Artemisinin activity-based probes identify multiple molecular targets within the asexual stage of the malaria parasites Plasmodium falciparum 3D7
- PMID: 26858419
- PMCID: PMC4776496
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1600459113
Artemisinin activity-based probes identify multiple molecular targets within the asexual stage of the malaria parasites Plasmodium falciparum 3D7
Abstract
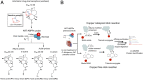
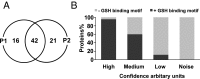
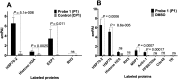
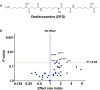
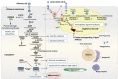
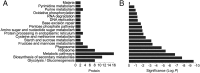
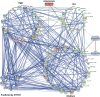
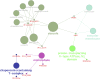
The artemisinin (ART)-based antimalarials have contributed significantly to reducing global malaria deaths over the past decade, but we still do not know how they kill parasites. To gain greater insight into the potential mechanisms of ART drug action, we developed a suite of ART activity-based protein profiling probes to identify parasite protein drug targets in situ. Probes were designed to retain biological activity and alkylate the molecular target(s) of Plasmodium falciparum 3D7 parasites in situ. Proteins tagged with the ART probe can then be isolated using click chemistry before identification by liquid chromatography-MS/MS. Using these probes, we define an ART proteome that shows alkylated targets in the glycolytic, hemoglobin degradation, antioxidant defense, and protein synthesis pathways, processes essential for parasite survival. This work reveals the pleiotropic nature of the biological functions targeted by this important class of antimalarial drugs.
Keywords: antimalarial; artemisinin; bioactivation; chemical proteomics; molecular targets.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A Click Chemistry-Based Proteomic Approach Reveals that 1,2,4-Trioxolane and Artemisinin Antimalarials Share a Common Protein Alkylation Profile.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2016 May 23;55(22):6401-5. doi: 10.1002/anie.201512062. Epub 2016 Apr 18. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2016. PMID: 27089538 Free PMC article.
-
A small-molecule inhibitor of the DNA recombinase Rad51 from Plasmodium falciparum synergizes with the antimalarial drugs artemisinin and chloroquine.J Biol Chem. 2019 May 17;294(20):8171-8183. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.005009. Epub 2019 Apr 1. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 30936202 Free PMC article.
-
Stochastic Protein Alkylation by Antimalarial Peroxides.ACS Infect Dis. 2019 Dec 13;5(12):2067-2075. doi: 10.1021/acsinfecdis.9b00264. Epub 2019 Dec 2. ACS Infect Dis. 2019. PMID: 31626733
-
Synthetic chemistry fuels interdisciplinary approaches to the production of artemisinin.Nat Prod Rep. 2015 Mar;32(3):359-66. doi: 10.1039/c4np00113c. Nat Prod Rep. 2015. PMID: 25342519 Review.
-
Current scenario and future strategies to fight artemisinin resistance.Parasitol Res. 2019 Jan;118(1):29-42. doi: 10.1007/s00436-018-6126-x. Epub 2018 Nov 26. Parasitol Res. 2019. PMID: 30478733 Review.
Cited by
-
Advances in the research on the targets of anti-malaria actions of artemisinin.Pharmacol Ther. 2020 Dec;216:107697. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2020.107697. Epub 2020 Oct 6. Pharmacol Ther. 2020. PMID: 33035577 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The malaria parasite chaperonin containing TCP-1 (CCT) complex: Data integration with other CCT proteomes.Front Mol Biosci. 2022 Dec 8;9:1057232. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.1057232. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Biosci. 2022. PMID: 36567946 Free PMC article.
-
Micromolar Dihydroartemisinin Concentrations Elicit Lipoperoxidation in Plasmodium falciparum-Infected Erythrocytes.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Jul 21;12(7):1468. doi: 10.3390/antiox12071468. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37508006 Free PMC article.
-
Appraisal of Bioactive Compounds of Betel Fruit as Antimalarial Agents by Targeting Plasmepsin 1 and 2: A Computational Approach.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021 Dec 9;14(12):1285. doi: 10.3390/ph14121285. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34959685 Free PMC article.
-
Structure-Activity Relationships of the Antimalarial Agent Artemisinin 10. Synthesis and Antimalarial Activity of Enantiomers of rac-5β-Hydroxy-d-Secoartemisinin and Analogs: Implications Regarding the Mechanism of Action.Molecules. 2021 Jul 8;26(14):4163. doi: 10.3390/molecules26144163. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34299438 Free PMC article.
References
-
- WHO . World Malaria Report 2014. WHO; Geneva: 2014.
-
- Eckstein-Ludwig U, et al. Artemisinins target the SERCA of Plasmodium falciparum. Nature. 2003;424(6951):957–961. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

