Brain somatic mutations in MTOR leading to focal cortical dysplasia
- PMID: 26779999
- PMCID: PMC4915119
- DOI: 10.5483/bmbrep.2016.49.2.010
Brain somatic mutations in MTOR leading to focal cortical dysplasia
Abstract
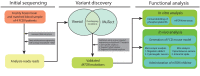
Focal cortical dysplasia type II (FCDII) is a focal malformation of the developing cerebral cortex and the major cause of intractable epilepsy. However, since the molecular genetic etiology of FCD has remained enigmatic, the effective therapeutic target for this condition has remained poorly understood. Our recent study on FCD utilizing various deep sequencing platforms identified somatic mutations in MTOR (existing as low as 1% allelic frequency) only in the affected brain tissues. We observed that these mutations induced hyperactivation of the mTOR kinase. In addition, focal cortical expression of mutant MTOR using in utero electroporation in mice, recapitulated the neuropathological features of FCDII, such as migration defect, cytomegalic neuron and spontaneous seizures. Furthermore, seizures and dysmorphic neurons were rescued by the administration of mTOR inhibitor, rapamycin. This study provides the first evidence that brain somatic activating mutations in MTOR cause FCD, and suggests the potential drug target for intractable epilepsy in FCD patients. [BMB Reports 2016; 49(2): 71-72].
Figures
Similar articles
-
Brain somatic mutations in MTOR cause focal cortical dysplasia type II leading to intractable epilepsy.Nat Med. 2015 Apr;21(4):395-400. doi: 10.1038/nm.3824. Epub 2015 Mar 23. Nat Med. 2015. PMID: 25799227
-
Somatic Mutations in the MTOR gene cause focal cortical dysplasia type IIb.Ann Neurol. 2015 Sep;78(3):375-86. doi: 10.1002/ana.24444. Epub 2015 Jul 3. Ann Neurol. 2015. PMID: 26018084
-
Somatic Mutations in TSC1 and TSC2 Cause Focal Cortical Dysplasia.Am J Hum Genet. 2017 Mar 2;100(3):454-472. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2017.01.030. Epub 2017 Feb 16. Am J Hum Genet. 2017. PMID: 28215400 Free PMC article.
-
Cortical Dysplasia and the mTOR Pathway: How the Study of Human Brain Tissue Has Led to Insights into Epileptogenesis.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jan 25;23(3):1344. doi: 10.3390/ijms23031344. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35163267 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Focal malformations of cortical development: new vistas for molecular pathogenesis.Neuroscience. 2013 Nov 12;252:262-76. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2013.07.037. Epub 2013 Jul 25. Neuroscience. 2013. PMID: 23892008 Review.
Cited by
-
Brain Tissue Low-Level Mosaicism for MTOR Mutation Causes Smith-Kingsmore Phenotype with Recurrent Hypoglycemia-A Novel Phenotype and a Further Proof for Testing of an Affected Tissue.Diagnostics (Basel). 2021 Jul 15;11(7):1269. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics11071269. Diagnostics (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34359351 Free PMC article.
-
SLC35A2 somatic variants in drug resistant epilepsy: FCD and MOGHE.Neurobiol Dis. 2023 Oct 15;187:106299. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2023.106299. Epub 2023 Sep 20. Neurobiol Dis. 2023. PMID: 37739137 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PI3K/mTOR Pathway Inhibition: Opportunities in Oncology and Rare Genetic Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Nov 18;20(22):5792. doi: 10.3390/ijms20225792. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31752127 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Correspondence on "Clinical spectrum of MTOR-related hypomelanosis of Ito with neurodevelopmental abnormalities," by Carmignac et al.Genet Med. 2021 Nov;23(11):2223-2224. doi: 10.1038/s41436-021-01256-0. Epub 2021 Jul 7. Genet Med. 2021. PMID: 34234302 No abstract available.
-
Genotype-phenotype correlations in focal malformations of cortical development: a pathway to integrated pathological diagnosis in epilepsy surgery.Brain Pathol. 2019 Jul;29(4):473-484. doi: 10.1111/bpa.12686. Epub 2019 Jan 27. Brain Pathol. 2019. PMID: 30485578 Free PMC article.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

