Inflammation and cancer: inhibiting the progression of residual hepatic VX2 carcinoma by anti-inflammatory drug after incomplete radiofrequency ablation
- PMID: 26823706
- PMCID: PMC4713492
Inflammation and cancer: inhibiting the progression of residual hepatic VX2 carcinoma by anti-inflammatory drug after incomplete radiofrequency ablation
Abstract
Background: Accelerated progression of residual hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) after incomplete radiofrequency ablation (RFA) has been reported more frequently. Recent data have redefined the concept of inflammation as a critical component of tumor progression. However, there has been little understanding regarding the relationship between progression of residual HCC and the inflammation induced by thermal destruction of the tumor after RFA. The present study was designed to determine whether inflammation facilitates rapid progression of residual hepatic VX2 carcinoma and to clarify the possible underlying mechanisms.
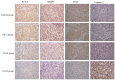
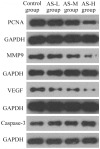
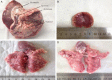
Methods: Forty-eight rabbits were each implanted with two VX2 hepatic tumors via supraumbilical median laparotomy. One of the tumors in two different lobes was ablated by RFA. All the rabbits were then randomly divided into four groups (12 rabbits in each group) receiving anti-inflammatory treatment with different doses of aspirin: control group, AS-L group (aspirin, 5 mg/kg/d), AS-M group (aspirin, 20 mg/kg/d), and AS-H group (aspirin, 100 mg/kg/d). The levels of serum interleukin-6 (IL-6), high sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP), and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) were detected to evaluate the effect of the anti-inflammation. Tumor growth, lung and kidney metastasis, and survival were assessed. The expression of proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA), matrix metalloproteinase 9 (MMP-9), vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), and cysteinyl aspartate specific proteinase 3 (caspase-3) in residual tumor was examined by immunohistochemistry and Western-blotting.
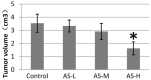
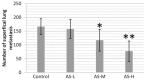
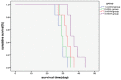
Results: The levels of serum IL-6, hs-CRP, and TNF-α in the AS-H group decreased significantly in comparison with those of the control group (P<0.05). The focal tumor volume and lung and kidney metastases of rabbits in the AS-H group were less significant compared with those of the control group (P<0.05). The expression of PCNA, MMP-9, and VEGF in the AS-H group decreased significantly compared with the control group (P<0.05). Finally, the survival time of the AS-H group was longer than that of the control group (P<0.05).
Conclusions: Inflammation induced by thermal destruction of the tumor following RFA could be an important cause of rapid progression of residual hepatic VX2 carcinoma. The anti-inflammation effect of aspirin can inhibit proliferation, invasion, and metastasis of residual tumor cells, and aspirin may be a good candidate drug as an adjuvant therapy with RFA for treating HCC.
Keywords: Hepatocellular carcinoma; IL-6; RFA; interleukin-6; radiofrequency ablation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Radio-frequency ablation-based studies on VX2rabbit models for HCC treatment.Infect Agent Cancer. 2016 Aug 12;11:38. doi: 10.1186/s13027-016-0082-9. eCollection 2016. Infect Agent Cancer. 2016. PMID: 27525037 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Low temperature of radiofrequency ablation at the target sites can facilitate rapid progression of residual hepatic VX2 carcinoma.J Transl Med. 2010 Jul 29;8:73. doi: 10.1186/1479-5876-8-73. J Transl Med. 2010. PMID: 20667141 Free PMC article.
-
Radiofrequency ablation suppresses distant tumour growth in a novel rat model of multifocal hepatocellular carcinoma.Clin Sci (Lond). 2014 Feb;126(3):243-52. doi: 10.1042/CS20130089. Clin Sci (Lond). 2014. PMID: 23822114
-
Sorafenib suppresses the rapid progress of hepatocellular carcinoma after insufficient radiofrequency ablation therapy: an experiment in vivo.Acta Radiol. 2013 Mar 1;54(2):199-204. doi: 10.1258/ar.2012.120249. Epub 2012 Nov 21. Acta Radiol. 2013. PMID: 23171528
-
Progression of hepatocellular carcinoma after radiofrequency ablation: Current status of research.Front Oncol. 2022 Nov 22;12:1032746. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1032746. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36483051 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Platelet lysates in Hepatocellular Carcinoma patients after radiofrequency ablation facilitate tumor proliferation, invasion and vasculogenic mimicry.Int J Med Sci. 2020 Jul 29;17(14):2104-2112. doi: 10.7150/ijms.44405. eCollection 2020. Int J Med Sci. 2020. PMID: 32922171 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of the hepatic tumor extracellular matrix using elastin-specific molecular magnetic resonance imaging in an experimental rabbit cancer model.Sci Rep. 2020 Nov 27;10(1):20785. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-77624-8. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 33247185 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms and therapeutic strategies to combat the recurrence and progression of hepatocellular carcinoma after thermal ablation.J Interv Med. 2023 Oct 18;6(4):160-169. doi: 10.1016/j.jimed.2023.10.004. eCollection 2023 Nov. J Interv Med. 2023. PMID: 38312128 Free PMC article.
-
Radio-frequency ablation-based studies on VX2rabbit models for HCC treatment.Infect Agent Cancer. 2016 Aug 12;11:38. doi: 10.1186/s13027-016-0082-9. eCollection 2016. Infect Agent Cancer. 2016. PMID: 27525037 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Early Identification of Residual Tumors following Microwave Ablation Using Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasonography in a Rabbit VX2 Liver Cancer Model.Biomed Res Int. 2020 Sep 26;2020:2462058. doi: 10.1155/2020/2462058. eCollection 2020. Biomed Res Int. 2020. PMID: 33029496 Free PMC article.
References
-
- El-Serag HB. Hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2011;365:1118–1127. - PubMed
-
- Shiina S, Teratani T, Obi S, Hamamura K, Koike Y, Omata M. Nonsurgical treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma: from percutaneous ethanol injection therapy and percutaneous microwave coagulation therapy to radiofrequency ablation. Oncology. 2002;62(Suppl 1):64–68. - PubMed
-
- Boulin M, Ciboulet A, Guiu B, Maillard E, Bonnetain F, Minello A, Gagnaire A, Lepage C, Krause D, Hillon P, Bedenne L, Cercueil JP, Chauffert B, Jouve JL. Randomised controlled trial of lipiodol transarterial chemoembolisation with or without amiodarone for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. Dig Liver Dis. 2011;43:905–911. - PubMed
-
- Lee DH, Lee JM, Lee JY, Kim SH, Yoon JH, Kim YJ, Han JK, Choi BI. Radiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma as first-line treatment: long-term results and prognostic factors in 162 patients with cirrhosis. Radiology. 2014;270:900–909. - PubMed
-
- Lau WY, Lai EC. The current role of radiofrequency ablation in the management of hepatocellular carcinoma: a systematic review. Ann Surg. 2009;249:20–25. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
