ZEB1 Mediates Acquired Resistance to the Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
- PMID: 26789630
- PMCID: PMC4720447
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0147344
ZEB1 Mediates Acquired Resistance to the Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
Abstract
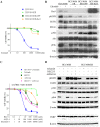
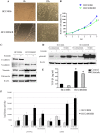
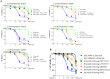
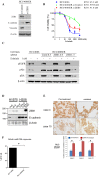
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) is one mechanism of acquired resistance to inhibitors of the epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinases (EGFR-TKIs) in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). The precise mechanisms of EMT-related acquired resistance to EGFR-TKIs in NSCLC remain unclear. We generated erlotinib-resistant HCC4006 cells (HCC4006ER) by chronic exposure of EGFR-mutant HCC4006 cells to increasing concentrations of erlotinib. HCC4006ER cells acquired an EMT phenotype and activation of the TGF-β/SMAD pathway, while lacking both T790M secondary EGFR mutation and MET gene amplification. We employed gene expression microarrays in HCC4006 and HCC4006ER cells to better understand the mechanism of acquired EGFR-TKI resistance with EMT. At the mRNA level, ZEB1 (TCF8), a known regulator of EMT, was >20-fold higher in HCC4006ER cells than in HCC4006 cells, and increased ZEB1 protein level was also detected. Furthermore, numerous ZEB1 responsive genes, such as CDH1 (E-cadherin), ST14, and vimentin, were coordinately regulated along with increased ZEB1 in HCC4006ER cells. We also identified ZEB1 overexpression and an EMT phenotype in several NSCLC cells and human NSCLC samples with acquired EGFR-TKI resistance. Short-interfering RNA against ZEB1 reversed the EMT phenotype and, importantly, restored erlotinib sensitivity in HCC4006ER cells. The level of micro-RNA-200c, which can negatively regulate ZEB1, was significantly reduced in HCC4006ER cells. Our results suggest that increased ZEB1 can drive EMT-related acquired resistance to EGFR-TKIs in NSCLC. Attempts should be made to explore targeting ZEB1 to resensitize TKI-resistant tumors.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Epithelial to mesenchymal transition in an epidermal growth factor receptor-mutant lung cancer cell line with acquired resistance to erlotinib.J Thorac Oncol. 2011 Jul;6(7):1152-61. doi: 10.1097/JTO.0b013e318216ee52. J Thorac Oncol. 2011. PMID: 21597390
-
Effect of dasatinib on EMT-mediated-mechanism of resistance against EGFR inhibitors in lung cancer cells.Lung Cancer. 2017 Feb;104:85-90. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2016.12.012. Epub 2016 Dec 21. Lung Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28213007
-
CRIPTO1 expression in EGFR-mutant NSCLC elicits intrinsic EGFR-inhibitor resistance.J Clin Invest. 2014 Jul;124(7):3003-15. doi: 10.1172/JCI73048. Epub 2014 Jun 9. J Clin Invest. 2014. PMID: 24911146 Free PMC article.
-
Current mechanism of acquired resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitors and updated therapy strategies in human nonsmall cell lung cancer.J Cancer Res Ther. 2016 Dec;12(Supplement):C131-C137. doi: 10.4103/0973-1482.200613. J Cancer Res Ther. 2016. PMID: 28230005 Review.
-
[Research Progress of the Role of EMT in EGFR-TKIs Resistance of Non-small Cell Lung Cancer].Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2018 Dec 20;21(12):907-911. doi: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2018.12.08. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2018. PMID: 30591098 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Zinc finger proteins in cancer progression.J Biomed Sci. 2016 Jul 13;23(1):53. doi: 10.1186/s12929-016-0269-9. J Biomed Sci. 2016. PMID: 27411336 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of phenotypic plasticity in the escape of cancer cells from targeted therapy.Biochem Pharmacol. 2016 Dec 15;122:1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2016.06.014. Epub 2016 Jun 25. Biochem Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27349985 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Potential Utility of a 4th-Generation EGFR-TKI and Exploration of Resistance Mechanisms-An In Vitro Study.Biomedicines. 2024 Jun 25;12(7):1412. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12071412. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39061985 Free PMC article.
-
A YAP/FOXM1 axis mediates EMT-associated EGFR inhibitor resistance and increased expression of spindle assembly checkpoint components.Sci Transl Med. 2020 Sep 2;12(559):eaaz4589. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aaz4589. Sci Transl Med. 2020. PMID: 32878980 Free PMC article.
-
Epithelial-mesenchymal-transition-inducing transcription factors: new targets for tackling chemoresistance in cancer?Oncogene. 2018 Nov;37(48):6195-6211. doi: 10.1038/s41388-018-0378-x. Epub 2018 Jul 12. Oncogene. 2018. PMID: 30002444 Review.
References
-
- Kobayashi S, Boggon TJ, Dayaram T, Janne PA, Kocher O, Meyerson M, et al. EGFR mutation and resistance of non-small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N Engl J Med. 2005;352(8):786–92. - PubMed
-
- Engelman JA, Zejnullahu K, Mitsudomi T, Song Y, Hyland C, Park JO, et al. MET amplification leads to gefitinib resistance in lung cancer by activating ERBB3 signaling. Science. 2007;316(5827):1039–43. - PubMed
-
- Yauch RL, Januario T, Eberhard DA, Cavet G, Zhu W, Fu L, et al. Epithelial versus mesenchymal phenotype determines in vitro sensitivity and predicts clinical activity of erlotinib in lung cancer patients. Clin Cancer Res. 2005;11(24 Pt 1):8686–98. - PubMed
-
- Thomson S, Buck E, Petti F, Griffin G, Brown E, Ramnarine N, et al. Epithelial to mesenchymal transition is a determinant of sensitivity of non-small-cell lung carcinoma cell lines and xenografts to epidermal growth factor receptor inhibition. Cancer Res. 2005;65(20):9455–62. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

