The Sphingosine-1-Phosphate Lyase (LegS2) Contributes to the Restriction of Legionella pneumophila in Murine Macrophages
- PMID: 26741365
- PMCID: PMC4704736
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0146410
The Sphingosine-1-Phosphate Lyase (LegS2) Contributes to the Restriction of Legionella pneumophila in Murine Macrophages
Abstract
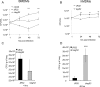
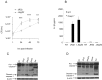
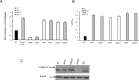
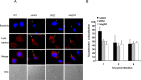
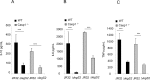
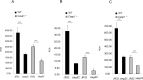
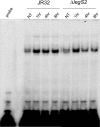
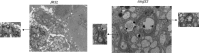
L. pneumophila is the causative agent of Legionnaires' disease, a human illness characterized by severe pneumonia. In contrast to those derived from humans, macrophages derived from most mouse strains restrict L. pneumophila replication. The restriction of L. pneumophila replication has been shown to require bacterial flagellin, a component of the type IV secretion system as well as the cytosolic NOD-like receptor (NLR) Nlrc4/ Ipaf. These events lead to caspase-1 activation which, in turn, activates caspase-7. Following caspase-7 activation, the phagosome-containing L. pneumophila fuses with the lysosome, resulting in the restriction of L. pneumophila growth. The LegS2 effector is injected by the type IV secretion system and functions as a sphingosine 1-phosphate lyase. It is homologous to the eukaryotic sphingosine lyase (SPL), an enzyme required in the terminal steps of sphingolipid metabolism. Herein, we show that mice Bone Marrow-Derived Macrophages (BMDMs) and human Monocyte-Derived Macrophages (hMDMs) are more permissive to L. pneumophila legS2 mutants than wild-type (WT) strains. This permissiveness to L. pneumophila legS2 is neither attributed to abolished caspase-1, caspase-7 or caspase-3 activation, nor due to the impairment of phagosome-lysosome fusion. Instead, an infection with the legS2 mutant resulted in the reduction of some inflammatory cytokines and their corresponding mRNA; this effect is mediated by the inhibition of the nuclear transcription factor kappa-B (NF-κB). Moreover, BMDMs infected with L. pneumophila legS2 mutant showed elongated mitochondria that resembles mitochondrial fusion. Therefore, the absence of LegS2 effector is associated with reduced NF-κB activation and atypical morphology of mitochondria.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Caspase-1 but Not Caspase-11 Is Required for NLRC4-Mediated Pyroptosis and Restriction of Infection by Flagellated Legionella Species in Mouse Macrophages and In Vivo.J Immunol. 2015 Sep 1;195(5):2303-11. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1501223. Epub 2015 Jul 31. J Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26232428
-
Caspase-7 activation by the Nlrc4/Ipaf inflammasome restricts Legionella pneumophila infection.PLoS Pathog. 2009 Apr;5(4):e1000361. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000361. Epub 2009 Apr 3. PLoS Pathog. 2009. PMID: 19343209 Free PMC article.
-
Restriction of Legionella pneumophila replication in macrophages requires concerted action of the transcriptional regulators Irf1 and Irf8 and nod-like receptors Naip5 and Nlrc4.Infect Immun. 2009 Nov;77(11):4794-805. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01546-08. Epub 2009 Aug 31. Infect Immun. 2009. PMID: 19720760 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of caspases and their non-apoptotic functions by Legionella pneumophila.Cell Microbiol. 2010 Feb;12(2):140-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2009.01401.x. Epub 2009 Oct 27. Cell Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 19863553 Review.
-
Inflammasome Recognition and Regulation of the Legionella Flagellum.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2016;397:161-81. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-41171-2_8. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27460809 Review.
Cited by
-
The role of HDAC6 in enhancing macrophage autophagy via the autophagolysosomal pathway to alleviate legionella pneumophila-induced pneumonia.Virulence. 2024 Dec;15(1):2327096. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2024.2327096. Epub 2024 Mar 11. Virulence. 2024. PMID: 38466143 Free PMC article.
-
Factors Mediating Environmental Biofilm Formation by Legionella pneumophila.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2018 Feb 27;8:38. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2018.00038. eCollection 2018. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29535972 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Glycolipids: Linchpins in the Organization and Function of Membrane Microdomains.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Oct 29;8:589799. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.589799. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 33195253 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Combinatorial selection in amoebal hosts drives the evolution of the human pathogen Legionella pneumophila.Nat Microbiol. 2020 Apr;5(4):599-609. doi: 10.1038/s41564-019-0663-7. Epub 2020 Jan 27. Nat Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 31988381 Free PMC article.
-
Tailored approach to study Legionella infection using a lattice light sheet microscope (LLSM).Biomed Opt Express. 2022 Jul 7;13(8):4134-4159. doi: 10.1364/BOE.459012. eCollection 2022 Aug 1. Biomed Opt Express. 2022. PMID: 36032581 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

