ZYG11A serves as an oncogene in non-small cell lung cancer and influences CCNE1 expression
- PMID: 26771237
- PMCID: PMC4884973
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.6904
ZYG11A serves as an oncogene in non-small cell lung cancer and influences CCNE1 expression
Abstract
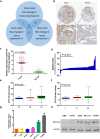
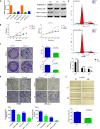
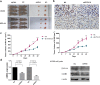
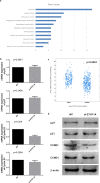
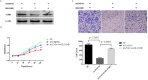
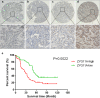
By analyzing The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database, we identified ZYG11A as a potential oncogene. We determined the expression of ZYG11A in NSCLC tissues and explored its clinical significance. And also evaluated the effects of ZYG11A on NSCLC cell proliferation, migration, and invasion both in vitro and in vivo. Our results show that ZYG11A is hyper-expressed in NSCLC tissues compared to adjacent normal tissues, and increased expression of ZYG11A is associated with a poor prognosis (HR: 2.489, 95%CI: 1.248-4.963, p = 0.010). ZYG11A knockdown induces cell cycle arrest and inhibits proliferation, migration, and invasion of NSCLC cells. ZYG11A knockdown also results in decreased expression of CCNE1. Over-expression of CCNE1 in cells with ZYG11A knockdown restores their oncogenic activities. Our data suggest that ZYG11A may serve as a novel oncogene promoting tumorigenicity of NSCLC cells by inducing cell cycle alterations and increasing CCNE1 expression.
Keywords: CCNE1; NSCLC; ZYG11A; bioinformatics; oncogene.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Twist may be associated with invasion and metastasis of hypoxic NSCLC cells.Tumour Biol. 2016 Jul;37(7):9979-87. doi: 10.1007/s13277-016-4896-2. Epub 2016 Jan 27. Tumour Biol. 2016. PMID: 26819207
-
Retinoic acid-related orphan receptor C isoform 2 expression and its prognostic significance for non-small cell lung cancer.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2016 Jan;142(1):263-72. doi: 10.1007/s00432-015-2040-0. Epub 2015 Aug 30. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2016. PMID: 26319393
-
RBX1 expression is an unfavorable prognostic factor in patients with non-small cell lung cancer.Surg Oncol. 2016 Sep;25(3):147-51. doi: 10.1016/j.suronc.2016.05.006. Epub 2016 May 10. Surg Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27566015
-
[Advances on driver oncogenes of squamous cell lung cancer].Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2014 May;17(5):433-6. doi: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2014.05.13. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2014. PMID: 24854563 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
-
Genomic landscape of squamous cell carcinoma of the lung.Am Soc Clin Oncol Educ Book. 2013:348-53. doi: 10.14694/EdBook_AM.2013.33.348. Am Soc Clin Oncol Educ Book. 2013. PMID: 23714544 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of the prognostic and therapeutic values of cyclin E1 (CCNE1) gene expression in Lung Adenocarcinoma and Lung Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A database mining approach.Heliyon. 2022 Aug 29;8(9):e10367. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e10367. eCollection 2022 Sep. Heliyon. 2022. PMID: 36091953 Free PMC article.
-
Circular RNA has_circ_0067934 is upregulated in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and promoted proliferation.Sci Rep. 2016 Oct 18;6:35576. doi: 10.1038/srep35576. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27752108 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of ZYG11A as a candidate IGF1-dependent proto-oncogene in endometrial cancer.Oncotarget. 2019 Jul 9;10(43):4437-4448. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.27055. eCollection 2019 Jul 9. Oncotarget. 2019. PMID: 31320996 Free PMC article.
-
TFAP2A Induced KRT16 as an Oncogene in Lung Adenocarcinoma via EMT.Int J Biol Sci. 2019 Jun 2;15(7):1419-1428. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.34076. eCollection 2019. Int J Biol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31337972 Free PMC article.
-
HOXC13 promotes proliferation of lung adenocarcinoma via modulation of CCND1 and CCNE1.Am J Cancer Res. 2017 Sep 1;7(9):1820-1834. eCollection 2017. Am J Cancer Res. 2017. PMID: 28979806 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA: a cancer journal for clinicians. 2011;61:69–90. - PubMed
-
- Youlden DR, Cramb SM, Baade PD. The International Epidemiology of Lung Cancer: geographical distribution and secular trends. J Thorac Oncol. 2008;3:819–831. - PubMed
-
- Prensner JR, Iyer MK, Balbin OA, Dhanasekaran SM, Cao Q, Brenner JC, Laxman B, Asangani IA, Grasso CS, Kominsky HD, Cao X, Jing X, Wang X, Siddiqui J, Wei JT, Robinson D, et al. Transcriptome sequencing across a prostate cancer cohort identifies PCAT-1, an unannotated lincRNA implicated in disease progression. Nat Biotechnol. 2011;29:742–749. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

