Mycobacterium tuberculosis Type II Toxin-Antitoxin Systems: Genetic Polymorphisms and Functional Properties and the Possibility of Their Use for Genotyping
- PMID: 26658274
- PMCID: PMC4680722
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0143682
Mycobacterium tuberculosis Type II Toxin-Antitoxin Systems: Genetic Polymorphisms and Functional Properties and the Possibility of Their Use for Genotyping
Abstract
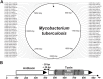
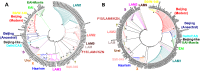
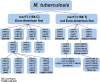
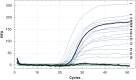
Various genetic markers such as IS-elements, DR-elements, variable number tandem repeats (VNTR), single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in housekeeping genes and other groups of genes are being used for genotyping. We propose a different approach. We suggest the type II toxin-antitoxin (TA) systems, which play a significant role in the formation of pathogenicity, tolerance and persistence phenotypes, and thus in the survival of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in the host organism at various developmental stages (colonization, infection of macrophages, etc.), as the marker genes. Most genes of TA systems function together, forming a single network: an antitoxin from one pair may interact with toxins from other pairs and even from other families. In this work a bioinformatics analysis of genes of the type II TA systems from 173 sequenced genomes of M. tuberculosis was performed. A number of genes of type II TA systems were found to carry SNPs that correlate with specific genotypes. We propose a minimally sufficient set of genes of TA systems for separation of M. tuberculosis strains at nine basic genotype and for further division into subtypes. Using this set of genes, we genotyped a collection consisting of 62 clinical isolates of M. tuberculosis. The possibility of using our set of genes for genotyping using PCR is also demonstrated.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Bioinformatic and mutational studies of related toxin-antitoxin pairs in Mycobacterium tuberculosis predict and identify key functional residues.J Biol Chem. 2019 Jun 7;294(23):9048-9063. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.006814. Epub 2019 Apr 24. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 31018964 Free PMC article.
-
Functional characterization of toxin-antitoxin system in Mycobacterium tuberculosis.Indian J Tuberc. 2023 Apr;70(2):149-157. doi: 10.1016/j.ijtb.2022.05.010. Epub 2022 May 27. Indian J Tuberc. 2023. PMID: 37100570 Review.
-
Killing activity and rescue function of genome-wide toxin-antitoxin loci of Mycobacterium tuberculosis.FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2009 Jan;290(1):45-53. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2008.01400.x. Epub 2008 Nov 10. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2009. PMID: 19016878
-
Computational insights into promoter architecture of toxin-antitoxin systems of Mycobacterium tuberculosis.Gene. 2018 Jan 30;641:161-171. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2017.10.054. Epub 2017 Oct 21. Gene. 2018. PMID: 29066303
-
Toxin-antitoxin systems and regulatory mechanisms in Mycobacterium tuberculosis.Pathog Dis. 2018 Jun 1;76(4). doi: 10.1093/femspd/fty039. Pathog Dis. 2018. PMID: 29788125 Review.
Cited by
-
Draft genome sequence of Mycobacterium tuberculosis strain B9741 of Beijing B0/W lineage from HIV positive patient from Siberia.Genom Data. 2016 Aug 3;10:61-62. doi: 10.1016/j.gdata.2016.08.001. eCollection 2016 Dec. Genom Data. 2016. PMID: 27761405 Free PMC article.
-
Distribution of lineages and type II toxin-antitoxin systems among rifampin-resistant Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Isolates.PLoS One. 2024 Oct 24;19(10):e0309292. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0309292. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39446830 Free PMC article.
-
Toxin-Activating Stapled Peptides Discovered by Structural Analysis Were Identified as New Therapeutic Candidates That Trigger Antibacterial Activity against Mycobacterium tuberculosis in the Mycobacterium smegmatis Model.Microorganisms. 2021 Mar 10;9(3):568. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms9030568. Microorganisms. 2021. PMID: 33801872 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of Mycobacterium salfingeri sp. nov.: A novel nontuberculous mycobacteria isolated from a human wound infection.Front Microbiol. 2022 Oct 10;13:992610. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.992610. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36299734 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of Two Toxin-Antitoxin Systems in Deep-Sea Streptomyces sp. SCSIO 02999.Mar Drugs. 2019 Apr 4;17(4):211. doi: 10.3390/md17040211. Mar Drugs. 2019. PMID: 30987346 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lasunskaia E, Ribeiro SC, Manicheva O, Gomes LL, Suffys PN, Mokrousov I, et al. Emerging multidrug resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis strains of the Beijing genotype circulating in Russia express a pattern of biological properties associated with enhanced virulence. Microbes Infect. 2010. June; 12(6): 467–475. 10.1016/j.micinf.2010.02.008 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

