Induction of endothelium-dependent constriction of mesenteric arteries in endotoxemic hypotensive shock
- PMID: 26694894
- PMCID: PMC5341340
- DOI: 10.1111/bph.13415
Induction of endothelium-dependent constriction of mesenteric arteries in endotoxemic hypotensive shock
Abstract
Background and purpose: Effective management of hypotension refractory to vasoconstrictors in severe sepsis is limited. A new strategy to ameliorate endotoxemic hypotension by inducing endothelium-dependent constriction of large arteries was assessed.
Experimental approach: Endotoxemia in rats was induced by injection of LPS (10 mg·kg(-1), i.v.). Haemodynamics were measured in vivo, reactivity of isolated mesenteric arteries by myography and expression of proteins and enzyme activities by immunohistochemistry, biochemistry and molecular biology.
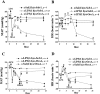
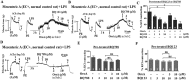
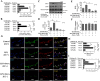
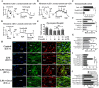
Key results: Six hours after LPS, the hypotension was promptly reversed following injection (i.v. or i.p.) of oroxylin-A (OroA) . In isolated LPS-treated but not normal mesenteric arteries, OroA (1-10 μM) induced endothelium-dependent, sustained constriction, blocked by endothelin-1 (ET-1) receptor antagonists. OroA further enhanced LPS-induced expression of endothelin-converting enzyme, ET-1 mRNA and proteins and ET-1 release, OroA also enhanced phosphorylation of Rho-associated protein kinase (ROCK) and reversed LPS-induced suppression of RhoA activities in smooth muscle of arteries with endothelium. Activated- phosphorylation of smooth muscle ROCK was blocked by ET-1-receptor antagonists and ROCK inhibitors. Moreover, OroA post-treatment suppressed, via inhibiting NF-κB activation, inducible NOS expression and circulating NO.
Conclusions and implications: Reversal of endotoxemic hypotensive by OroA was due to release of endothelial ET-1, upregulated by LPS, from mesenteric arteries, inducing prompt and sustained vasoconstriction via activation of vascular smooth muscle RhoA/ROCK-pathway. In late endotoxemia, OroA-induced vasoconstriction was partly due to decreased circulating NO. Activation of endothelium-dependent constriction in large resistance arteries and suppression of systemic inflammation offer new strategies for acute management of endotoxemic hypotensive shock.
© 2015 The British Pharmacological Society.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Rho-Proteins and Downstream Pathways as Potential Targets in Sepsis and Septic Shock: What Have We Learned from Basic Research.Cells. 2021 Jul 21;10(8):1844. doi: 10.3390/cells10081844. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34440613 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Rho-A/Rho-kinase pathway is up-regulated but remains inhibited by cyclic guanosine monophosphate-dependent mechanisms during endotoxemia in small mesenteric arteries.Crit Care Med. 2009 May;37(5):1716-23. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0b013e31819efb43. Crit Care Med. 2009. PMID: 19325475 Free PMC article.
-
Oroxylin-A rescues LPS-induced acute lung injury via regulation of NF-κB signaling pathway in rodents.PLoS One. 2012;7(10):e47403. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0047403. Epub 2012 Oct 10. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23071799 Free PMC article.
-
OroxylinA reverses lipopolysaccharide-induced adhesion molecule expression and endothelial barrier disruption in the rat aorta.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2020 Aug 1;400:115070. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2020.115070. Epub 2020 May 25. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32464219
-
Recombinant human activated protein C improves endotoxemia-induced endothelial dysfunction: a blood-free model in isolated mouse arteries.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2009 Jul;297(1):H277-82. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.01133.2008. Epub 2009 Apr 24. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19395546
Cited by
-
Enhanced Endothelin A and B Receptor Expression and Receptor-Mediated Vasoconstriction in Rat Mesenteric arteries after Lipopolysaccharide Challenge.Mediators Inflamm. 2019 Nov 14;2019:6248197. doi: 10.1155/2019/6248197. eCollection 2019. Mediators Inflamm. 2019. PMID: 31827377 Free PMC article.
-
Resveratrol enhances vascular reactivity in mice following lipopolysaccharide challenge via the RhoA-ROCK-MLCP pathway.Exp Ther Med. 2017 Jul;14(1):308-316. doi: 10.3892/etm.2017.4486. Epub 2017 May 22. Exp Ther Med. 2017. PMID: 28672931 Free PMC article.
-
Role of PVAT in obesity-related cardiovascular disease through the buffering activity of ATF3.iScience. 2022 Nov 18;25(12):105631. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2022.105631. eCollection 2022 Dec 22. iScience. 2022. PMID: 36458260 Free PMC article.
-
Rho-Proteins and Downstream Pathways as Potential Targets in Sepsis and Septic Shock: What Have We Learned from Basic Research.Cells. 2021 Jul 21;10(8):1844. doi: 10.3390/cells10081844. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34440613 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Andrographolide Attenuates Established Pulmonary Hypertension via Rescue of Vascular Remodeling.Biomolecules. 2021 Nov 30;11(12):1801. doi: 10.3390/biom11121801. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 34944445 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aird WC (2003). The role of the endothelium in severe sepsis and multiple organ dysfunction syndrome. Blood 101: 3765–3777. - PubMed
-
- Arqués O, Chicote I, Tenbaum S, Puig I, Palmer GH (2012). Standardized Relative Quantification of Immunofluorescence Tissue Staining. Protocol Exchange doi:10.1038/protex.2012.008. - DOI
-
- Azevedo LC, Park M, Schettino GP (2008). Novel potential therapies for septic shock. Shock 30: 60–66. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

