The Antitumor Efficacy of IL2/IL21-Cultured Polyfunctional Neu-Specific T Cells Is TNFα/IL17 Dependent
- PMID: 26660518
- PMCID: PMC4854769
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-15-2273
The Antitumor Efficacy of IL2/IL21-Cultured Polyfunctional Neu-Specific T Cells Is TNFα/IL17 Dependent
Abstract
Purpose: Infusion of HER2-specific T cells, derived from vaccine-primed patients and expanded with IL2/IL12, has induced tumor regression in a minority of patients with metastatic treatment-refractory HER2(+) breast cancer. We questioned whether alteration of cytokine growth factors used to culture vaccine-primed T cells could improve antitumor activity.
Experimental design: Using the TgMMTV-neu murine mammary tumor model, we cultured T cells derived from mice immunized with a previously defined neu class II peptide, p98-114 (neu p98), and evaluated different cytokine combinations for expansion.
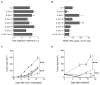
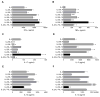
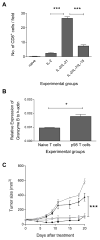
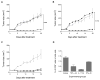
Results: Infusion of neu p98-specific T-cell lines derived from all cytokine conditions evaluated resulted in significant antitumor activity compared with infused naïve splenocytes (P < 0.05). T cells cultured with IL2/IL21 could uniquely mediate complete regression of spontaneous mammary tumors. IL2/IL21 cultured neu-specific T cells demonstrated a different cytokine secretion pattern as compared with other cultured T cells; secreting high levels of TNFα and IL17 (P < 0.05). Moreover, tumor-infiltrating CD8(+) cells were significantly increased after the infusion of IL2/IL21 cultured T cells as compared with tumors treated with T cells expanded under other cytokine conditions (P < 0.001). The antitumor effect of the infusion of IL2/IL21 cultured cells was mediated by CD8 T cells. Depletion of TNFα or IL17, but not IFNγ, abrogated the tumor growth inhibition induced by the IL2/IL21 T cells and markedly decreased the influx of CD8 into tumors. Finally, IL2/IL21-cultured human antigen specific T cells also displayed a similar polyfunctional Th1/Th17 phenotype.
Conclusions: Expansion of HER2 vaccine-primed T cells with IL2/IL21 may have the potential to effectively mediate tumor regression when used in adoptive transfer. Clin Cancer Res; 22(9); 2207-16. ©2015 AACR.
©2015 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: MLD is a stockholder in Epithany and VentiRx and receives grant support from Celgene, EMD Serono, VentiRx and Seattle Genetics. The remaining authors have no COI.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Targeting of the non-mutated tumor antigen HER2/neu to mature dendritic cells induces an integrated immune response that protects against breast cancer in mice.Breast Cancer Res. 2012 Mar 7;14(2):R39. doi: 10.1186/bcr3135. Breast Cancer Res. 2012. PMID: 22397502 Free PMC article.
-
Peptide vaccination breaks tolerance to HER-2/neu by generating vaccine-specific FasL(+) CD4(+) T cells: first evidence for intratumor apoptotic regulatory T cells.Cancer Res. 2010 Apr 1;70(7):2686-96. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-2517. Epub 2010 Mar 16. Cancer Res. 2010. PMID: 20233867
-
Expansion of HER2/neu-specific T cells ex vivo following immunization with a HER2/neu peptide-based vaccine.Clin Breast Cancer. 2001 Apr;2(1):73-9. doi: 10.3816/CBC.2001.n.014. Clin Breast Cancer. 2001. PMID: 11899386 Review.
-
A Therapeutic Her2/neu Vaccine Targeting Dendritic Cells Preferentially Inhibits the Growth of Low Her2/neu-Expressing Tumor in HLA-A2 Transgenic Mice.Clin Cancer Res. 2016 Aug 15;22(16):4133-44. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-16-0044. Epub 2016 Mar 22. Clin Cancer Res. 2016. PMID: 27006496
-
The future of interleukin-2: enhancing therapeutic anticancer vaccines.Cancer J Sci Am. 2000 Feb;6 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S76-80. Cancer J Sci Am. 2000. PMID: 10685664 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Comparative study on the impacts of visnagin and its methoxy derivative khellin on human lymphocyte proliferation and Th1/Th2 balance.Pharmacol Rep. 2023 Apr;75(2):411-422. doi: 10.1007/s43440-023-00452-w. Epub 2023 Feb 6. Pharmacol Rep. 2023. PMID: 36745338
-
Mesenchymal stromal cell delivery of oncolytic immunotherapy improves CAR-T cell antitumor activity.Mol Ther. 2021 May 5;29(5):1808-1820. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2021.02.004. Epub 2021 Feb 9. Mol Ther. 2021. PMID: 33571680 Free PMC article.
-
Toxoplasma gondii: CD8 T Cells Cry for CD4 Help.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2019 May 1;9:136. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2019.00136. eCollection 2019. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31119107 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Follicular helper-T cells restore CD8+-dependent antitumor immunity and anti-PD-L1/PD-1 efficacy.J Immunother Cancer. 2021 Jun;9(6):e002157. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2020-002157. J Immunother Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34103351 Free PMC article.
-
TLR8 ligation induces apoptosis of monocytic myeloid-derived suppressor cells.J Leukoc Biol. 2018 Jan;103(1):157-164. doi: 10.1002/JLB.5AB0217-070R. Epub 2017 Dec 14. J Leukoc Biol. 2018. PMID: 29345064 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Magee MS, Snook AE. Challenges to chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-T cell therapy for cancer. Discovery Medicine. 2014;18:265–71. - PubMed
-
- Rapoport AP, Aqui NA, Stadtmauer EA, Vogl DT, Xu YY, Kalos M, et al. Combination immunotherapy after ASCT for multiple myeloma using MAGE-A3/Poly-ICLC immunizations followed by adoptive transfer of vaccine-primed and costimulated autologous T cells. Clinical Cancer Research. 2014;20:1355–65. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

