IL-18 and Cutaneous Inflammatory Diseases
- PMID: 26690141
- PMCID: PMC4691115
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms161226172
IL-18 and Cutaneous Inflammatory Diseases
Abstract
Interleukin (IL)-18, an IL-1 family cytokine, is a pleiotropic immune regulator. IL-18 plays a strong proinflammatory role by inducing interferon (IFN)-γ. Previous studies have implicated IL-18 in the pathogenesis of various diseases. However, it is not well understood biologic activities of IL-18 in the diverse skin diseases. Here, we have reviewed the expression and function of IL-18 in skin diseases including inflammatory diseases. This article provides an evidence-based understanding of the role of IL-18 in skin diseases and its relationship with disease activities.
Keywords: IL-18; alopecia areata; atopic dermatitis; contact dermatitis; drug eruption; fibrosis; graft-versus-host disease; lupus erythematosus; psoriasis; skin disease; skin tumor; urticaria.
Figures
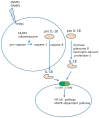
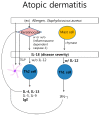
 : pro IL-18,
: pro IL-18,  : active IL-18,
: active IL-18,  : IL-18Rα,
: IL-18Rα,  : IL-18Rβ).
: IL-18Rβ).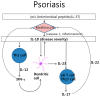
Similar articles
-
CXCR3 <-> ligand-mediated skin inflammation in cutaneous lichenoid graft-versus-host disease.J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008 Mar;58(3):437-42. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2007.10.647. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008. PMID: 18280341
-
The role of IL-22 and Th22 cells in human skin diseases.J Dermatol Sci. 2013 Oct;72(1):3-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jdermsci.2013.04.028. Epub 2013 May 3. J Dermatol Sci. 2013. PMID: 23746568 Review.
-
IL-21 in the pathogenesis and treatment of skin diseases.J Dermatol Sci. 2010 Nov;60(2):61-6. doi: 10.1016/j.jdermsci.2010.08.016. Epub 2010 Sep 15. J Dermatol Sci. 2010. PMID: 20888735 Review.
-
Role of Toll-like receptor 4 signaling in cutaneous chronic graft-versus-host disease.Clin Transplant. 2015 Jun;29(6):547-54. doi: 10.1111/ctr.12551. Epub 2015 May 5. Clin Transplant. 2015. PMID: 25845646
-
The role of IL-37 in skin and connective tissue diseases.Biomed Pharmacother. 2020 Feb;122:109705. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109705. Epub 2019 Dec 30. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020. PMID: 31918276 Review.
Cited by
-
Review of Prominent Cytokines as Superior Therapeutic Targets for Moderate-to-Severe Atopic Dermatitis.Cureus. 2020 Aug 20;12(8):e9901. doi: 10.7759/cureus.9901. Cureus. 2020. PMID: 32968566 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long-Term and Clinically Relevant Full-Thickness Human Skin Equivalent for Psoriasis.ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2020 Oct 19;3(10):6639-6647. doi: 10.1021/acsabm.0c00202. Epub 2020 Sep 17. ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2020. PMID: 35019390 Free PMC article.
-
The Correlation of CD206, CD209, and Disease Severity in Behçet's Disease with Arthritis.Mediators Inflamm. 2017;2017:7539529. doi: 10.1155/2017/7539529. Epub 2017 Mar 9. Mediators Inflamm. 2017. PMID: 28377641 Free PMC article.
-
TNF Is Partially Required for Cell-Death-Triggered Skin Inflammation upon Acute Loss of cFLIP.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Nov 23;21(22):8859. doi: 10.3390/ijms21228859. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33238518 Free PMC article.
-
Commercial Diagnostics and Emerging Precision Medicine Technologies in Psoriasis and Atopic Dermatitis.Psoriasis (Auckl). 2024 Aug 5;14:87-92. doi: 10.2147/PTT.S478377. eCollection 2024. Psoriasis (Auckl). 2024. PMID: 39132449 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bellora F., Castriconi R., Doni A., Cantoni C., Moretta L., Mantovani A., Moretta A., Bottino C. M-CSF induces the expression of a membrane-bound form of IL-18 in a subset of human monocytes differentiating in vitro toward macrophages. Eur. J. Immunol. 2012;42:1618–1626. doi: 10.1002/eji.201142173. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Gerdes N., Sukhova G.K., Libby P., Reynolds R.S., Young J.L., Schonbeck U. Expression of interleukin (IL)-18 and functional IL-18 receptor on human vascular endothelial cells, smooth muscle cells, and macrophages: Implications for atherogenesis. J. Exp. Med. 2002;195:245–257. doi: 10.1084/jem.20011022. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

