DARPP-32: from neurotransmission to cancer
- PMID: 26872373
- PMCID: PMC4951238
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.7268
DARPP-32: from neurotransmission to cancer
Abstract
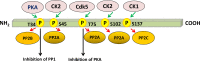
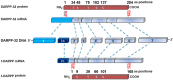
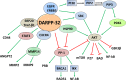
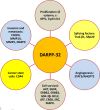
Dopamine and cAMP-regulated phosphoprotein Mr 32,000 (DARPP-32), also known as phosphoprotein phosphatase-1 regulatory subunit 1B (PPP1R1B), was initially discovered as a substrate of dopamine-activated protein kinase A (PKA) in the neostriatum in the brain. While phosphorylation at Thr-34 by PKA converts DARPP-32 into a potent inhibitor of protein phosphatase 1 (PP1), phosphorylation at Thr-75 transforms DARPP-32 into an inhibitor of PKA. Through regulation of DARPP-32 phosphorylation and modulation of protein phosphatase and kinase activities, DARPP-32 plays a critical role in mediating the biochemical, electrophysiological, and behavioral effects controlled by dopamine and other neurotransmitters in response to drugs of abuse and psychostimulants. Altered expression of DARPP-32 and its truncated isoform (t-DARPP), specifically in the prefrontal cortex, has been associated with schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. Moreover, cleavage of DARPP-32 by calpain has been implicated in Alzheimer's disease. Amplification of the genomic locus of DARPP-32 at 17q12 has been described in several cancers. DARPP-32 and t-DARPP are frequently overexpressed at the mRNA and protein levels in adenocarcinomas of the breast, prostate, colon, and stomach. Several studies demonstrated the pro-survival, pro-invasion, and pro-angiogenic functions of DARPP-32 in cancer. Overexpression of DARPP-32 and t-DARPP also promotes chemotherapeutic drug resistance and cell proliferation in gastric and breast cancers through regulation of pro-oncogenic signal transduction pathways. The expansion of DARPP-32 research from neurotransmission to cancer underscores the broad scope and implication of this protein in disparate human diseases.
Keywords: DARPP-32; PPP1R1B; cancer; neurotransmission; t-DARPP.
Conflict of interest statement
There is no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Darpp-32 and t-Darpp protein products of PPP1R1B: Old dogs with new tricks.Biochem Pharmacol. 2019 Feb;160:71-79. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2018.12.008. Epub 2018 Dec 12. Biochem Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30552871 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DARPP-32 mediates the actions of multiple drugs of abuse.AAPS J. 2005 Oct 5;7(2):E353-60. doi: 10.1208/aapsj070235. AAPS J. 2005. PMID: 16353915 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DARPP-32: an integrator of neurotransmission.Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2004;44:269-96. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pharmtox.44.101802.121415. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2004. PMID: 14744247 Review.
-
DARPP-32 40 years later.Adv Pharmacol. 2021;90:67-87. doi: 10.1016/bs.apha.2020.09.004. Epub 2020 Dec 2. Adv Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33706939 Review.
-
Overexpression of the 32-kilodalton dopamine and cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate-regulated phosphoprotein in common adenocarcinomas.Cancer. 2003 Oct 1;98(7):1547-51. doi: 10.1002/cncr.11654. Cancer. 2003. PMID: 14508844
Cited by
-
Emerging Roles of SRSF3 as a Therapeutic Target for Cancer.Front Oncol. 2020 Sep 25;10:577636. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.577636. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 33072610 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Darpp-32 and t-Darpp protein products of PPP1R1B: Old dogs with new tricks.Biochem Pharmacol. 2019 Feb;160:71-79. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2018.12.008. Epub 2018 Dec 12. Biochem Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30552871 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The involvement of DARPP-32 in the pathophysiology of schizophrenia.Oncotarget. 2017 Apr 21;8(32):53791-53803. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.17339. eCollection 2017 Aug 8. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28881851 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evidence that polyploidy in esophageal adenocarcinoma originates from mitotic slippage caused by defective chromosome attachments.Cell Death Differ. 2021 Jul;28(7):2179-2193. doi: 10.1038/s41418-021-00745-8. Epub 2021 Mar 1. Cell Death Differ. 2021. PMID: 33649470 Free PMC article.
-
Intrinsic epigenetic state of primary osteosarcoma drives metastasis.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Nov 13:2023.11.09.566446. doi: 10.1101/2023.11.09.566446. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Mol Cancer Res. 2024 Sep 4;22(9):864-878. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-23-0055. PMID: 38014160 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Walaas SI, Aswad DW, Greengard P. A dopamine- and cyclic AMP-regulated phosphoprotein enriched in dopamine-innervated brain regions. Nature. 1983b;301:69–71. - PubMed
-
- Meister B, Fryckstedt J, Schalling M, Cortes R, Hokfelt T, Aperia A, Hemmings HC, Jr, Nairn AC, Ehrlich M, Greengard P. Dopamine- and cAMP-regulated phosphoprotein (DARPP-32) and dopamine DA1 agonist-sensitive Na+,K+-ATPase in renal tubule cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989;86:8068–8072. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

