Ultraviolet light-emitting diode irradiation-induced cell death in HL-60 human leukemia cells in vitro
- PMID: 26820261
- PMCID: PMC4768973
- DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2016.4812
Ultraviolet light-emitting diode irradiation-induced cell death in HL-60 human leukemia cells in vitro
Abstract
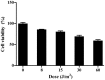
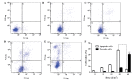
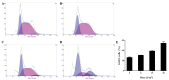
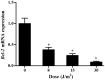
Ultraviolet (UV) radiation is considered to be a potent cell-damaging agent in various cell lineages; however, the effect of UV light‑emitting diode (LED) irradiation on human cells remains unclear. The aim of the present study was to examine the effect of UV LED irradiation emitting at 280 nm on cultured HL‑60 human leukemia cells, and to explore the underlying mechanisms. HL‑60 cells were irradiated with UV LED (8, 15, 30 and 60 J/m2) and incubated for 2 h after irradiation. The rates of cell proliferation and apoptosis, the cell cycle profiles and the mRNA expression of B‑cell lymphoma 2 (Bcl‑2) were detected using cell counting kit‑8, multicaspase assays, propidium iodide staining and reverse transcription‑quantitative polymerase chain reaction, respectively. The results showed that UV LED irradiation (8‑60 J/m2) inhibited the proliferation of HL‑60 cells in a dose‑dependent manner. UV LED at 8‑30 J/m2 induced dose‑dependent apoptosis and G0/G1 cell cycle arrest, and inhibited the expression of Bcl‑2 mRNA, while UV LED at 60 J/m2 induced necrosis. In conclusion, 280 nm UV LED irradiation inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis and necrosis in cultured HL‑60 cells. In addition, the cell cycle arrest at the G0/G1 phase and the downregulation of Bcl‑2 mRNA expression were shown to be involved in UV LED-induced apoptosis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Ultraviolet light-emitting diode irradiation induces reactive oxygen species production and mitochondrial membrane potential reduction in HL-60 cells.J Int Med Res. 2021 May;49(5):3000605211016623. doi: 10.1177/03000605211016623. J Int Med Res. 2021. PMID: 34038212 Free PMC article.
-
Chlorogenic acid induced apoptosis and inhibition of proliferation in human acute promyelocytic leukemia HL‑60 cells.Mol Med Rep. 2013 Oct;8(4):1106-10. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2013.1652. Epub 2013 Aug 27. Mol Med Rep. 2013. PMID: 23982123
-
G2/M-phase arrest and death by apoptosis of HL60 cells irradiated with exponentially decreasing low-dose-rate gamma radiation.Radiat Res. 1999 Jun;151(6):659-69. Radiat Res. 1999. PMID: 10360785
-
Effect of light irradiation by light emitting diode on colon cancer cells.Anticancer Res. 2014 Sep;34(9):4709-16. Anticancer Res. 2014. PMID: 25202048
-
UVC radiation-induced effect on human primary thyroid cell proliferation and HLA-DR expression.Horm Metab Res. 2010 Nov;42(12):846-53. doi: 10.1055/s-0030-1265215. Epub 2010 Sep 30. Horm Metab Res. 2010. PMID: 20886415
Cited by
-
[Effect of ultraviolet irradiation on the proliferation of acute promyelocytic leukemia cells under hypoxic conditions and related mechanisms].Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2019 May;21(5):491-496. doi: 10.7499/j.issn.1008-8830.2019.05.018. Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2019. PMID: 31104669 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Ultraviolet Radiation Promoted Hypoxia-Induced Apoptosis in HL-60 Human Promyelocytic Leukemia Cell Line.J Oncol. 2022 Oct 31;2022:7702481. doi: 10.1155/2022/7702481. eCollection 2022. J Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36353706 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Tripodal Polyamine Tris-Pyrene: DNA/RNA Binding and Photodynamic Antiproliferative Activity.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Aug 25;15(9):2197. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15092197. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37765167 Free PMC article.
-
Ultraviolet light-emitting diode irradiation induces reactive oxygen species production and mitochondrial membrane potential reduction in HL-60 cells.J Int Med Res. 2021 May;49(5):3000605211016623. doi: 10.1177/03000605211016623. J Int Med Res. 2021. PMID: 34038212 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

