Antiproliferative and proapoptotic effects of a pyrrole containing arylthioindole in human Jurkat leukemia cell line and multidrug-resistant Jurkat/A4 cells
- PMID: 26785947
- PMCID: PMC4847820
- DOI: 10.1080/15384047.2015.1078026
Antiproliferative and proapoptotic effects of a pyrrole containing arylthioindole in human Jurkat leukemia cell line and multidrug-resistant Jurkat/A4 cells
Abstract
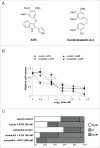
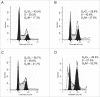
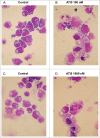
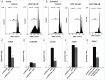
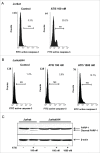
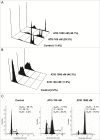
Recently, a series of novel arylthioindole compounds, potent inhibitors of tubulin polymerization and cancer cell growth, were synthesized. In the present study the effects of 2-(1H-pyrrol-3-yl)-3-((3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)thio)-1H-indole (ATI5 compound) on cell proliferation, cell cycle progression, and induction of apoptosis in human T-cell acute leukemia Jurkat cells and their multidrug resistant Jurkat/A4 subline were investigated. Treatment of the Jurkat cells with the ATI5 compound for 48 hrs resulted in a strong G2/M cell cycle arrest and p53-independent apoptotic cell death accompanied by the induction of the active form of caspase-3 and poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 (PARP-1) cleavage. ATI5 treatment also caused non-cell death related mitotic arrest in multidrug resistant Jurkat/A4 cells after 48 hrs of treatment suggesting promising opportunities for the further design of pyrrole-containing ATI compounds as anticancer agents. Cell death resistance of Jurkat/A4 cells to ATI5 compound was associated with alterations in the expression of pro-survival and anti-apoptotic protein-coding and microRNA genes. More importantly, findings showing that ATI5 treatment induced p53-independent apoptosis are of great importance from a therapeutic point of view since p53 mutations are common genetic alterations in human neoplasms.
Keywords: G2/M arrest; Jurkat leukemia cells; apoptosis; arylthioindoles; drug resistance; gene expression; microRNA.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pyrrolotetrazinones deazaanalogues of temozolomide induce apoptosis in Jurkat cell line: involvement of tubulin polymerization inhibition.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2009 Nov;64(6):1235-51. doi: 10.1007/s00280-009-0994-9. Epub 2009 Apr 11. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19363609
-
DAT-230, a Novel Microtubule Inhibitor, Induced Aberrant Mitosis and Apoptosis in SGC-7901 Cells.Biol Pharm Bull. 2013;36(2):193-201. doi: 10.1248/bpb.b12-00321. Biol Pharm Bull. 2013. PMID: 23370351
-
Induction of G2/M phase arrest and apoptosis of human leukemia cells by potent antitumor triazoloacridinone C-1305.Biochem Pharmacol. 2006 Dec 15;72(12):1668-79. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2006.07.035. Epub 2006 Sep 12. Biochem Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 16970926
-
Escin sodium induces apoptosis of human acute leukemia Jurkat T cells.Phytother Res. 2011 Dec;25(12):1747-55. doi: 10.1002/ptr.3457. Epub 2011 Mar 31. Phytother Res. 2011. PMID: 21452372
-
MPT0B169, a novel tubulin inhibitor, induces apoptosis in taxol-resistant acute myeloid leukemia cells through mitochondrial dysfunction and Mcl-1 downregulation.Tumour Biol. 2016 May;37(5):6065-72. doi: 10.1007/s13277-015-4380-4. Epub 2015 Nov 25. Tumour Biol. 2016. PMID: 26608370
Cited by
-
Mitotic cell death induction by targeting the mitotic spindle with tubulin-inhibitory indole derivative molecules.Oncotarget. 2017 Mar 21;8(12):19738-19759. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.14980. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28160569 Free PMC article.
-
Novel insights on [1,2]oxazolo[5,4-e]isoindoles on multidrug resistant acute myeloid leukemia cell line.Drug Dev Res. 2022 Sep;83(6):1331-1341. doi: 10.1002/ddr.21962. Epub 2022 Jun 24. Drug Dev Res. 2022. PMID: 35749723 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Beckers T, Mahboobi S. Natural, semisynthetic and synthetic microtubule inhibitors for cancer therapy. Drugs Future 2003; 28:767-85; http://dx.doi.org/10.1358/dof.2003.028.08.744356 - DOI
-
- Li Q, Sham HL. Discovery and development of antimitotic agents that inhibit tubulin polymerization for the treatment of cancer. Expert Opin Ther Pat 2002; 12:1663-702; http://dx.doi.org/10.1517/13543776.12.11.1663 - DOI
-
- La Regina G, Bai R, Rensen W, Coluccia A, Piscitelli F, Gatti V, Bolognesi A, Lavecchia A, Granata I, Porta A, et al.. Design and synthesis of 2-heterocyclyl-3-arylthio-1H-indoles as potent tubulin polymerization and cell growth inhibitors with improved metabolic stability. J Med Chem 2011; 54:8394-406; PMID:22044164; http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/jm2012886 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- La Regina G, Bai R, Rensen WM, Di Cesare E, Coluccia A, Piscitelli F, Famiglini V, Reggio A, Nalli M, Pelliccia S, et al.. Toward highly potent cancer agents by modulating the C-2 group of the arylthioindole class of tubulin polymerization inhibitors. J Med Chem 2013; 56:123-49; PMID:23214452; http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/jm3013097 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ciapetti P, Giethlen B. Molecular variations based on isosteric replacement. Carboxylic esters bioisosteres In: The Practice of Medicinal Chemistry, 3rd ed. Wermuth CG, ed. Elsevier Ltd, Oxford, 2008: 310−3.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
