Microvascular basis for growth of small infarcts following occlusion of single penetrating arterioles in mouse cortex
- PMID: 26661182
- PMCID: PMC4976746
- DOI: 10.1177/0271678X15608388
Microvascular basis for growth of small infarcts following occlusion of single penetrating arterioles in mouse cortex
Abstract
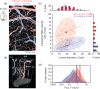
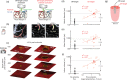
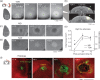
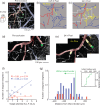
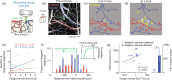
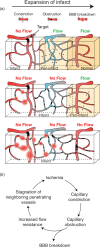
Small cerebral infarcts, i.e. microinfarcts, are common in the aging brain and linked to vascular cognitive impairment. However, little is known about the acute growth of these minute lesions and their effect on blood flow in surrounding tissues. We modeled microinfarcts in the mouse cortex by inducing photothrombotic clots in single penetrating arterioles. The resultant hemodynamic changes in tissues surrounding the occluded vessel were then studied using in vivo two-photon microscopy. We were able to generate a spectrum of infarct volumes by occluding arterioles that carried a range of blood fluxes. Those resulting from occlusion of high-flux penetrating arterioles (flux of 2 nL/s or higher) exhibited a radial outgrowth that encompassed unusually large tissue volumes. The gradual expansion of these infarcts was propagated by an evolving insufficiency in capillary flow that encroached on territories of neighboring penetrating arterioles, leading to the stagnation and recruitment of their perfusion domains into the final infarct volume. Our results suggest that local collapse of microvascular function contributes to tissue damage incurred by single penetrating arteriole occlusions in mice, and that a similar mechanism may add to pathophysiology induced by microinfarcts of the human brain.
Keywords: Ischemia; cerebral blood flow; microcirculation; two-photon microscopy; venous thrombosis.
© The Author(s) 2015.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Functional deficits induced by cortical microinfarcts.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2017 Nov;37(11):3599-3614. doi: 10.1177/0271678X16685573. Epub 2017 Jan 16. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2017. PMID: 28090802 Free PMC article.
-
Penumbral microcirculatory changes associated with peri-infarct depolarizations in the rat.Stroke. 2002 Feb;33(2):606-12. doi: 10.1161/hs0202.102738. Stroke. 2002. PMID: 11823677
-
Collateral blood flow in different cerebrovascular hierarchy provides endogenous protection in cerebral ischemia.Brain Pathol. 2017 Nov;27(6):809-821. doi: 10.1111/bpa.12458. Epub 2017 Mar 27. Brain Pathol. 2017. PMID: 27859886 Free PMC article.
-
Robust and fragile aspects of cortical blood flow in relation to the underlying angioarchitecture.Microcirculation. 2015 Apr;22(3):204-218. doi: 10.1111/micc.12195. Microcirculation. 2015. PMID: 25705966 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Does pathology of small venules contribute to cerebral microinfarcts and dementia?J Neurochem. 2018 Mar;144(5):517-526. doi: 10.1111/jnc.14228. Epub 2017 Nov 7. J Neurochem. 2018. PMID: 28950410 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Detection, risk factors, and functional consequences of cerebral microinfarcts.Lancet Neurol. 2017 Sep;16(9):730-740. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(17)30196-5. Epub 2017 Jul 14. Lancet Neurol. 2017. PMID: 28716371 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeted photothrombotic subcortical small vessel occlusion using in vivo real-time fiber bundle endomicroscopy in mice.Biomed Opt Express. 2023 Jan 9;14(2):687-702. doi: 10.1364/BOE.473407. eCollection 2023 Feb 1. Biomed Opt Express. 2023. PMID: 36874485 Free PMC article.
-
Imaging the construction of capillary networks in the neonatal mouse brain.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021 Jun 29;118(26):e2100866118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2100866118. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021. PMID: 34172585 Free PMC article.
-
Functional deficits induced by cortical microinfarcts.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2017 Nov;37(11):3599-3614. doi: 10.1177/0271678X16685573. Epub 2017 Jan 16. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2017. PMID: 28090802 Free PMC article.
-
Pericytes as Inducers of Rapid, Matrix Metalloproteinase-9-Dependent Capillary Damage during Ischemia.J Neurosci. 2017 Jan 4;37(1):129-140. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2891-16.2016. J Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28053036 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kövari E, Gold G, Herrmann FR, et al. Cortical microinfarcts and demyelination significantly affect cognition in brain aging. Stroke 2004; 35: 410–414. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

