Genome-Wide Epigenetic Studies in Human Disease: A Primer on -Omic Technologies
- PMID: 26721890
- PMCID: PMC4706679
- DOI: 10.1093/aje/kwv187
Genome-Wide Epigenetic Studies in Human Disease: A Primer on -Omic Technologies
Abstract
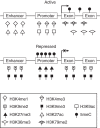
Epigenetic information encoded in covalent modifications of DNA and histone proteins regulates fundamental biological processes through the action of chromatin regulators, transcription factors, and noncoding RNA species. Epigenetic plasticity enables an organism to respond to developmental and environmental signals without genetic changes. However, aberrant epigenetic control plays a key role in pathogenesis of disease. Normal epigenetic states could be disrupted by detrimental mutations and expression alteration of chromatin regulators or by environmental factors. In this primer, we briefly review the epigenetic basis of human disease and discuss how recent discoveries in this field could be translated into clinical diagnosis, prevention, and treatment. We introduce platforms for mapping genome-wide chromatin accessibility, nucleosome occupancy, DNA-binding proteins, and DNA methylation, primarily focusing on the integration of DNA methylation and chromatin immunoprecipitation-sequencing technologies into disease association studies. We highlight practical considerations in applying high-throughput epigenetic assays and formulating analytical strategies. Finally, we summarize current challenges in sample acquisition, experimental procedures, data analysis, and interpretation and make recommendations on further refinement in these areas. Incorporating epigenomic testing into the clinical research arsenal will greatly facilitate our understanding of the epigenetic basis of disease and help identify novel therapeutic targets.
Keywords: DNA methylation; cancer; complex diseases; epigenome; histone modification.
© The Author 2015. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Investigation of epigenetics in kidney cell biology.Methods Cell Biol. 2019;153:255-278. doi: 10.1016/bs.mcb.2019.04.015. Epub 2019 Jun 13. Methods Cell Biol. 2019. PMID: 31395383 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Next-generation technologies and data analytical approaches for epigenomics.Environ Mol Mutagen. 2014 Apr;55(3):155-70. doi: 10.1002/em.21841. Epub 2013 Dec 10. Environ Mol Mutagen. 2014. PMID: 24327356 Review.
-
Genome-wide epigenomic profiling for biomarker discovery.Clin Epigenetics. 2016 Nov 21;8:122. doi: 10.1186/s13148-016-0284-4. eCollection 2016. Clin Epigenetics. 2016. PMID: 27895806 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Assaying the epigenome in limited numbers of cells.Methods. 2015 Jan 15;72:51-6. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2014.10.010. Epub 2014 Oct 22. Methods. 2015. PMID: 25461774 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chromatin Profiling Techniques: Exploring the Chromatin Environment and Its Contributions to Complex Traits.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jul 16;22(14):7612. doi: 10.3390/ijms22147612. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34299232 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Efficient generation of epigenetic disease model mice by epigenome editing using the piggyBac transposon system.Epigenetics Chromatin. 2022 Dec 16;15(1):40. doi: 10.1186/s13072-022-00474-3. Epigenetics Chromatin. 2022. PMID: 36522780 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic interplay between methylation and miRNA in bladder cancer: focus on isoform expression.BMC Genomics. 2021 Oct 21;22(Suppl 3):754. doi: 10.1186/s12864-021-08052-9. BMC Genomics. 2021. PMID: 34674656 Free PMC article.
-
Non-Coding Variants in Cancer: Mechanistic Insights and Clinical Potential for Personalized Medicine.Noncoding RNA. 2021 Aug 2;7(3):47. doi: 10.3390/ncrna7030047. Noncoding RNA. 2021. PMID: 34449663 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Differential ATAC-seq and ChIP-seq peak detection using ROTS.NAR Genom Bioinform. 2021 Jul 2;3(3):lqab059. doi: 10.1093/nargab/lqab059. eCollection 2021 Sep. NAR Genom Bioinform. 2021. PMID: 34235431 Free PMC article.
-
The Human Islet: Mini-Organ With Mega-Impact.Endocr Rev. 2021 Sep 28;42(5):605-657. doi: 10.1210/endrev/bnab010. Endocr Rev. 2021. PMID: 33844836 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Mill J, Heijmans BT. From promises to practical strategies in epigenetic epidemiology. Nat Rev Genet. 2013;148:585–594. - PubMed
-
- Satterlee JS, Schübeler D, Ng HH. Tackling the epigenome: challenges and opportunities for collaboration. Nat Biotechnol. 2010;2810:1039–1044. - PubMed
-
- Zentner GE, Henikoff S. High-resolution digital profiling of the epigenome. Nat Rev Genet. 2014;1512:814–827. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

