T-bet expression in CD8+ T cells associated with chronic hepatitis B virus infection
- PMID: 26809262
- PMCID: PMC4727400
- DOI: 10.1186/s12985-016-0473-y
T-bet expression in CD8+ T cells associated with chronic hepatitis B virus infection
Abstract
Background: The mechanisms leading to virus-specific CD8+ T cell dysfuction in chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection remain to be elucidated. Our study focused on the role of transcription factor T-bet in HBV infection because it is a crucial regulator of T cell immunity.
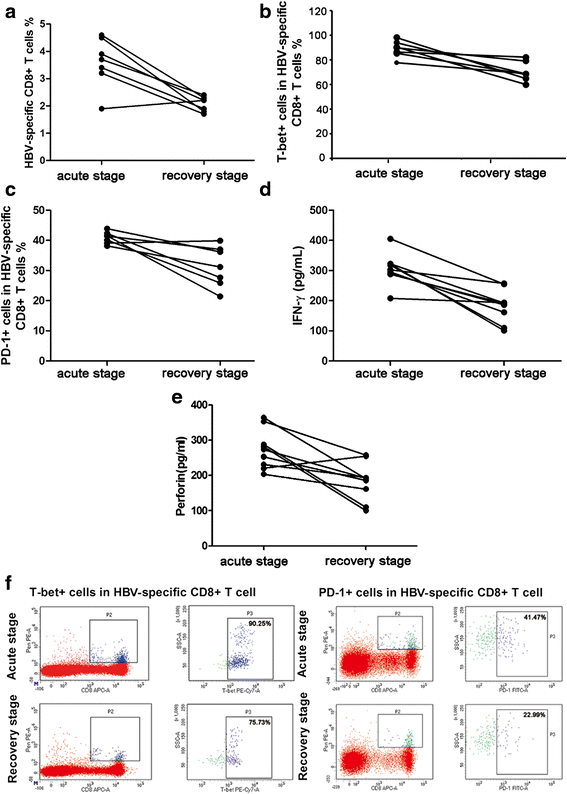
Methods: We assessed the expression of T-bet along with PD-1, IFN-γ and perforin, in HBV-specific CD8+ T cells from resolved acute hepatitis B (rAHB) patients, chronic hepatitis B (CHB) patients, as well as asymptomatic HBV carriers (ASCs). We observed dynamic changes of T-bet, PD-1, IFN-γ and perforin in acute stage and recovery stage of acute hepatitis B (AHB).
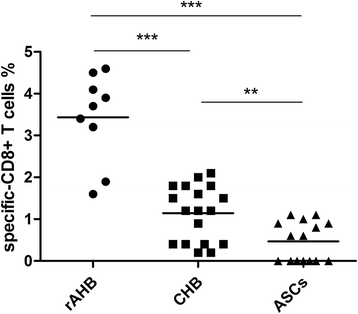
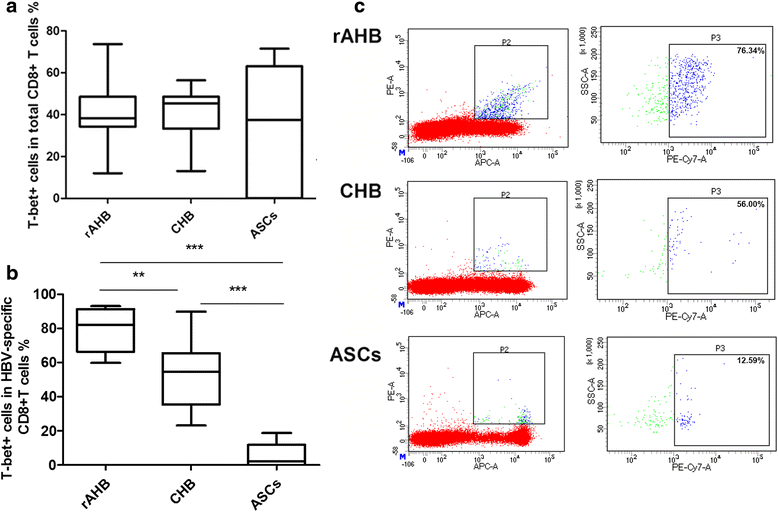
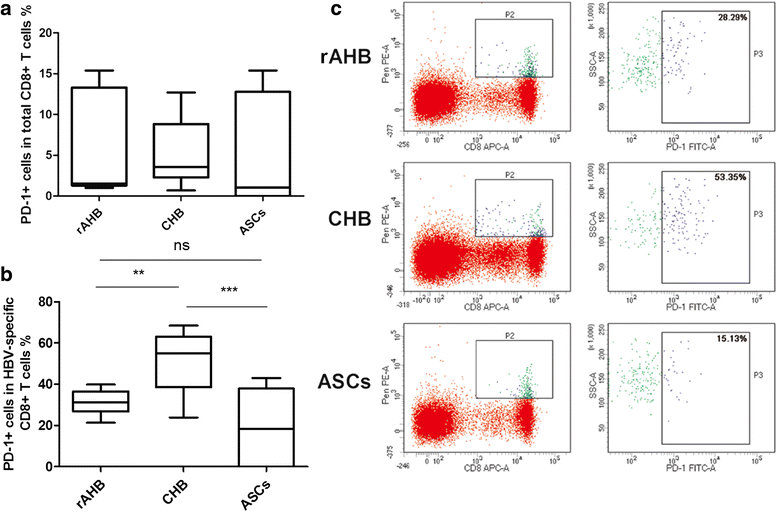
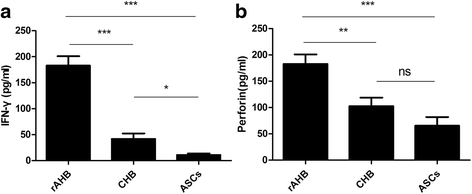
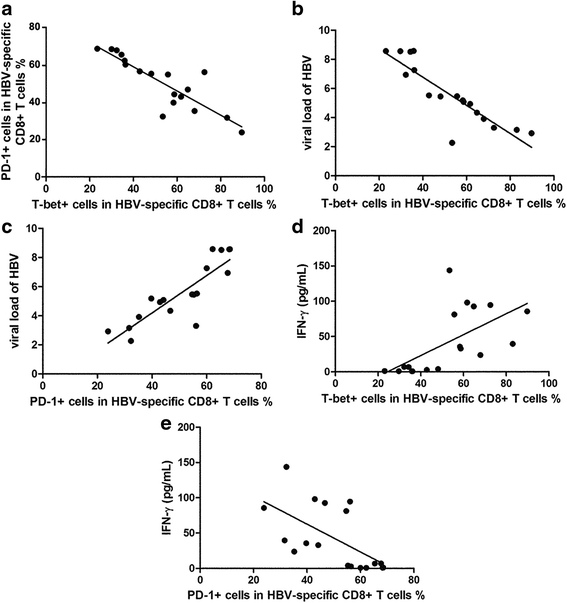
Results: Comparing with other cohorts, HBV-specific CD8+ T cells from rAHB demonstrated a superior ability in T-bet, IFN-γ and perforin expression, but an inferior ability in PD-1 expression. In the CHB group, the level of T-bet has a linear relationship with the level of PD-1, IFN-γ and HBV DNA, respectively. A lower expression of T-bet and PD-1 was observed in ASCs when compared with CHB. A higher expression of T-bet, PD-1, IFN-r and perforin was observed in acute stage when compared with the recovery stage of AHB.
Conclusions: Our results suggest that expression of T-bet may influence the function of HBV-specific CD8+ T cells and thus can be an attractive target for modulation to improve HBV-specific immunity in CHB.
Figures
Similar articles
-
PD-1 upregulation is associated with HBV-specific T cell dysfunction in chronic hepatitis B patients.Mol Immunol. 2008 Feb;45(4):963-70. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2007.07.038. Epub 2007 Sep 14. Mol Immunol. 2008. PMID: 17868872
-
Dynamic programmed death 1 expression by virus-specific CD8 T cells correlates with the outcome of acute hepatitis B.Gastroenterology. 2008 Jun;134(7):1938-49, 1949.e1-3. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2008.03.037. Epub 2008 Mar 22. Gastroenterology. 2008. PMID: 18455515
-
[Alterations of IFN-γ and IL-4 of peripheral blood T cells in patients with chronic HBV infection].Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2016 Feb;32(2):240-4. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2016. PMID: 26927386 Chinese.
-
T-cell exhaustion in chronic hepatitis B infection: current knowledge and clinical significance.Cell Death Dis. 2015 Mar 19;6(3):e1694. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2015.42. Cell Death Dis. 2015. PMID: 25789969 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immune Regulation by T Regulatory Cells in Hepatitis B Virus-Related Inflammation and Cancer.Scand J Immunol. 2017 Mar;85(3):175-181. doi: 10.1111/sji.12524. Scand J Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28109025 Review.
Cited by
-
Hepatitis B virus polymerase-specific T cell epitopes shift in a mouse model of chronic infection.Virol J. 2021 Dec 7;18(1):242. doi: 10.1186/s12985-021-01712-y. Virol J. 2021. PMID: 34876153 Free PMC article.
-
Delineation of an immunosuppressive gradient in hepatocellular carcinoma using high-dimensional proteomic and transcriptomic analyses.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017 Jul 18;114(29):E5900-E5909. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1706559114. Epub 2017 Jul 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017. PMID: 28674001 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

