What Is Trophoblast? A Combination of Criteria Define Human First-Trimester Trophoblast
- PMID: 26862703
- PMCID: PMC4750161
- DOI: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2016.01.006
What Is Trophoblast? A Combination of Criteria Define Human First-Trimester Trophoblast
Abstract
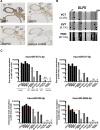
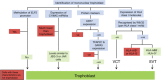
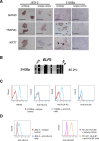
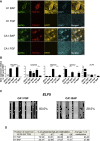
Controversy surrounds reports describing the derivation of human trophoblast cells from placentas and embryonic stem cells (ESC), partly due to the difficulty in identifying markers that define cells as belonging to the trophoblast lineage. We have selected criteria that are characteristic of primary first-trimester trophoblast: a set of protein markers, HLA class I profile, methylation of ELF5, and expression of microRNAs (miRNAs) from the chromosome 19 miRNA cluster (C19MC). We tested these criteria on cells previously reported to show some phenotypic characteristics of trophoblast: bone morphogenetic protein (BMP)-treated human ESC and 2102Ep, an embryonal carcinoma cell line. Both cell types only show some, but not all, of the four trophoblast criteria. Thus, BMP-treated human ESC have not fully differentiated to trophoblast. Our study identifies a robust panel, including both protein and non-protein-coding markers that, in combination, can be used to reliably define cells as characteristic of early trophoblast.
Copyright © 2016 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
ELF5-enforced transcriptional networks define an epigenetically regulated trophoblast stem cell compartment in the human placenta.Hum Mol Genet. 2010 Jun 15;19(12):2456-67. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddq128. Epub 2010 Mar 30. Hum Mol Genet. 2010. PMID: 20354077
-
Single-stranded DNA binding protein Ssbp3 induces differentiation of mouse embryonic stem cells into trophoblast-like cells.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2016 May 28;7(1):79. doi: 10.1186/s13287-016-0340-1. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2016. PMID: 27236334 Free PMC article.
-
The expression profile of C19MC microRNAs in primary human trophoblast cells and exosomes.Mol Hum Reprod. 2012 Aug;18(8):417-24. doi: 10.1093/molehr/gas013. Epub 2012 Feb 29. Mol Hum Reprod. 2012. PMID: 22383544 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA expression profiles of trophoblastic cells.Placenta. 2012 Sep;33(9):725-34. doi: 10.1016/j.placenta.2012.05.009. Epub 2012 Jun 19. Placenta. 2012. PMID: 22721760
-
The Role of Cluster C19MC in Pre-Eclampsia Development.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 10;23(22):13836. doi: 10.3390/ijms232213836. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36430313 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
All models are wrong, but some are useful: Establishing standards for stem cell-based embryo models.Stem Cell Reports. 2021 May 11;16(5):1117-1141. doi: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2021.03.019. Stem Cell Reports. 2021. PMID: 33979598 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Differential gene expression elicited by ZIKV infection in trophoblasts from congenital Zika syndrome discordant twins.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2020 Aug 3;14(8):e0008424. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0008424. eCollection 2020 Aug. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2020. PMID: 32745093 Free PMC article.
-
Trophoblast Differentiation: Mechanisms and Implications for Pregnancy Complications.Nutrients. 2023 Aug 12;15(16):3564. doi: 10.3390/nu15163564. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37630754 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human trophoblast stem cells restrict human cytomegalovirus replication.J Virol. 2024 Apr 16;98(4):e0193523. doi: 10.1128/jvi.01935-23. Epub 2024 Mar 7. J Virol. 2024. PMID: 38451085 Free PMC article.
-
Large-scale transcriptome-wide profiling of microRNAs in human placenta and maternal plasma at early to mid gestation.RNA Biol. 2021 Oct 15;18(sup1):507-520. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2021.1963105. Epub 2021 Aug 19. RNA Biol. 2021. PMID: 34412547 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Al-Lamki R.S., Skepper J.N., Burton G.J. Are human placental bed giant cells merely aggregates of small mononuclear trophoblast cells? An ultrastructural and immunocytochemical study. Hum. Reprod. 1999;14:496–504. - PubMed
-
- Anderson D.J., Narayan P., DeWolf W.C. Major histocompatibility antigens are not detectable on post-meiotic human testicular germ cells. J. Immunol. 1984;133:1962–1965. - PubMed
-
- Apps R., Gardner L., Moffett A. A critical look at HLA-G. Trends Immunol. 2008;29:313–321. - PubMed
-
- Apps R., Murphy S.P., Fernando R., Gardner L., Ahad T., Moffett A. Human leucocyte antigen (HLA) expression of primary trophoblast cells and placental cell lines, determined using single antigen beads to characterize allotype specificities of anti-HLA antibodies. Immunology. 2009;127:26–39. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

