Epstein-Barr virus glycoprotein gM can interact with the cellular protein p32 and knockdown of p32 impairs virus
- PMID: 26773383
- PMCID: PMC4761307
- DOI: 10.1016/j.virol.2015.12.019
Epstein-Barr virus glycoprotein gM can interact with the cellular protein p32 and knockdown of p32 impairs virus
Abstract
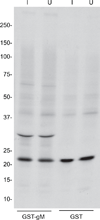
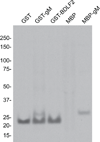
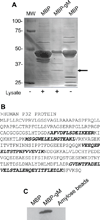
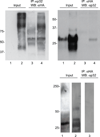
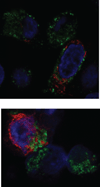
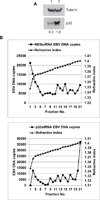
The Epstein-Barr virus glycoprotein complex gMgN has been implicated in assembly and release of fully enveloped virus, although the precise role that it plays has not been elucidated. We report here that the long predicted cytoplasmic tail of gM is not required for complex formation and that it interacts with the cellular protein p32, which has been reported to be involved in nuclear egress of human cytomegalovirus and herpes simplex virus. Although redistribution of p32 and colocalization with gM was not observed in virus infected cells, knockdown of p32 expression by siRNA or lentivirus-delivered shRNA recapitulated the phenotype of a virus lacking expression of gNgM. A proportion of virus released from cells sedimented with characteristics of virus lacking an intact envelope and there was an increase in virus trapped in nuclear condensed chromatin. The observations suggest the possibility that p32 may also be involved in nuclear egress of Epstein-Barr virus.
Keywords: Epstein–Barr virus; Glycoprotein gM; Glycoprotein gN; Virus egress; p32.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Epstein-Barr virus that lacks glycoprotein gN is impaired in assembly and infection.J Virol. 2000 Dec;74(23):11162-72. doi: 10.1128/jvi.74.23.11162-11172.2000. J Virol. 2000. PMID: 11070013 Free PMC article.
-
Human p32: a coactivator for Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen-1-mediated transcriptional activation and possible role in viral latent cycle DNA replication.Virology. 2000 Sep 15;275(1):145-57. doi: 10.1006/viro.2000.0508. Virology. 2000. PMID: 11017796
-
P32/TAP, a cellular protein that interacts with EBNA-1 of Epstein-Barr virus.Virology. 1997 Sep 15;236(1):18-29. doi: 10.1006/viro.1997.8739. Virology. 1997. PMID: 9299613
-
Role of Viral miRNAs and Epigenetic Modifications in Epstein-Barr Virus-Associated Gastric Carcinogenesis.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016;2016:6021934. doi: 10.1155/2016/6021934. Epub 2016 Feb 10. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016. PMID: 26977250 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Research Advances in Target Genes of Epstein-Barr Virus-encoded MicroRNAs].Bing Du Xue Bao. 2016 Mar;32(2):229-34. Bing Du Xue Bao. 2016. PMID: 27396169 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
N-Linked Glycosylation and Expression of Duck Plague Virus pUL10 Promoted by pUL49.5.Microbiol Spectr. 2023 Aug 17;11(4):e0162523. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01625-23. Epub 2023 Jun 28. Microbiol Spectr. 2023. PMID: 37378543 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear Egress Complexes of HCMV and Other Herpesviruses: Solving the Puzzle of Sequence Coevolution, Conserved Structures and Subfamily-Spanning Binding Properties.Viruses. 2020 Jun 24;12(6):683. doi: 10.3390/v12060683. Viruses. 2020. PMID: 32599939 Free PMC article. Review.
-
'Come together'-The Regulatory Interaction of Herpesviral Nuclear Egress Proteins Comprises Both Essential and Accessory Functions.Cells. 2022 Jun 4;11(11):1837. doi: 10.3390/cells11111837. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35681532 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Patterns of Autologous and Nonautologous Interactions Between Core Nuclear Egress Complex (NEC) Proteins of α-, β- and γ-Herpesviruses.Viruses. 2020 Mar 11;12(3):303. doi: 10.3390/v12030303. Viruses. 2020. PMID: 32168891 Free PMC article.
-
The Roles of Envelope Glycoprotein M in the Life Cycle of Some Alphaherpesviruses.Front Microbiol. 2021 Feb 19;12:631523. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.631523. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33679658 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Yaswen LR, Stephens EB, Davenport LC, Hutt-Fletcher LM. Epstein-Barr virus glycoprotein gp85 associates with the BKRF2 gene product and is incompletely processed as a recombinant protein. Virology. 1993;195:387–396. - PubMed
-
- Ren Y, Bell S, Zenner HL, Lau S-YK, Crump CM. Glycoprotein M is important for the efficient incorporation of glycoprotein H-L inot herpes simplex virus type 1 particles. J. Gen. Virol. 2012;93:319–329. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

