Leptin signalling pathways in hypothalamic neurons
- PMID: 26786898
- PMCID: PMC11108307
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-016-2133-1
Leptin signalling pathways in hypothalamic neurons
Abstract
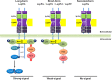
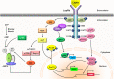
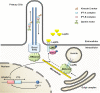
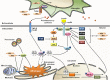
Leptin is the most critical hormone in the homeostatic regulation of energy balance among those so far discovered. Leptin primarily acts on the neurons of the mediobasal part of hypothalamus to regulate food intake, thermogenesis, and the blood glucose level. In the hypothalamic neurons, leptin binding to the long form leptin receptors on the plasma membrane initiates multiple signaling cascades. The signaling pathways known to mediate the actions of leptin include JAK-STAT signaling, PI3K-Akt-FoxO1 signaling, SHP2-ERK signaling, AMPK signaling, and mTOR-S6K signaling. Recent evidence suggests that leptin signaling in hypothalamic neurons is also linked to primary cilia function. On the other hand, signaling molecules/pathways mitigating leptin actions in hypothalamic neurons have been extensively investigated in an effort to treat leptin resistance observed in obesity. These include SOCS3, tyrosine phosphatase PTP1B, and inflammatory signaling pathways such as IKK-NFκB and JNK signaling, and ER stress-mitochondrial signaling. In this review, we discuss leptin signaling pathways in the hypothalamus, with a particular focus on the most recently discovered pathways.
Keywords: Cilia; Hypothalamus; Leptin; Neurons; Obesity; Signaling.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Chronic sleep fragmentation during the sleep period induces hypothalamic endoplasmic reticulum stress and PTP1b-mediated leptin resistance in male mice.Sleep. 2015 Jan 1;38(1):31-40. doi: 10.5665/sleep.4320. Sleep. 2015. PMID: 25325461 Free PMC article.
-
Recent advances in understanding leptin signaling and leptin resistance.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2009 Dec;297(6):E1247-59. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00274.2009. Epub 2009 Sep 1. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2009. PMID: 19724019 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phlorotannins from Ecklonia cava Attenuates Palmitate-Induced Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Leptin Resistance in Hypothalamic Neurons.Mar Drugs. 2019 Oct 9;17(10):570. doi: 10.3390/md17100570. Mar Drugs. 2019. PMID: 31600939 Free PMC article.
-
Diet-Induced Obesity and the Mechanism of Leptin Resistance.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;960:381-397. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-48382-5_16. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017. PMID: 28585208 Review.
-
Disrupted Leptin Signaling in the Lateral Hypothalamus and Ventral Premammillary Nucleus Alters Insulin and Glucagon Secretion and Protects Against Diet-Induced Obesity.Endocrinology. 2016 Jul;157(7):2671-85. doi: 10.1210/en.2015-1998. Epub 2016 May 16. Endocrinology. 2016. PMID: 27183315
Cited by
-
Presence of leptin and its receptor in the ram reproductive system and in vitro effect of leptin on sperm quality.PeerJ. 2022 Sep 26;10:e13982. doi: 10.7717/peerj.13982. eCollection 2022. PeerJ. 2022. PMID: 36187750 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Advances in the Knowledge of the Mechanisms of Leptin Physiology and Actions in Neurological and Metabolic Pathologies.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 11;24(2):1422. doi: 10.3390/ijms24021422. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36674935 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of intestinal growth in response to variations in energy supply and demand.Obes Rev. 2018 Dec;19 Suppl 1(Suppl Suppl 1):61-72. doi: 10.1111/obr.12780. Obes Rev. 2018. PMID: 30511508 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hypothalamic primary cilium: A hub for metabolic homeostasis.Exp Mol Med. 2021 Jul;53(7):1109-1115. doi: 10.1038/s12276-021-00644-5. Epub 2021 Jul 1. Exp Mol Med. 2021. PMID: 34211092 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Emerging Role of Cyclin-Dependent Kinase Inhibitors in Treating Diet-Induced Obesity: New Opportunities for Breast and Ovarian Cancers?Cancers (Basel). 2022 May 30;14(11):2709. doi: 10.3390/cancers14112709. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35681689 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Schwartz MW, Woods SC, Porte D, Jr, Seeley RJ, Baskin DG. Central nervous system control of food intake. Nature. 2000;404:661–671. - PubMed
-
- Ingalls AM, Dickie MM, Snell GD. Obese, a new mutation in the house mouse. J Hered. 1950;41:317–318. - PubMed
-
- Coleman DL, Hummel KP. Effects of parabiosis of normal with genetically diabetic mice. Am J Physiol. 1969;217:1298–1304. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

