A mechanism for the suppression of homologous recombination in G1 cells
- PMID: 26649820
- PMCID: PMC4880051
- DOI: 10.1038/nature16142
A mechanism for the suppression of homologous recombination in G1 cells
Retraction in
-
Retraction Note: A mechanism for the suppression of homologous recombination in G1 cells.Nature. 2025 Feb;638(8051):844. doi: 10.1038/s41586-025-08644-5. Nature. 2025. PMID: 39870925 No abstract available.
Abstract
DNA repair by homologous recombination is highly suppressed in G1 cells to ensure that mitotic recombination occurs solely between sister chromatids. Although many homologous recombination factors are cell-cycle regulated, the identity of the events that are both necessary and sufficient to suppress recombination in G1 cells is unknown. Here we report that the cell cycle controls the interaction of BRCA1 with PALB2-BRCA2 to constrain BRCA2 function to the S/G2 phases in human cells. We found that the BRCA1-interaction site on PALB2 is targeted by an E3 ubiquitin ligase composed of KEAP1, a PALB2-interacting protein, in complex with cullin-3 (CUL3)-RBX1 (ref. 6). PALB2 ubiquitylation suppresses its interaction with BRCA1 and is counteracted by the deubiquitylase USP11, which is itself under cell cycle control. Restoration of the BRCA1-PALB2 interaction combined with the activation of DNA-end resection is sufficient to induce homologous recombination in G1, as measured by RAD51 recruitment, unscheduled DNA synthesis and a CRISPR-Cas9-based gene-targeting assay. We conclude that the mechanism prohibiting homologous recombination in G1 minimally consists of the suppression of DNA-end resection coupled with a multi-step block of the recruitment of BRCA2 to DNA damage sites that involves the inhibition of BRCA1-PALB2-BRCA2 complex assembly. We speculate that the ability to induce homologous recombination in G1 cells with defined factors could spur the development of gene-targeting applications in non-dividing cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
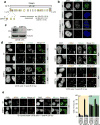
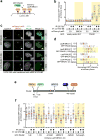
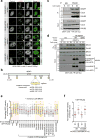
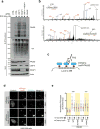
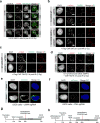
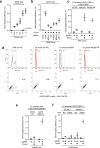


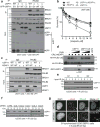
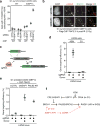
Comment in
-
DNA repair: The cell cycle flavours of repair.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2016 Feb;17(2):65. doi: 10.1038/nrm.2015.24. Epub 2015 Dec 23. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2016. PMID: 26695192 No abstract available.
-
DNA repair: The cell cycle flavours of repair.Nat Rev Genet. 2016 Feb;17(2):65. doi: 10.1038/nrg.2015.35. Epub 2016 Jan 5. Nat Rev Genet. 2016. PMID: 26729256 No abstract available.
-
Keeping homologous recombination in check.Cell Res. 2016 Apr;26(4):397-8. doi: 10.1038/cr.2016.25. Epub 2016 Feb 23. Cell Res. 2016. PMID: 26902288 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
PALB2 chromatin recruitment restores homologous recombination in BRCA1-deficient cells depleted of 53BP1.Nat Commun. 2020 Feb 10;11(1):819. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-14563-y. Nat Commun. 2020. PMID: 32041954 Free PMC article.
-
Depressing time: Waiting, melancholia, and the psychoanalytic practice of care.In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. PMID: 36137063 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Proline variants in the BRCA1 coiled-coil domain disrupt folding and binding to PALB2.Protein Sci. 2025 Jan;34(1):e5240. doi: 10.1002/pro.5240. Protein Sci. 2025. PMID: 39673470 Free PMC article.
-
Competence induction of homologous recombination genes protects pneumococcal cells from genotoxic stress.mBio. 2025 Jan 8;16(1):e0314224. doi: 10.1128/mbio.03142-24. Epub 2024 Nov 29. mBio. 2025. PMID: 39611665 Free PMC article.
-
The effectiveness of abstinence-based and harm reduction-based interventions in reducing problematic substance use in adults who are experiencing homelessness in high income countries: A systematic review and meta-analysis: A systematic review.Campbell Syst Rev. 2024 Apr 21;20(2):e1396. doi: 10.1002/cl2.1396. eCollection 2024 Jun. Campbell Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 38645303 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
PRMT1-dependent methylation of BRCA1 contributes to the epigenetic defense of breast cancer cells against ionizing radiation.Sci Rep. 2020 Aug 6;10(1):13275. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-70289-3. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32764667 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction with PALB2 Is Essential for Maintenance of Genomic Integrity by BRCA2.PLoS Genet. 2016 Aug 4;12(8):e1006236. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1006236. eCollection 2016 Aug. PLoS Genet. 2016. PMID: 27490902 Free PMC article.
-
Beta human papillomavirus 8 E6 allows colocalization of non-homologous end joining and homologous recombination repair factors.PLoS Pathog. 2022 Feb 11;18(2):e1010275. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1010275. eCollection 2022 Feb. PLoS Pathog. 2022. PMID: 35148356 Free PMC article.
-
POGZ promotes homology-directed DNA repair in an HP1-dependent manner.EMBO Rep. 2022 Jan 5;23(1):e51041. doi: 10.15252/embr.202051041. Epub 2021 Nov 10. EMBO Rep. 2022. PMID: 34758190 Free PMC article.
-
Sleeping Beauty Transposon Insertions into Nucleolar DNA by an Engineered Transposase Localized in the Nucleolus.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 7;24(19):14978. doi: 10.3390/ijms241914978. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37834425 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Panier S, Durocher D. Push back to respond better: regulatory inhibition of the DNA double-strand break response. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2013;14:661–672. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

