Three-dimensional reconstruction of coronary arteries and plaque morphology using CT angiography--comparison and registration with IVUS
- PMID: 26785613
- PMCID: PMC4719213
- DOI: 10.1186/s12880-016-0111-6
Three-dimensional reconstruction of coronary arteries and plaque morphology using CT angiography--comparison and registration with IVUS
Abstract
Background: The aim of this study is to present a new methodology for three-dimensional (3D) reconstruction of coronary arteries and plaque morphology using Computed Tomography Angiography (CTA).
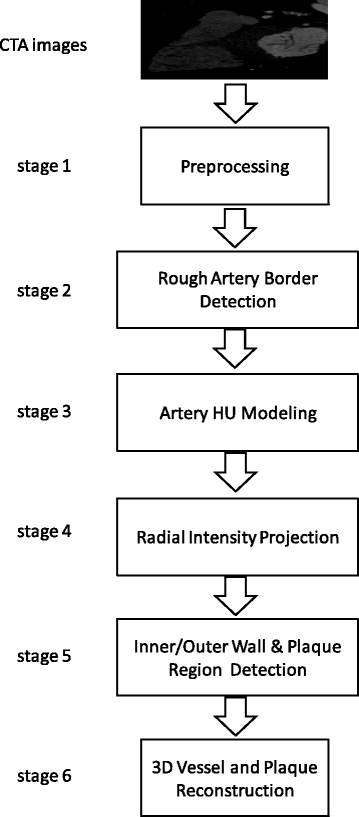
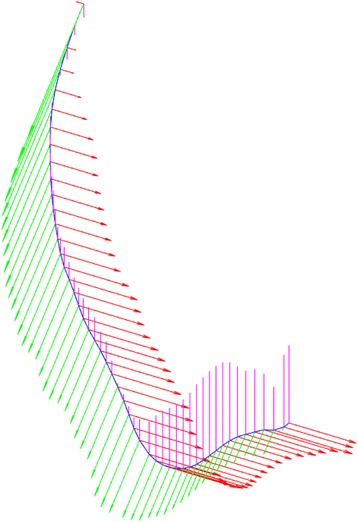
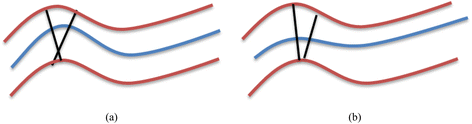
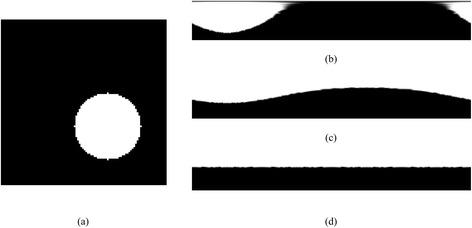
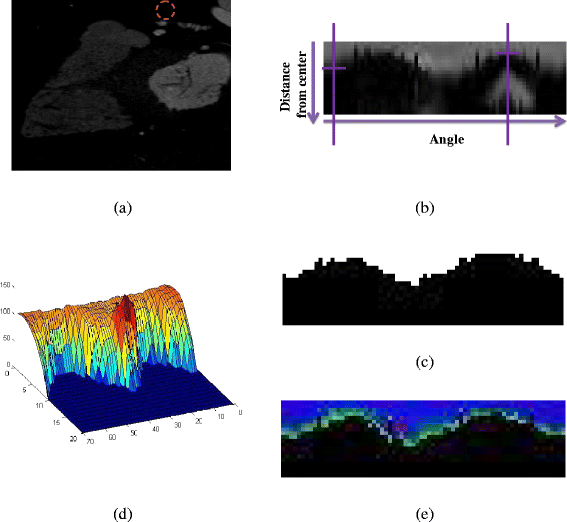
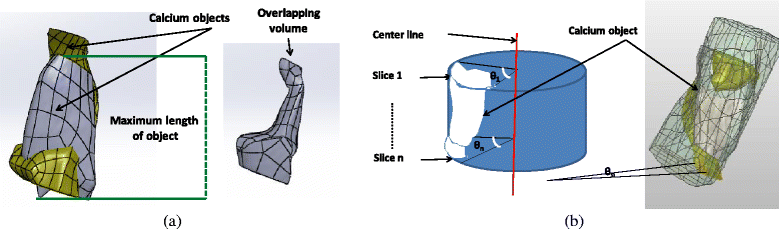
Methods: The methodology is summarized in six stages: 1) pre-processing of the initial raw images, 2) rough estimation of the lumen and outer vessel wall borders and approximation of the vessel's centerline, 3) manual adaptation of plaque parameters, 4) accurate extraction of the luminal centerline, 5) detection of the lumen - outer vessel wall borders and calcium plaque region, and 6) finally 3D surface construction.
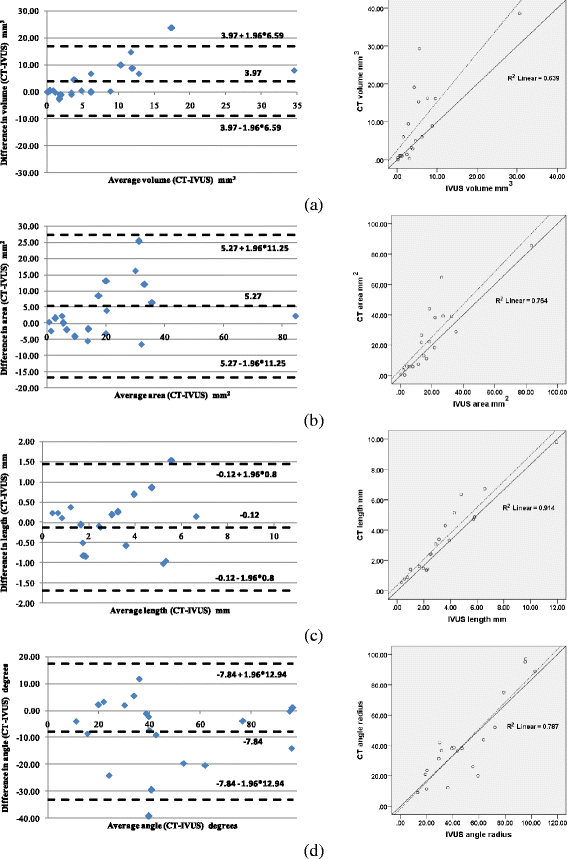
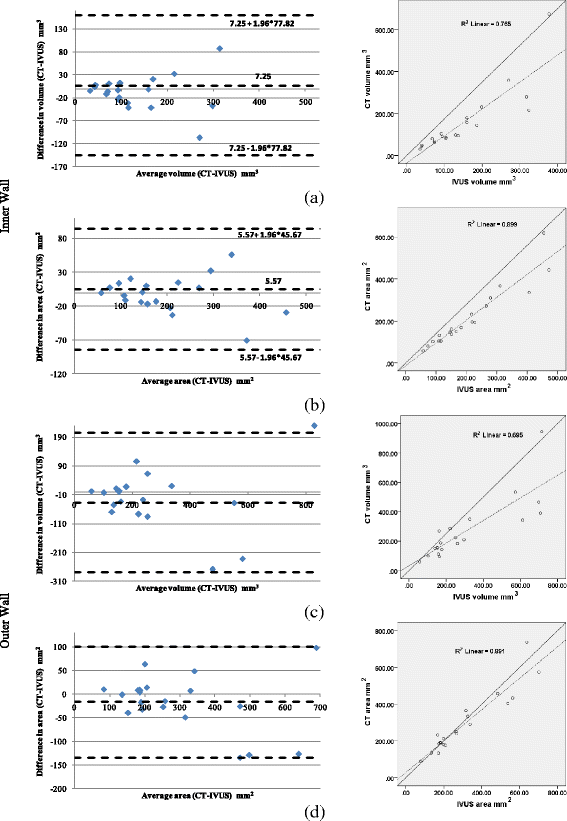
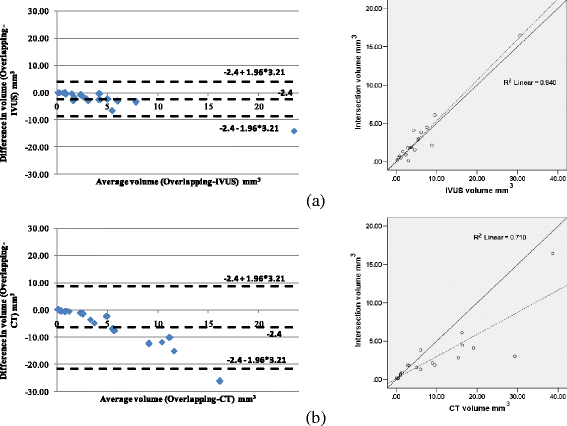
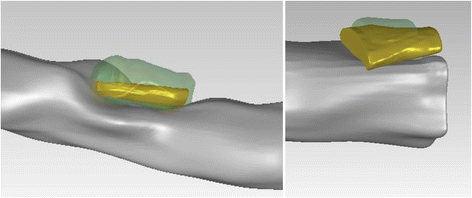
Results: The methodology was compared to the estimations of a recently presented Intravascular Ultrasound (IVUS) plaque characterization method. The correlation coefficients for calcium volume, surface area, length and angle vessel were 0.79, 0.86, 0.95 and 0.88, respectively. Additionally, when comparing the inner and outer vessel wall volumes of the reconstructed arteries produced by IVUS and CTA the observed correlation was 0.87 and 0.83, respectively.
Conclusions: The results indicated that the proposed methodology is fast and accurate and thus it is likely in the future to have applications in research and clinical arena.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Three-dimensional reconstruction of coronary arteries and plaque morphology using CT angiography - comparison and registration using IVUS.Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2015 Aug;2015:5638-41. doi: 10.1109/EMBC.2015.7319671. Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2015. PMID: 26737571
-
Coronary CT angiography versus intravascular ultrasound for estimation of coronary stenosis and atherosclerotic plaque burden: a meta-analysis.J Cardiovasc Comput Tomogr. 2013 Jul-Aug;7(4):256-66. doi: 10.1016/j.jcct.2013.08.006. Epub 2013 Aug 23. J Cardiovasc Comput Tomogr. 2013. PMID: 24148779 Review.
-
Implications of computed tomography reconstruction algorithms on coronary atheroma quantification: Comparison with intravascular ultrasound.J Cardiovasc Comput Tomogr. 2023 Jan-Feb;17(1):43-51. doi: 10.1016/j.jcct.2022.09.004. Epub 2022 Sep 21. J Cardiovasc Comput Tomogr. 2023. PMID: 36270952
-
Automated quantification of coronary plaque with computed tomography: comparison with intravascular ultrasound using a dedicated registration algorithm for fusion-based quantification.Eur Heart J. 2012 Apr;33(8):1007-16. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehr465. Epub 2012 Jan 26. Eur Heart J. 2012. PMID: 22285583
-
Three-dimensional reconstruction of coronary arteries with intravascular ultrasound.Herz. 1995 Aug;20(4):277-89. Herz. 1995. PMID: 7557831 Review.
Cited by
-
Assessment of the value of 3D-DSA combined with neurointerventional thrombolysis in the treatment of senile cerebrovascular occlusion.Exp Ther Med. 2020 Feb;19(2):891-896. doi: 10.3892/etm.2019.8274. Epub 2019 Dec 4. Exp Ther Med. 2020. PMID: 32010249 Free PMC article.
-
Novel preclinical method for evaluating the efficacy of a percutaneous treatment in human ex vivo calcified plaque.Med Biol Eng Comput. 2021 Apr;59(4):799-811. doi: 10.1007/s11517-021-02334-w. Epub 2021 Mar 12. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2021. PMID: 33710527
-
Position Paper Computational Cardiology.IEEE J Biomed Health Inform. 2019 Jan;23(1):4-11. doi: 10.1109/JBHI.2018.2877044. Epub 2018 Oct 19. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform. 2019. PMID: 30346296 Free PMC article.
-
Intraoperative Imaging and Image Fusion for Venous Interventions.Methodist Debakey Cardiovasc J. 2018 Jul-Sep;14(3):200-207. doi: 10.14797/mdcj-14-3-200. Methodist Debakey Cardiovasc J. 2018. PMID: 30410650 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A comparative analysis of deep learning-based location-adaptive threshold method software against other commercially available software.Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2024 Jun;40(6):1269-1281. doi: 10.1007/s10554-024-03099-7. Epub 2024 Apr 18. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2024. PMID: 38634943 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Stone GW, Maehara A, Lansky AJ, de Bruyne B, Cristea E, Mintz GS, Mehran R, McPherson J, Farhat N, Marso SP, Parise H, Templin B, White R, Zhang Z, Serruys PW. A prospective natural-history study of coronary atherosclerosis. N Engl J Med. 2011;364:226–35 - PubMed
-
- Calvert PA, Obaid DR, O'Sullivan M, Shapiro LM, McNab D, Densem CG, et al. Association between IVUS findings and adverse outcomes in patients with coronary artery diseasethe VIVA (VH-IVUS in vulnerable atherosclerosis) study. JACC: Cardiovascular Imaging. 2011;4(8):894–901. - PubMed
-
- Mintz GS, Nissen SE, Anderson WD, Bailey SR, Erbel R, Fitzgerald PJ, et al. American college of cardiology clinical expert consensus document on standards for acquisition, measurement and reporting of Intravascular Ultrasound Studies (IVUS). A report of the American College of Cardiology Task Force on Clinical Expert Consensus Documents. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2001;37(5):1478–92. doi: 10.1016/S0735-1097(01)01175-5. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bourantas CV, Kourtis IC, Plissiti ME, Fotiadis DI, Katsouras CS, Papafaklis MI et al. A method for 3D reconstruction of coronary arteries using biplane angiography and intravascular ultrasound images. Comput Med Imag Grap. 2005;29(8):597–606. doi:DOI 10.1016/j.compmedimag.2005.07.001. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

