathol. 2023. PMID: 37144631 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Buchman TG, Rossier M, Merz WG, Charache P. Detection of surgical pathogens by in vitro DNA amplification. Part I. Rapid identification of Candida albicans by in vitro amplification of a fungus-specific gene. Surgery. 1990;108:338–347. - PubMed
-
- Cruz MDL, Ramirez F, Hernandez H. DNA isolation and amplification from cacti. Plant Mol Biol Rep. 1997;15:319–325. doi: 10.1023/A:1007428818078. - DOI
-
- Chang M, Hyun IH, Lee YH. Bipolaris stem rot of cactus caused by Bipolaris cactivora (Petrak) Alcorn. Korean J Plant Pathol. 1998;14:661–663.
-
- Choi M-O, Kim SG, Hyun I-H, Kim JH, Cho C-H, Park MS, Kim YH. First report of black spot caused by Alternaria alternata on grafted cactus. Plant Pathol J. 2010;26:80–82. doi: 10.5423/PPJ.2010.26.1.080. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

