Systems Proteomics View of the Endogenous Human Claudin Protein Family
- PMID: 26680015
- PMCID: PMC4777318
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.5b00769
Systems Proteomics View of the Endogenous Human Claudin Protein Family
Abstract
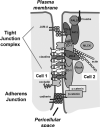
Claudins are the major transmembrane protein components of tight junctions in human endothelia and epithelia. Tissue-specific expression of claudin members suggests that this protein family is not only essential for sustaining the role of tight junctions in cell permeability control but also vital in organizing cell contact signaling by protein-protein interactions. How this protein family is collectively processed and regulated is key to understanding the role of junctional proteins in preserving cell identity and tissue integrity. The focus of this review is to first provide a brief overview of the functional context, on the basis of the extensive body of claudin biology research that has been thoroughly reviewed, for endogenous human claudin members and then ascertain existing and future proteomics techniques that may be applicable to systematically characterizing the chemical forms and interacting protein partners of this protein family in human. The ability to elucidate claudin-based signaling networks may provide new insight into cell development and differentiation programs that are crucial to tissue stability and manipulation.
Keywords: Membrane protein complexes; cell-contact signaling; chemical proteomics; membrane proteomics; systems proteomics; targeted proteomics; top-down proteomics.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Functions of claudin tight junction proteins and their complex interactions in various physiological systems.Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2010;279:1-32. doi: 10.1016/S1937-6448(10)79001-8. Epub 2010 Jan 29. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2010. PMID: 20797675 Review.
-
Claudins and the modulation of tight junction permeability.Physiol Rev. 2013 Apr;93(2):525-69. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00019.2012. Physiol Rev. 2013. PMID: 23589827 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integration of tight junctions and claudins with the barrier functions of the retinal pigment epithelium.Prog Retin Eye Res. 2011 Sep;30(5):296-323. doi: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2011.06.002. Epub 2011 Jun 17. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2011. PMID: 21704180 Review.
-
In tight junctions, claudins regulate the interactions between occludin, tricellulin and marvelD3, which, inversely, modulate claudin oligomerization.J Cell Sci. 2013 Jan 15;126(Pt 2):554-64. doi: 10.1242/jcs.114306. Epub 2012 Nov 30. J Cell Sci. 2013. PMID: 23203797
-
Claudins of intestine and nephron - a correlation of molecular tight junction structure and barrier function.Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2011 Jan;201(1):133-40. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.2010.02148.x. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2011. PMID: 20518752 Review.
Cited by
-
Nanostructure-Mediated Transport of Therapeutics through Epithelial Barriers.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jun 28;25(13):7098. doi: 10.3390/ijms25137098. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39000205 Free PMC article. Review.
-
LY75 Ablation Mediates Mesenchymal-Epithelial Transition (MET) in Epithelial Ovarian Cancer (EOC) Cells Associated with DNA Methylation Alterations and Suppression of the Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Mar 7;21(5):1848. doi: 10.3390/ijms21051848. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32156068 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive analysis of metastatic gastric cancer tumour cells using single-cell RNA-seq.Sci Rep. 2021 Jan 13;11(1):1141. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-80881-2. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33441952 Free PMC article.
-
Biophysics of claudin proteins in tight junction architecture: Three decades of progress.Biophys J. 2024 Aug 20;123(16):2363-2378. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2024.06.010. Epub 2024 Jun 10. Biophys J. 2024. PMID: 38859584 Review.
-
Editorial: Editors' showcase 2023: insights in cell adhesion and migration.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024 Oct 3;12:1497689. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1497689. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 39421022 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Schneeberger EE, Lynch RD. The tight junction: a multifunctional complex. Am. J. Physiol Cell Physiol. 2004;286:C1213–C1228. - PubMed
-
- Tsukita S, Furuse M, Itoh M. Structural and signalling molecules come together at tight junctions. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 1999;11:628–633. - PubMed
-
- Tsukita S, Furuse M. The structure and function of claudins, cell adhesion molecules at tight junctions. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2000;915:129–135. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

