c-Jun N-terminal Kinase (JNK) Signaling as a Therapeutic Target for Alzheimer's Disease
- PMID: 26793112
- PMCID: PMC4709475
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2015.00321
c-Jun N-terminal Kinase (JNK) Signaling as a Therapeutic Target for Alzheimer's Disease
Abstract
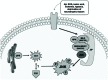
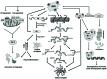
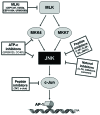
c-Jun N-terminal kinases (JNKs) are a family of protein kinases that play a central role in stress signaling pathways implicated in gene expression, neuronal plasticity, regeneration, cell death, and regulation of cellular senescence. It has been shown that there is a JNK pathway activation after exposure to different stressing factors, including cytokines, growth factors, oxidative stress, unfolded protein response signals or Aβ peptides. Altogether, JNKs have become a focus of screening strategies searching for new therapeutic approaches to diabetes, cancer or liver diseases. In addition, activation of JNK has been identified as a key element responsible for the regulation of apoptosis signals and therefore, it is critical for pathological cell death associated with neurodegenerative diseases and, among them, with Alzheimer's disease (AD). In addition, in vitro and in vivo studies have reported alterations of JNK pathways potentially associated with pathogenesis and neuronal death in AD. JNK's, particularly JNK3, not only enhance Aβ production, moreover it plays a key role in the maturation and development of neurofibrillary tangles. This review aims to explain the rationale behind testing therapies based on inhibition of JNK signaling for AD in terms of current knowledge about the pathophysiology of the disease. Keeping in mind that JNK3 is specifically expressed in the brain and activated by stress-stimuli, it is possible to hypothesize that inhibition of JNK3 might be considered as a potential target for treating neurodegenerative mechanisms associated with AD.
Keywords: D-JNKI1; SP600125; apoptosis; inhibitors; kinase; tau; βamyloid.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The regulation of p53 up-regulated modulator of apoptosis by JNK/c-Jun pathway in β-amyloid-induced neuron death.J Neurochem. 2015 Sep;134(6):1091-103. doi: 10.1111/jnc.13128. Epub 2015 Apr 28. J Neurochem. 2015. PMID: 25891762
-
Activation and redistribution of c-jun N-terminal kinase/stress activated protein kinase in degenerating neurons in Alzheimer's disease.J Neurochem. 2001 Jan;76(2):435-41. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.2001.00046.x. J Neurochem. 2001. PMID: 11208906
-
Targeting the JNK MAPK cascade for inhibition: basic science and therapeutic potential.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004 Mar 11;1697(1-2):89-101. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2003.11.016. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004. PMID: 15023353 Review.
-
Rg1 exhibits neuroprotective effects by inhibiting the endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated c-Jun N-terminal protein kinase apoptotic pathway in a rat model of Alzheimer's disease.Mol Med Rep. 2015 Sep;12(3):3862-3868. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2015.3853. Epub 2015 May 27. Mol Med Rep. 2015. PMID: 26016457
-
JNK: a stress-activated protein kinase therapeutic strategies and involvement in Alzheimer's and various neurodegenerative abnormalities.J Mol Neurosci. 2011 Mar;43(3):376-90. doi: 10.1007/s12031-010-9454-6. Epub 2010 Sep 28. J Mol Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 20878262 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of Potential Key circRNAs in Aged Mice With Postoperative Delirium.Front Mol Neurosci. 2022 Apr 14;15:836534. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2022.836534. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35493320 Free PMC article.
-
Tau-targeting therapies for Alzheimer disease.Nat Rev Neurol. 2018 Jul;14(7):399-415. doi: 10.1038/s41582-018-0013-z. Nat Rev Neurol. 2018. PMID: 29895964 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of potential JNK3 inhibitors through virtual screening, molecular docking and molecular dynamics simulation as therapeutics for Alzheimer's disease.Mol Divers. 2024 Dec;28(6):4361-4380. doi: 10.1007/s11030-024-10820-0. Epub 2024 Apr 4. Mol Divers. 2024. PMID: 38573427
-
Zinc Finger E-Box Binding Protein 2 (ZEB2) Suppress Apoptosis of Vascular Endothelial Cells Induced by High Glucose Through Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinases (MAPK) Pathway Activation.Med Sci Monit. 2017 May 28;23:2590-2598. doi: 10.12659/msm.904678. Med Sci Monit. 2017. PMID: 28551696 Free PMC article.
-
Apoptosis in Alzheimer's disease: insight into the signaling pathways and therapeutic avenues.Apoptosis. 2023 Aug;28(7-8):943-957. doi: 10.1007/s10495-023-01848-y. Epub 2023 Apr 26. Apoptosis. 2023. PMID: 37186274 Review.
References
-
- Bamji-Mirza M., Callaghan D., Najem D., Shen S., Hasim M. S., Yang Z., et al. (2014). Stimulation of insulin signaling and inhibition of JNK-AP1 activation protect cells from amyloid-beta-induced signaling dysregulation and inflammatory response. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 40 105–122. 10.3233/JAD-131949 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

