Extraembryonic but not embryonic SUMO-specific protease 2 is required for heart development
- PMID: 26883797
- PMCID: PMC4756675
- DOI: 10.1038/srep20999
Extraembryonic but not embryonic SUMO-specific protease 2 is required for heart development
Abstract
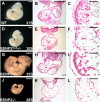
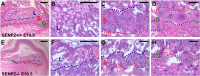
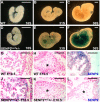
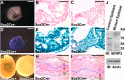
SUMO-specific protease 2 (SENP2) activities to remove SUMO from its substrates is essential for development of trophoblast stem cells, niches and lineages. Global deletion of SENP2 leads to midgestation lethality, and causes severe defects in the placenta which is accompanied by embryonic brain and heart abnormalities. Because of the placental deficiencies, the role of SENP2 in development of the embryonic tissues has not been properly determined. The brain and heart abnormalities may be secondary to placental insufficiency. Here we have created a new mouse strain permitting conditional inactivation of SENP2. Mice homozygous for germline deletion of the conditional allele exhibit trophoblast defects and embryonic abnormalities resembling the global SENP2 knockout. However, tissue-specific disruptions of SENP2 demonstrate its dispensable role in embryogenesis. Placental expression of SENP2 is necessary and sufficient for embryonic heart and brain development. Using a protease deficient model, we further demonstrate the requirement of SENP2-dependent SUMO modification in development of all major trophoblast lineages. SENP2 regulates sumoylation of Mdm2 which controls p53 activities critical for G-S transition of mitotic division and endoreduplication in trophoblast proliferation and differentiation, respectively. The differentiation of trophoblasts is also dependent on SENP2-mediated activation of p57(Kip2), a CDK-specific inhibitor required for endoreduplication.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The requirement of SUMO2/3 for SENP2 mediated extraembryonic and embryonic development.Dev Dyn. 2020 Feb;249(2):237-244. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.125. Epub 2019 Nov 1. Dev Dyn. 2020. PMID: 31625212 Free PMC article.
-
SUMO-specific protease 2 is essential for modulating p53-Mdm2 in development of trophoblast stem cell niches and lineages.PLoS Biol. 2008 Dec 16;6(12):e310. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0060310. PLoS Biol. 2008. PMID: 19090619 Free PMC article.
-
SUMO-specific protease 2 in Mdm2-mediated regulation of p53.Cell Death Differ. 2011 Jun;18(6):1005-15. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2010.168. Epub 2010 Dec 24. Cell Death Differ. 2011. PMID: 21183956 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic insights into trophoblast differentiation and placental morphogenesis.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2000 Apr;11(2):105-13. doi: 10.1006/scdb.2000.0156. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2000. PMID: 10873707 Review.
-
Sub-cellular localization specific SUMOylation in the heart.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2017 Aug;1863(8):2041-2055. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2017.01.018. Epub 2017 Jan 24. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2017. PMID: 28130202 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The requirement of SUMO2/3 for SENP2 mediated extraembryonic and embryonic development.Dev Dyn. 2020 Feb;249(2):237-244. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.125. Epub 2019 Nov 1. Dev Dyn. 2020. PMID: 31625212 Free PMC article.
-
Forebrain excitatory neuron-specific SENP2 knockout mouse displays hyperactivity, impaired learning and memory, and anxiolytic-like behavior.Mol Brain. 2020 Apr 14;13(1):59. doi: 10.1186/s13041-020-00591-8. Mol Brain. 2020. PMID: 32290845 Free PMC article.
-
Secondary Placental Defects in Cxadr Mutant Mice.Front Physiol. 2019 May 29;10:622. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2019.00622. eCollection 2019. Front Physiol. 2019. PMID: 31338035 Free PMC article.
-
Protein sumoylation in normal and cancer stem cells.Front Mol Biosci. 2022 Dec 19;9:1095142. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.1095142. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Biosci. 2022. PMID: 36601585 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SENP2 restrains the generation of pathogenic Th17 cells in mouse models of colitis.Commun Biol. 2023 Jun 10;6(1):629. doi: 10.1038/s42003-023-05009-4. Commun Biol. 2023. PMID: 37301920 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Melchior F. SUMO-nonclassical ubiquitin. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 16, 591–626 (2000). - PubMed
-
- Schwartz D. C. & Hochstrasser M. A superfamily of protein tags: ubiquitin, SUMO and related modifiers. Trends Biochem Sci 28, 321–328 (2003). - PubMed
-
- Seeler J. S. & Dejean A. Nuclear and unclear functions of SUMO. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 4, 690–699 (2003). - PubMed
-
- Ouyang J., Valin A. & Gill G. Regulation of transcription factor activity by SUMO modification. Methods Mol Biol 497, 141–152 (2009). - PubMed
-
- Geoffroy M. C. & Hay R. T. An additional role for SUMO in ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 10, 564–568 (2009). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

